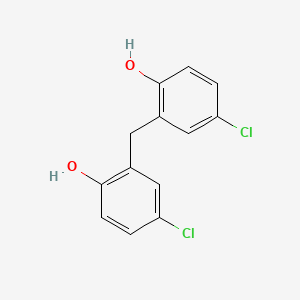

1. Panacide
1. Dichlorophene
2. 97-23-4
3. 2,2'-methylenebis(4-chlorophenol)
4. Didroxane
5. Anthiphen
6. Dichlorofen
7. Dichlorphen
8. Parabis
9. Dicestal
10. Didroxan
11. Trivex
12. Antiphen
13. Cordocel
14. Difentan
15. Embephen
16. Panacide
17. Prevental
18. Taeniatol
19. Teniathane
20. Teniatol
21. Teniotol
22. Vermithana
23. Antifen
24. Halenol
25. Hyosan
26. Korium
27. Palacel
28. Dichlorophen B
29. Dichlorophene 10
30. Dichloorfeen
31. Gingivit
32. Wespuril
33. Gefir
34. Phenol, 2,2'-methylenebis[4-chloro-
35. Fungicide M
36. Dddm
37. Plath-lyse
38. Bis(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methane
39. Fungicide Gm
40. Preventol Gd
41. Preventol Gdc
42. Diphenthane 70
43. Sandocide
44. Super Mosstox
45. Di-phentane-70
46. 2,2'-dihydroxy-5,5'-dichlorodiphenylmethane
47. Bis(chlorohydroxyphenyl)methane
48. 1322-43-6
49. Bis(2-hydroxy-5-chlorophenyl)methane
50. Giv Gard G 4-40
51. Di-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methane
52. 5,5'-dichloro-2,2'-dihydroxydiphenylmethane
53. 4-chloro-2-[(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]phenol
54. Bis-2-hydroxy-5-chlorfenylmethan
55. Dichlorofen [czech]
56. Bis(5-chlor-2-hydroxyphenyl)-methan
57. 4,4'-dichloro-2,2'-methylenediphenol
58. Methanedichlorofen
59. O,o-metilen-bis(4-cloro-fenolo)
60. G-4 Technical
61. G-4 Pure
62. ((dihydroxydichloro)diphenyl)methane
63. Nsc-38642
64. 2,2'-methylenebis-(4-chlorophenol)
65. G-4
66. 2,2'-methylene-bis (4-chlorophenol)
67. Phenol, 2,2'-methylenebis(4-chloro-
68. T1j0jou64o
69. Chembl33845
70. Mls000069468
71. G 4
72. 2,2/'-methylenebis(4-chlorophenol)
73. 4-chloro-2-(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzyl)phenol
74. Chebi:34689
75. Nsc38642
76. 2,2'-methylenebis[4-chlorophenol]
77. O,o-methyleen-bis-(4-chloorfenol)
78. 2,2'-methanediylbis(4-chlorophenol)
