
1. Dihydroquinidine
2. Dihydroquinine
3. Hydroquinidine
4. Hydroquinidine Dihydrochloride, (1beta,4beta,3s)-(+-)-isomer
5. Hydroquinidine Dihydrochloride, (3alpha,9s)-(+-)-isomer
6. Hydroquinidine Hydrochloride
7. Hydroquinidine Monosulfate
8. Hydroquinidine Monosulfate, (1beta,3alpha,4beta,8alpha,9r)-isomer
9. Hydroquinidine Monosulfate, (1beta,3alpha,4beta,9s)-isomer
10. Hydroquinidine Sulfate
11. Hydroquinidine Sulfate, (9s)-isomer
12. Hydroquinidine, (+-)-isomer
13. Hydroquinidine, (1beta, 3alpha,4beta,8alpha,9r)-isomer
14. Hydroquinidine, (1beta,3alpha,4beta,9s)-isomer
15. Hydroquinidine, (1beta,4beta,9s)-(+-)-isomer
16. Hydroquinidine, (3alpha,9s)-(+-)-isomer
17. Hydroquinidine, (8alpha,9r)-isomer
18. Hydroquinidine, (8alpha,9s)-isomer
19. Hydroquinidine, (9r)-isomer
20. Hydroquinidine, (9s)-(+-)-isomer
21. Lcn 834
22. Lcn-834
23. Lentoquine
24. Srcor
1. Dihydroquinine
2. Chembl2079611
3. (-)-hydroquinine
4. 10,11-dihydroquinine
5. (-)-10,11-dihydroquinine
6. Nsc-41799
7. 522-66-7
8. Schembl109602
9. Bdbm50407154
10. Cs-w019883
11. Hy-42034
12. J3.558.731d
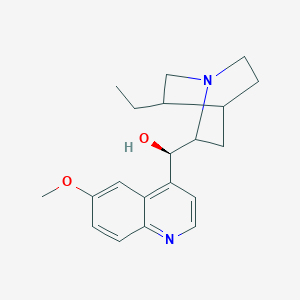
13. (r)-(5-ethyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-yl)(6-methoxy-4-quinolinyl)methanol
| Molecular Weight | 326.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H26N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 326.199428076 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 326.199428076 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 45.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 432 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Parasympatholytics
Agents that inhibit the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system. The major group of drugs used therapeutically for this purpose is the MUSCARINIC ANTAGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Parasympatholytics.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M09 - Other drugs for disorders of the musculo-skeletal system
M09A - Other drugs for disorders of the musculo-skeletal system
M09AA - Quinine and derivatives
M09AA01 - Hydroquinine