
1. Apo Dimenhydrinate
2. Apo-dimenhydrinate
3. Aviomarin
4. Biodramina
5. Calm X
6. Calm-x
7. Cinfamar
8. Contramareo
9. Dimen Heumann
10. Dimen Lichtenstein
11. Dimetabs
12. Dinate
13. Diphenhydramine Theoclate
14. Dmh
15. Dramamine
16. Dramanate
17. Gravol
18. Heumann, Dimen
19. Lnopharm, Reisetabletten
20. Lichtenstein, Dimen
21. Marmine
22. Motion Aid
23. Motion-aid
24. Nausicalm
25. Reisegold
26. Reisetabletten Lnopharm
27. Reisetabletten Ratiopharm
28. Reisetabletten Stada
29. Reisetabletten-ratiopharm
30. Rodovan
31. Rubiemen
32. Stada, Reisetabletten
33. Superpep
34. Theoclate, Diphenhydramine
35. Travel Well
36. Triptone
37. Vertigo Vomex
38. Vertigo-vomex
39. Vomacur
40. Vomex A
41. Vomisin
42. Wehamine
1. 523-87-5
2. Dramamine
3. Chloranautine
4. Vomex A
5. Diphenhydrinate
6. Anautine
7. Travelin
8. Amosyt
9. Aviomarin
10. Gravol
11. Menhydrinate
12. Andramine
13. Antemin
14. Diamarin
15. Dimenest
16. Dimentabs
17. Dramalen
18. Dramamin
19. Dramarin
20. Dramilin
21. Eldodram
22. Gravinol
23. Hydrinate
24. Novamine
25. Permital
26. Supremal
27. Teodramin
28. Travelmin
29. Troversin
30. Xamamina
31. Dimate
32. Dramyl
33. Dromyl
34. Reise-engletten
35. Neo-navigan
36. Diphenhydramine Theoclate
37. Diphenhydramine 8-chlorotheophylline
38. Diphenhydramine 8-chlorotheophyllinate
39. Nsc 117855
40. Jb937per5c
41. O-benzhydryldimethylaminoethanol 8-chlorotheophyllinate
42. Nsc-117855
43. 1h-purine-2,6-dione, 8-chloro-3,7-dihydro-1,3-dimethyl-, Compd. With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethanamine (1:1)
44. 8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-1h-purine-2,6(3h,7h)-dione Compound With 2-(benzhydryloxy)-n,n-dimethylethanamine (1:1)
45. (o-benzhydryl(dimethylamino)ethanol) 8-chlorotheophyllinate
46. Benzhydryl-beta-dimethylaminoethylether 8-chlorotheophylline
47. N,n-dimethyl-2-diphenylmethoxyethylamine 8-chlorotheophyllinate
48. 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethylamine 8-chlorotheophyllinate
49. Beta-dimethylaminoethyl Benzhydryl Ether 1,3-dimethyl-8-chloroxanthine
50. 2-(benzhydryloxy)-n,n-dimethylethylamine Compd. With 8-chlorotheophylline
51. 8-chlorotheophylline, Compound With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethylamine (1:1)
52. Dimenhydrinat
53. Theohydramine
54. Dommanate
55. Lomarin
56. Reidamine
57. Removine
58. Emedyl
59. Faston
60. 2-benzhydryloxy-n,n-dimethylethanamine;8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-7h-purine-2,6-dione
61. Novamin (van)
62. Gravinol (antiemetic)
63. Dimenidrinato [dcit]
64. Sr-05000001608
65. [o-benzhydryl(dimethylamino)ethanol] 8-chlorotheophyllinate
66. Dimenhydrinatum [inn-latin]
67. Dimenidrinato
68. Dimenhidrinato [inn-spanish]
69. Ccris 4798
70. Hsdb 3064
71. Dramamine (tn)
72. Nci-c60639
73. 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethanamine And 8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-3,9-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
