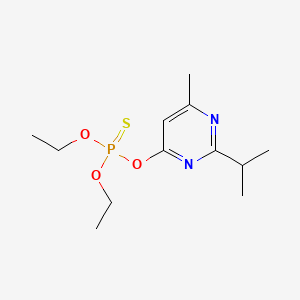

1. Bazudine
2. Dimpylate
3. Neocidol
4. Neotsidol
1. Dimpylate
2. 333-41-5
3. Diazinone
4. Oleodiazinon
5. Ciazinon
6. Neocidol
7. Dassitox
8. Diazitol
9. Ektoband
10. Nedcidol
11. Spectracide
12. Antigal
13. Basudin
14. Bazuden
15. Dacutox
16. Dazzel
17. Diazide
18. Diazol
19. Exodin
20. Flytrol
21. Galesan
22. Nucidol
23. Sarolex
24. Dicid
25. Alfa-tox
26. Diazajet
27. Dimpylat
28. Garden Tox
29. Neocidol (oil)
30. Bassadinon
31. Terminator
32. Compass
33. Disonex
34. Dizinon
35. Drawizon
36. Kayazinon
37. Kayazol
38. Meodinon
39. Dyzol
40. Nipsan
41. Diazinon Ag 500
42. Knox-out
43. Delzinon
44. Dimpylatum
45. Dipofene
46. Dizictol
47. Neodinon
48. Optimizer
49. Bazudin
50. Dizinil
51. Srolex
52. Basudin 10 G
53. Geigy 24480
54. Basudin S
55. Knox Out 2fm
56. Diagran
57. Fezudin
58. Nci-c08673
59. Ag-500
60. G-24480
61. Dimpylate [inn]
62. Ent 19,507
63. Isopropylmethylpyrimidyl Diethyl Thiophosphate
64. Diziktol
65. O,o-diethyl 2-isopropyl-4-methylpyrimidyl-6-thiophosphate
66. New Z Diazinon
67. G 301
68. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl) Phosphorothioate
69. 4-pyrimidinol, 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-, O-ester With O,o-diethyl Phosphorothioate
70. Diethyl 4-(2-isopropyl-6-methylpyrimidinyl)phosphorothionate
71. O-2-isopropyl-4-methylpyrimidyl-o,o-diethyl Phosphorothioate
72. Optimizer Insecticide
73. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidyl) Thionophosphate
74. Chebi:34682
75. O,o-diethyl O-6-methyl-2-isopropyl-4-pyrimidinyl Phosphorothioate
76. Nsc-8938
77. Phosphorothioate, O,o-diethyl O-6-(2-isopropyl-4-methylpyrimidyl)
78. Thiophosphate De O,o-diethyle Et De O-2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidyle
79. Diethyl 2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidyl Thionophosphate
80. Phosphorothioic Acid, O,o-diethyl O-(6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl) Ester
81. Yus1m1q929
82. Diethyl 2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidinyl Phosphorothionate
83. O,o-diethyl 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinylphosphorothioate
84. Nsc8938
85. Dimpylate (inn)
86. O,o-diethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-pyrimidin-6-yl)-monothiofosfaat
87. Phosphorothioic Acid, O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl) Ester
88. Ncgc00091073-01
89. Bazudine
90. Neotsidol
91. Dsstox_cid_407
92. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidinyl) Phosphorothioate
93. O,o-diethyl O-[6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl] Thiophosphate
94. Kleen-dok
95. Dsstox_rid_75567
96. Phosphorothioic Acid, O,o-diethylo-[6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl] Ester
97. Dsstox_gsid_20407
98. Diazinon, Analytical Standard
99. Kfm Blowfly Dressing
100. Compass (insecticide)
101. Caswell No. 342
102. Gardentox
103. Dimpilato
104. Antlak
105. Diaterr-fos
106. Dimpylatum [inn-latin]
107. O,o-diaethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-pyrinidin-6-yl)-monothiophosphat
108. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidyl) Phosphorothioate
109. Cooper's Flystrike Powder
110. Dimpilato [inn-spanish]
111. Nsc 8938
112. Phosphorothioic Acid, O,o-diethyl O-[6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl] Ester
113. Diazinon [ansi:bsi:iso]
114. Cas-333-41-5
115. Ccris 204
116. Hsdb 303
117. Knox Out Yellow Jacket Contorl
118. Oms 469
119. Einecs 206-373-8
120. Pt 265
121. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 057801
122. Brn 0273790
123. Unii-yus1m1q929
124. Spertacide
125. Bazanon
126. Ai3-19507
127. Root Guard
128. Diethyl Dimpylatum
129. Diethoxy-(6-methyl-2-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-4-yl)oxy-sulfanylidene-?^{5}-phosphane
130. Dimpylate, Inn
131. Basudin 5g
132. Spectracide 25ec
133. G 24480
134. Agridin 60
135. Basudin 10g
136. Spectrum_001777
137. Dimpylate [inn:ban]
