

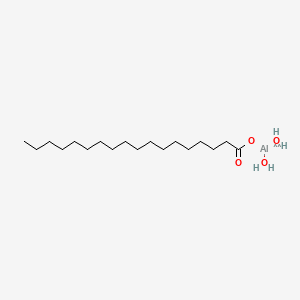

1. Aluminum Tristearate
2. Ammonium Stearate
3. Calcium Stearate
4. Magnesium Stearate
5. Octadecanoic Acid
6. Sodium Stearate
7. Stearic Acid
8. Zinc Stearate
1. 7047-84-9
2. Dibasic Aluminum Stearate
3. Dihydroxyaluminum Stearate
4. Dihydroxy(stearato)aluminium
5. Dihydroxy(stearato)aluminum
6. Dihydroxyaluminium Stearate, Pure
7. Chebi:31197
8. Ncgc00160596-02
9. Aluminum, Monostearate
10. Aluminum, Dihydroxide Stearate
11. Einecs 230-325-5
12. Aluminum, Dihydroxy(stearato)-
13. Aluminum Dihydroxide Stearate
14. Unii-p9bc99461e
15. Aluminum Dextran
16. Aluminum Monostearate [jan:nf]
17. Stearic Acid Aluminum Dihydroxide Salt
18. Aluminum, Dihydroxy(octadecanoato-kappao)-
19. Aluminum, Dihydroxy(octadecanoato-.kappa.o)-
20. Schembl4101
21. Dsstox_cid_28623
22. Dsstox_rid_82893
23. Dsstox_gsid_48697
24. Chembl3185220
25. Dtxsid9048697
26. Dihydroxido(octadecanoato)aluminium
27. Aluminum Monostearate (jp17/nf)
28. Tox21_113090
29. Akos024319334
30. Db01375
31. Ncgc00160596-01
32. Ncgc00160596-03
33. Cas-7047-84-9
34. D01867
35. F20724
36. Sr-01000945248
37. Q4119955
38. Sr-01000945248-1
39. Aluminum Monostearate, Technical, ~75% (al), Powder
| Molecular Weight | 346.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H39AlO4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 18 |
| Exact Mass | 346.2663731 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 346.2663731 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 28.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 225 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Antacids perform a neutralization reaction, ie. they buffer gastric acid, raising the pH to reduce acidity in the stomach. When gastric hydrochloric acid reaches the nerves in the gasitrointestinal mucosa, they signal pain to the central nervous system. This happens when these nerves are exposed, as in peptic ulcers. The gastric acid may also reach ulcers in the esophagus or the duodenum. Other mechanisms may contribute, such as the effect of aluminum ions inhibiting smooth muscle cell contraction and delaying gastric emptying. Aluminum is known to bind troponin C (a muscle protein) and to interfere with voltage-dependent calcium transport. Aluminum also binds to and inhibits the activity of mitochondrial voltage gated channels (VDAC).