74. Dimenhydrinate,(s)
75. Einecs 208-350-8
76. Mfcd00054265
77. Spectrum_000974
78. Prestwick3_000265
79. Spectrum2_000992
80. Spectrum3_000397
81. Spectrum4_000517
82. Spectrum5_000909
83. Dsstox_cid_5087
84. Unii-jb937per5c
85. Dimenhydrinate [mi]
86. Schembl5128
87. Dimenhydrinate [inn]
88. Dimenhydrinate [jan]
89. Dsstox_rid_77660
90. Dsstox_gsid_25087
91. Bspbio_000110
92. Bspbio_002213
93. Dimenhydrinate [hsdb]
94. Kbiogr_001093
95. Kbioss_001454
96. Dimenhydrinate [vandf]
97. Divk1c_000049
98. Spectrum1500251
99. Spbio_001083
100. Dimenhydrinate [mart.]
101. Bpbio1_000122
102. Dimenhydrinate [usp-rs]
103. Dimenhydrinate [who-dd]
104. Chembl1200406
105. Dtxsid9025087
106. Chebi:94848
107. Hms500c11
108. Kbio1_000049
109. Kbio2_001454
110. Kbio2_004022
111. Kbio2_006590
112. Kbio3_001433
113. Dimenhydrinate (jp17/usp/inn)
114. Ninds_000049
115. Hms1920g20
116. Hms2091o08
117. Hms2095f12
118. Hms3712f12
119. Pharmakon1600-01500251
120. 2-(benzhydryloxy)-n,n-dimethylethylamine 8-chlorotheophyllinate
121. Hy-b1215
122. Dimenhydrinate [ep Impurity]
123. Dimenhydrinate [orange Book]
124. Dimenhydrinate [usp:inn:ban:jan]
125. Tox21_200323
126. Ccg-40210
127. Dimenhydrinate [ep Monograph]
128. Nsc117855
129. Nsc756740
130. S4672
131. Dimenhydrinate [usp Monograph]
132. Dimenhydrinate For Peak Identification
133. Akos015896341
134. Ac-8241
135. Cs-4841
136. Db00985
137. Nsc-756740
138. 8-chlorotheophylline, Compd. With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethylamine (1:1)
139. Ethylamine 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethyl-, Compd With 8-chlorotheophylline (1:1)
140. Ethylamine, 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n, N-dimethyl-, Compd. With 8-chlorothiophylline (1:1)
141. Ethylamine, N,n-dimethyl-2-(diphenylmethoxy)-, Compd. With 8-chlorotheophylline
142. Idi1_000049
143. Theophylline, 8-chloro-, Compd With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethyethylamine (1:1)
144. Theophylline, 8-chloro-, Compd. With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethylamine (1:1)
145. Ncgc00021154-01
146. Ncgc00021154-02
147. Ncgc00021154-03
148. Ncgc00021154-04
149. Ncgc00021154-05
150. Ncgc00021154-06
151. Ncgc00021154-07
152. Ncgc00091928-01
153. Ncgc00091928-02
154. Ncgc00091928-03
155. Ncgc00257877-01
156. 1h-pyrine-2,6-dione, 8-chloro-3,7-dihydro-1,3-dimethyl-, Compd. With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethanamine (1:1)
157. As-13166
158. Bd166163
159. Ethanamine, 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethyl-, Compd. With 8-chloro-3,7-dihydro-1,3-dimethyl-1h-purine-2,6-dione (1:1)
160. Sbi-0051350.p003
161. Ab00053833
162. Ft-0625019
163. Ft-0696921
164. D00520
165. D82297
166. Wln: T56 Bm Dn Fnvnvj Cg F H &622
167. 523d875
168. Q420439
169. Sr-05000001608-1
170. Sr-05000001608-2
171. Brd-m98649031-001-01-1
172. Dimenhydrinate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
173. Dimenhydrinate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
174. Ethylamine 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n, Compd. With 8-chlorotheophylline (1:1)
175. Theophylline, Compd. With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethylamine (1:1)
176. Dimenhydrinate For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
177. Dimenhydrinate, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
178. Theophylline, Compd. With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-(dimethylethyl)amine (1:1)