138. Diazinon [hsdb]
139. Diazinon [iarc]
140. New Z Diazinon (tn)
141. Specplus_000344
142. Diazinon [iso]
143. Diazinon [mi]
144. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl)phosphorothioate
145. O,o-diethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidyl)phosphorothioate
146. Spectrum2_001226
147. Spectrum3_000802
148. Spectrum4_000642
149. Spectrum5_001929
150. Thiophosphoric Acid 2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidyl Diethyl Ester
151. O,o-diethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidinyl)-phosphorothioate
152. Phosphorothioic Acid, O,o-diethyl O-(isopropylmethylpyrimidinyl) Ester
153. Dimpylate [mart.]
154. O,o-diaethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl)-6-pyrimidyl-thionophosphat [german]
155. O,o-diaethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-pyrimidin-6-yl)-monothiophosphat [german]
156. O,o-diethyl O-(6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl)phosphorothioate
157. O,o-diethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-pyrimidin-6-yl)-monothiofosfaat [dutch]
158. O,o-dietil-o-(2-isopropil-4-metil-pirimidin-6-il)-monotiofosfato [italian]
159. Dimpylate [who-dd]
160. Optimizer Insecticide (tn)
161. Thiophosphate De O,o-diethyle Et De O-2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidyle [french]
162. Schembl17453
163. Bspbio_002263
164. Kbiogr_000983
165. Kbioss_002258
166. 5-23-11-00187 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
167. Mls002207243
168. Bidd:er0457
169. Divk1c_006440
170. Spbio_001072
171. Chembl388560
172. Zinc1309
173. Dtxsid9020407
174. Fhivafmuckrcqo-uhfffaoysa-
175. Kbio1_001384
176. Kbio2_002257
177. Kbio2_004825
178. Kbio2_007393
179. Kbio3_001763
180. Amy3613
181. Hms3264i04
182. Pharmakon1600-00330017
183. Hy-b1113
184. O,o-diaethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl)-6-pyrimidyl-thionophosphat
185. O,o-diethyl O-2-isopropyl-6-methylpyrimidin-4-yl Phosphorothioate
186. Diazinon 100 Microg/ml In Acetone
187. Tox21_111077
188. Tox21_201409
189. Tox21_300730
190. Bdbm50005409
191. Ccg-39143
192. Ent 19507
193. Nsc755893
194. O,o-diaethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-pyrimidin-6-yl)-monothiophosphat
195. O,o-dietil-o-(2-isopropil-4-metil-pirimidin-6-il)-monotiofosfato
196. Diazinon 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
197. Diazinon 1000 Microg/ml In Toluene
198. Akos025311513
199. Diazinon 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
200. Diethoxy-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy-thioxo-$l^{5}-phosphane
201. O,o-diethyl O-(6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl) Phosphorothioate
202. O,o-diethyl O-[6-methyl-2-(propan-2-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl] Phosphorothioate
203. Tox21_111077_1
204. Cs-4712
205. Diazinon 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
206. Diazinon 100 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
207. Nsc-755893
208. Diazinon 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
209. Diethoxy-(6-methyl-2-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-4-yl)oxy-sulfanylidene-lambda5-phosphane
210. Ncgc00091073-02
211. Ncgc00091073-03
212. Ncgc00091073-04
213. Ncgc00091073-05
214. Ncgc00091073-06
215. Ncgc00091073-07
216. Ncgc00254636-01
217. Ncgc00258960-01
218. Smr000777921
219. Sbi-0052498.p002
220. Db-048387
221. Diazinon, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
222. Ft-0603088
223. Ft-0778116
224. D07856
225. Ab00053004_04
226. 333d415
227. Q411202
228. Sr-01000872734
229. Q-200952
230. Sr-01000872734-1
231. Brd-k60567437-001-04-5
232. Diazinon, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
233. 4-pyrimidinol, O-ester With O,o-diethyl Phosphorothioate
234. Wln: T6n Cnj By1 & 1 Dops & O2 & O2 F1
235. O, O-diethyl 2-isopropyl-4-methylpyrimidyl-6-thiophosphate
236. O,o-diethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methylpyrimidyl)thiophosphate