79. Dichlorofen (czech)
80. Ncgc00091325-05
81. Dichlorophenum
82. Diclorofeno
83. Smr000059095
84. Dsstox_cid_1824
85. Dsstox_rid_76351
86. Dsstox_gsid_21824
87. 2,5'-dichlorodiphenylmethane
88. 5,2'-dihydroxydiphenylmethane
89. Sindar G 4
90. Dichloorfeen [dutch]
91. Wln: Qr Dg B1r Bq Eg
92. Caswell No. 563
93. 4-chloranyl-2-[(5-chloranyl-2-oxidanyl-phenyl)methyl]phenol
94. Phenol,2'-methylenebis[4-chloro-
95. [(dihydroxydichloro)diphenyl]methane
96. Ddm (van)
97. Diclorofeno [inn-spanish]
98. Cas-97-23-4
99. Dichlorophene [inn-french]
100. Dichlorophene [iso-french]
101. Dichlorophenum [inn-latin]
102. Dichlorophen [inn:ban:dcf]
103. Dichlorophen [iso]
104. Ccris 6060
105. G 4 (van)
106. Hsdb 6033
107. Dichlorophen [bsi:iso]
108. Einecs 202-567-1
109. Nsc 38642
110. Unii-t1j0jou64o
111. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 055001
112. Brn 1884514
113. Algafen
114. Anthipen
115. Nuophene
116. Westpuril
117. Bis-2-hydroxy-5-chlorfenylmethan [czech]
118. Fungicide Fx
119. Ai3-02370
120. O,o-methyleen-bis(4-chloorfenol) [dutch]
121. Difent*n
122. O,o-metilen-bis(4-cloro-fenolo) [italian]
123. Acticide Ddm
124. Bis(5-chlor-2-hydroxyphenyl)-methan [german]
125. Diphentane 70
126. O,o-methyleen-bis(4-chloorfenol)
127. Mfcd00002322
128. Cuniphen (salt/mix)
129. Spectrum_000762
130. Opera_id_1730
131. Spectrum2_001214
132. Spectrum3_001405
133. Spectrum4_000390
134. Spectrum5_001519
135. Dichlorophen [mi]
136. Dichlorophen [inn]
137. Dichlorophen [hsdb]
138. Dichlorophene [inci]
139. Schembl18052
140. Bspbio_003050
141. Dichlorophen [mart.]
142. Kbiogr_000919
143. Kbioss_001242
144. Mls001076530
145. Bidd:er0237
146. Dichlorophen [who-dd]
147. Divk1c_000460
148. Spectrum1500626
149. Spbio_001028
150. 4-chloro-2-[(5-chloro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)methyl]phenol
151. Dtxsid6021824
152. Ecco Mp 2004 (salt/mix)
153. Hms501g22
154. Kbio1_000460
155. Kbio2_001242
156. Kbio2_003810
157. Kbio2_006378
158. Kbio3_002270
159. Zinc56435
160. Ninds_000460
161. Dichlorophene [green Book]
162. Hms1921m03
163. Hms2230h06
164. Hms3373o17
165. Kuc106446n
166. Kuc112931n
167. Pharmakon1600-01500626
168. Nsc39467
169. Tox21_111112
170. Tox21_201429
171. Tox21_303013
172. Bdbm50303912
173. Ccg-39772
174. Nsc-39467
175. Nsc757391
176. S5724
177. 2,2''-methylenebis(4-chlorophenol)
178. Akos015917706
179. Bis(2-hydroxy-5-chlorophenyl)-methane
180. Tox21_111112_1
181. 2,2'-methylene-bis(4-chloro-phenol)
182. Cs-3867
183. Db11396
184. Ksc-19-050
185. Nsc-757391
186. Bis-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-methane
187. Idi1_000460
188. Qtl1_000030
189. Ncgc00091325-01
190. Ncgc00091325-03
191. Ncgc00091325-04
192. Ncgc00091325-06
193. Ncgc00091325-07
194. Ncgc00091325-09
195. Ncgc00256543-01
196. Ncgc00258980-01
197. Ac-10330
198. As-12817
199. Hy-12638
200. Ksc-336-005-1
201. Sbi-0051563.p002
202. Bis(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methane, 95%
203. Ft-0609137
204. Ft-0739351
205. M0213
206. E79441
207. 3,3''-dichloro-6,6''-dihydroxydiphenylmethane
208. Ab00052130_15
209. Dichlorophene, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
210. A845699
211. Q377552
212. Sr-01000721928
213. Dichlorophene; Bis(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methane
214. Sr-01000721928-3
215. W-100114
216. Bis(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methane, Technical Grade, 90%
217. Jal
| Molecular Weight | 269.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H10Cl2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 268.0057849 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 268.0057849 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 40.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 226 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anticestodal Agents; Antifungal Agents; Antiprotozoal Agents; Cathartics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
/SRP/: Dichlorophen is primarily effective against the large tapeworms of man & domestic animals. ... Dichlorophen is effective in clearing a large proportion of infections by Taenia saginata. Taenia solium is also susceptible... Available data suggest it may be useful against Diphyllobothrium latum & Hymenolepis mana infections.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1014
Dichlorophen is given orally without preliminary fasting or other prior preparation of the patient. Satisfactory results have been obtained by giving 2-3 g every 8 hr for 3 doses (children, 1-2 g). Alternatively, single dose of 6 g (children, 2-4 g) may be given on each of 2 successive days.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1014
Medication (Vet): Antihelmintic. Targets Cestodes. ... antiprotozoal,... antifungal agent
Milne, G.W.A. Veterinary Drugs: Synonyms and Properties. Ashgate Publishing Limited, Aldershot, Hampshire, England 2002., p. 17
Anthelmintic agent for Tapeworms in human & vet medicine
SRI
...Usually nothing recognizable or only partially disintegrated mature segments can be seen in the stool. This presents difficulty in diagnosing cure, &, therefore, careful follow-up of the patient is required.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1014
...There may be danger of cysticereosis from liberated ova.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1014
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: Probable oral lethal dose (human) 0.5-5 g/kg, between 1 oz & 1 pint (or 1 lb) for 70 kg person (150 lbs).