237. O,o-dietil-o-(2-isopropil-4-metil-pirimidin-il)-monotiofosato
238. Phosphorothioate,o-diethyl O-6-(2-isopropyl-4-methylpyrimidyl)
239. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-primidinyl)phosphorothioate
240. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl) Thiophosphate
241. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl) Thiophosphate #
242. O,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl)thio-phosphate
243. O,o-diethyl-o-(2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-pyrimidyl) Thiophosphate
244. Diethoxy-(6-methyl-2-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-4-yl)oxy-sulfanylidenephosphorane
245. O,o-diethyl-o-(6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl)phosophorothioate
246. Phosphorothioic Acid, O,o-diethyl 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl Ester
247. Phosphorothioic Acid,o-diethyl O-(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl) Ester
248. Diazinon Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Acetonitrile, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
249. Diethoxy-(6-methyl-2-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-4-yl)oxy-sulfanylidene-$l^{5-phosphane
250. Ethyl 6-methyl-2-(propan-2-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl Ethoxy(sulfanylidene)phosphonite
251. Phosphorothioic Acid O,o-diethyl O-(6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl) Ester
252. Phosphorothioic Acid, O,o-diethyl {o-[6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl]} Ester
253. Phosphorothioic Acid,o-diethyl O-[6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl] Ester
| Molecular Weight | 304.35 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H21N2O3PS |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 304.10105071 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 304.10105071 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 85.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 307 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
VET: Used against ... flies and ticks in veterinary practice.
Worthing, C.R. and S.B. Walker (eds.). The Pesticide Manual - A World Compendium. 8th ed. Thornton Heath, UK: The British Crop Protection Council, 1987., p. 248
The estimated adult oral fatal dose is approximately 25 g.
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 1071
Estimated adult oral fatal dose is approximately 25 g.
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 1071
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
Four laying Leghorn hens were treated with 2-14C-diazinon (specific activity 30.3 uCi/mg) in gelatin capsules for seven consecutive days at daily doses of 1.7 mg/kg body weight, corresponding to a dietary exposure of 25 mg/kg in feed. ... Elimination of most of the administered radioactivity occurred via the excreta, with 78.6% of the total dose being excreted during the study period. Approximately 0.1% of the radioactivity was found in tissues and blood, less than 0.01% appeared in the egg yolks and 0.07% was detected in the egg whites. The residual radioactivity in the tissues amounted to 0.148 mg/kg diazinon equivalents in the kidney, 0.137 mg/kg in blood, 0.11 mg/kg in the liver and 0.01-0.025 mg/kg in the other tissues examined. The residues in the egg yolks ranged from 0.006 mg/kg diazinon equivalents to 0.065 mg/kg while those in the egg whites ranged from 0.038 mg/kg to 0.066 mg/kg. On a whole egg basis, a plateau concentration of 0.047 mg/kg was reached on day 4 of treatment.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 198: Diazinon (333-41-5) (1998); Available from, as of August 31, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