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-131
Antifungal Agents
Substances that destroy fungi by suppressing their ability to grow or reproduce. They differ from FUNGICIDES, INDUSTRIAL because they defend against fungi present in human or animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antifungal Agents.)
Anticestodal Agents
Agents used to treat tapeworm infestations in man or animals. (See all compounds classified as Anticestodal Agents.)
Antiprotozoal Agents
Substances that are destructive to protozoans. (See all compounds classified as Antiprotozoal Agents.)
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P02 - Anthelmintics
P02D - Anticestodals
P02DX - Other anticestodals
P02DX02 - Dichlorophen
Following oral administration to the rat, (14)C-dichlorophen was well absorbed with 78% of the dose excreted in the urine and 15% in the feces in 2 days.
Dixon PAF, Caldwell J; Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 3 (2): 95 (1978)
/Investigators/ dosed female Wistar albino rats (3/group) orally with 50 mg/kg [14C]-dichlorophene dissolved in propane-1,2-diol. One group of rats was bile-duct cannulated 1 hr after oral administration of [14C]-dichlorophene. An average of 95% [14C]-dichlorophene was excreted in the urine and feces 2 days after dosing. Most (78%) of the biocide was recovered in the urine, and 17% was recovered in the feces.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
/Investigators/ dosed female Wistar albino rats (3/group) orally with 50 mg/kg [14C]-dichlorophene dissolved in propane-1,2-diol. ... The following urinary metabolites were identified: 4% dichlorophene; 17% dichlorophene sulfate; 25% dichlorophene monoglucuronide; and 19% dichlorophene diglucuronide. Bile duct-cannulated rats excreted 36% of the dose of [14C]-dichlorophene 1 to 4 hr after dosing. The intestinal contents and the intestinal wall had 32% and 11% [14C]-dichlorophene, respectively, whereas 2% was found in the urine. Only the monoglucuronide metabolite of [14C]-dichlorophene was found in the bile. The investigators suggested that dichlorophene underwent enterohepatic circulation.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
/Investigators examined/ the metabolites of dichlorophene from enterohepatic circulation in female Vom strain rats. Female rats were dosed orally with 50 mg/kg [14C]-dichlorophene (5 uCi/kg) and were bile-duct cannulated 1 hr later. Bile and urine were collected for 3 hr. The bile was then infused into the duodenum of another set of cannulated rats, from which bile and urine were collected. This process was repeated with a third set of rats. Five rats were used in each experiment. The only biliary metabolite was the monoglucuronide in all three experiments. In the urine, dichlorophene sulfate and diglucuronide were the major metabolites. Blood from the hepatic portal vein in rats receiving bile contained free dichlorophene and its monoglucuronide.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
/After/ orally administered dichlorophene: (1) dichlorophene is absorbed from the gut, is conjugated to the sulfate and monoglucuronide in the gut wall, and passes to the liver where more of these metabolites can be formed; (2) the diglucuronide is formed in the liver or other organs perfused by systemic circulation; (3) the sulfate and diglucuronide are eliminated from the peripheral circulation via the kidneys; (4) the diglucuronide is too water soluble for biliary excretion; however, most of the monoglucuronide undergoes biliary excretion; (5) residual monoglucuronide is metabolized to sulfate and diglucuronide on subsequent passes through the enterohepatic cycle and these are eliminated via the kidneys.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)