A lactating Hereford cow (body weight 268 kg) was orally treated with a gelatin capsule containing 20 mg/kg 32P-diazinon (specific activity 518 cpm/ug). ... Within 36 hr, approximately 74% of the administered radioactivity was excreted with the urine, 6.5% appeared in the feces and 0.08% was found in the milk. A peak concentration of 2.27 mg/kg diazinon equivalents was reached 18 hr after the administration.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 198: Diazinon (333-41-5) (1998); Available from, as of August 31, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
Two lactating goats were orally treated with (pyrimidine-14C)-diazinon (specific activity 9.7 uCi/mg) in gelatin capsules for four consecutive days at a dose level of 4.5 mg/kg per day, corresponding to a dietary exposure of 100 mg/kg of feed. During the observation period, an average 64.1% of the administered radioactivity was excreted with urine, 10.4% with the feces and 0.31% with the milk. A plateau of radioactivity in the milk was reached after 3 days of dosing at a mean level of 0.46 mg/kg diazinon equivalent. At sacrifice, radioactivity in the blood accounted for 0.2% and the tissues examined accumulated 0.92% of the administered dose. The highest residual radioactivity was detected in the kidney (2.0 mg/kg) and the liver (1.2 mg/kg). The other tissues examined contained 0.23-0.3 mg/kg diazinon equivalents.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 198: Diazinon (333-41-5) (1998); Available from, as of August 31, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
Two female Beagle dogs were intravenously dosed with 0.2 mg/kg (ethoxy-14C)-diazinon (specific activity 3.4 uCi/mg) in 0.7 mL ethanol. ... The half-life of elimination from blood for this second phase was calculated to be 363 min. Approximately 58% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine within 24 hr after the administration. Another two female beagle dogs were orally dosed by capsule with 4.0 mg/kg (ethoxy-14C) diazinon in ethanol. Approximately 85% of the administered radioactivity was recovered within 24 hr after oral administration, with 53% of it occurring in urine.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 198: Diazinon (333-41-5) (1998); Available from, as of August 31, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DIAZINON (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The main metabolic pathways of degradation of diazinon are: cleavage of the ester bond leading to the hydroxypyrimidine derivatives; transformation of P-S moiety to the P-O derivative; oxidation of isopropyl substituent leading to the corresponding tertiary and primary alcohol derivatives; oxidation of the methyl substituent leading to the corresponding alcohol; glutathione-mediated cleavage of the ester bond leading to a glutathione conjugate.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 198: Diazinon (333-41-5) (1998); Available from, as of August 31, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
/STUDY OF METABOLISM IN RATS OF DIAZINON FOUND THAT/ THE METABOLITES 2-ISOPROPYL-4-METHYL-6-HYDROXYPYRIMIDINE ... /& TWO UNIDENTIFIED METABOLITES/ WHICH WERE EXCRETED IN THE URINE AND FECES, ACCOUNT FOR 70% OF THE DOSE. ... METB IN RATS OF DIAZINON ... LABELLED WITH (14)C, ... 3 METABOLITES WERE LOCATED ON GENERAL METABOLIC PATHWAY BY FOLLOWING THEIR METABOLIC FATE AFTER IV INJECTION. SINCE ACUTE ORAL TOXICITIES OF ALL 3 CMPD ARE LESS THAN 1/10 OF THAT OF DIAZINON, BIOTRANSFORMATION IS ASSOC WITH DETOXICATION.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 286
DIAZINON ... APPEARS TO BE METABOLIZED INTO CORRESPONDING PHOSPHATE IN LACTATING COWS, AND INTO THE HYDROLYTIC PRODUCTS DIETHYL PHOSPHOROTHIOATE AND DIETHYL PHOSPHATE WITH LIBERATION OF 2-HYDROXY-6-ISOPROPYL-4-METHYLPYRIMIDINE /PLUS METABOLITE DIAZOXON/.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 280
AFTER ADMIN OF DIAZINON BY STOMACH TUBE TO SHEEP, HYDROXYDIAZINON WAS FOUND IN TISSUES. DIAZINON, WHEN FED TO SHEEP, WAS METABOLIZED ALSO BY HYDROXYLATION OF C-4 METHYL GROUP. RESIDUES OF THIS & C-1' ISOPROPANOL ANALOG WERE FOUND ... .
Menzie, C. M. Metabolism of Pesticides, An Update. U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish, Wild-life Service, Special Scientific Report - Wildlife No. 184, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, l974., p. 154
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for DIAZINON (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Diazinon has known human metabolites that include Diazoxon, Diethyl thiophosphate, and Pyrimidinol.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
ORAL DOSE OF ECTOPARASITICIDE, (14)C DIAZINON, WAS RAPIDLY ELIMINATED FROM RAT (BIOLOGICAL HALF-LIFE WAS 12 HR). 80% OF (14)C WAS EXCRETED IN URINE & 18% IN FECES. COMPARABLE EXCRETION PATTERN & LOWER BIOLOGICAL HALF-LIFE OF 9 HR WAS OBTAINED AFTER IV ADMIN OF 3 (14)C METABOLITES OF DIAZINON.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 148
AFTER ORAL ADMIN TO RATS, EXCRETION OF RING & SIDE CHAIN LABELED DIAZINON EXCEEDED 90% AFTER 168 HR. BIOLOGICAL HALF-LIFE VARIED FROM 7 HR IN MALE RATS FOR ETHYL-(14)C-DIAZINON TO 12 HR FOR 2-(14)C-DIAZINON IN MALE & FEMALE RATS.
Menzie, C. M. Metabolism of Pesticides, An Update. U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish, Wild-life Service, Special Scientific Report - Wildlife No. 184, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, l974., p. 154
Two female Beagle dogs were intravenously dosed with 0.2 mg/kg (ethoxy-14C)-diazinon (specific activity 3.4 uCi/mg) in 0.7 mL ethanol. ... The half-life of elimination from blood for this second phase was calculated to be 363 min. ...
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 198: Diazinon (333-41-5) (1998); Available from, as of August 31, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
PURE DIAZINON IS POOR ANTICHOLINESTERASE, BUT IS READILY CONVERTED TO STRONG INHIBITOR UPON STORAGE OR HEATING, PARTICULARLY IN PRESENCE OF TRACE OF MOISTURE. THERMAL DECOMPOSITION OF PURE DIAZINON ... PRODUCTS OBTAINED ARE PYROPHOSPHATES THAT PROBABLY ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR INCR IN ANTICHOLINESTERASE ACTIVITY.
White-Stevens, R. (ed.). Pesticides in the Environment: Volume 1, Part 1, Part 2. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1971., p. 170
The organothiophosphate diazinon inhibits the target site acetylcholinesterase only after activation to its metabolite diazoxon. Commonly, the toxicity of xenobiotics toward aquatic organisms is expressed as a function of the external concentration and the resulting effect on the individual level after fixed exposure times. This approach does not account for the time dependency of internal processes such as uptake, metabolism, and interaction of the toxicant with the target site. Here, ...a mechanistic toxicodynamic model for Daphnia magna and diazoxon /is developed/, which accounts for the inhibition of the internal target site acetylcholinesterase and its link to the observable effect, immobilization, and mortality. The model was parametrized by experiments performed in vitro with the active metabolite diazoxon on enzyme extracts and in vivo with the parent compound diazinon. The mechanism of acetylcholinesterase inhibition was shown to occur irreversibly in two steps via formation of a reversible enzyme-inhibitor complex. The corresponding kinetic parameters revealed a very high sensitivity of acetylcholinesterase from D. magna toward diazoxon, which corresponds well with the high toxicity of diazinon toward this species. Recovery of enzyme activity but no recovery from immobilization was observed after in vivo exposure to diazinon. The toxicodynamic model combining all in vitro and in vivo parameters was successfully applied to describe the time course of immobilization in dependence of acetylcholinesterase activity during exposure to diazinon. The threshold value for enzyme activity below which immobilization set in amounted to 40% of the control activity. Furthermore, the model enabled the prediction of the time-dependent diazoxon concentration directly present at the target site.
PMID:21539304 Kretschmann A et al; Environ Sci Technol 45 (11): 4980-7 (2011)