179. 1h-purine-2, 8-chloro-3,7-dihydro-1,3-dimethyl-, Compd. With 2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethylethanamine (1:1)
180. 8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-1h-purine-2,6(3h,7h)-dione 2-(benzhydryloxy)-n,n-dimethylethanamine Salt
181. 8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-1h-purine-2,6(3h,7h)-dionecompoundwith2-(benzhydryloxy)-n,n-dimethylethanamine(1:1)
| Molecular Weight | 470.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H28ClN5O3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 469.1880675 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 469.1880675 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 81.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 509 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Antiemetics; Histamine H1 Antagonists
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
ABILITY TO INHIBIT EFFECTS OF HISTAMINE ON CAPILLARY PERMEABILITY & ON VASCULAR, BRONCHIAL, & MANY OTHER TYPES OF SMOOTH MUSCLE IS PROPERTY THAT CHARACTERIZES H1 ANTAGONISTS & THAT PROVIDES BASIS FOR THEIR PREVALENT CLINICAL USE... /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 603
"FLARE" COMPONENT OF TRIPLE RESPONSE & ITCHING CAUSED BY INTRADERMAL INJECTION OF HISTAMINE... H1-BLOCKING DRUGS SUPPRESS BOTH. ...HAVE LOCAL ANESTHETIC PROPERTIES... H1-BLOCKING DRUGS SELECTIVELY SUPPRESS STIMULANT EFFECT OF HISTAMINE ON ADRENAL CHROMAFFIN CELLS.../&/ AUTONOMIC GANGLION CELLS. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 605
...EFFICACY...IN COUNTERING HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS WILL VARY, DEPENDING ON DEG TO WHICH SYMPTOMS ARE DUE TO HISTAMINE. ...IN MAN...SOME PHENOMENA, INCL EDEMA FORMATION & ITCH, ARE FAIRLY WELL CONTROLLED; OTHERS, SUCH AS HYPOTENSION ARE LESS SO; & BRONCHOCONSTRICTION...LITTLE IF AT ALL. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 605
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DIMENHYDRINATE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
SEE ANTIHISTAMINICS. CONSIDERABLE MARGIN OF SAFETY SEPARATES THERAPEUTIC DOSE FROM USUAL LETHAL ONE. HOWEVER, BECAUSE CONVULSANT DOSE LIES NEAR LETHAL DOSE, CONVULSIONS INDICATE POOR PROGNOSIS. ADULTS HAVE SURVIVED SINGLE DOSES OF 2.5-5.0 G. CHILDREN...30-60 MG/KG HAS PRODUCED...POISONINGS. /ANTIHISTAMINICS/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-231
IN THERAPEUTIC DOSES, ALL H1 ANTAGONISTS ELICIT SIDE EFFECTS. ...RARELY SERIOUS & OFTEN DISAPPEAR...SOMETIMES...DRUG MUST BE WITHDRAWN. SOME DIFFERENCE...WITH DIFFERENT PREPN IS DISCERNIBLE...MARKED VARIATION IN RESPONSES OF INDIVIDUAL SUBJECTS... /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 607
...ANTICHOLINERGIC ACTIVITY, WHICH ACCOUNTS FOR DRYNESS OF MOUTH...&... DIFFICULTY IN MICTURATION & IMPOTENCE. SOME INTENSIFY RESPONSES TO NOREPINEPHRINE OR STIMULATION OF ADRENERGIC NERVES & INHIBIT RESPONSES TO TYRAMINE... RAPID IV INJECTION OF H1 ANTAGONISTS CAUSES TRANSIENT FALL IN BLOOD PRESSURE... /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 606
H1 ANTAGONISTS CAN BOTH STIMULATE & DEPRESS CNS. ...CENTRAL EXCITATION IS STRIKING FEATURE OF POISONING WITH ANTIHISTAMINES & CAN RESULT IN CONVULSIONS, PARTICULARLY IN INFANTS. CENTRAL DEPRESSION...IS USUAL ACCOMPANIMENT OF THERAPEUTIC DOSES. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 606
PERSONS TAKING ANTIHISTAMINES SHOULD BE ALERTED TO THEIR SEDATIVE EFFECTS & SHOULD BE CAUTIONED NOT TO DRIVE AN AUTOMOBILE, FLY AN AIRPLANE, OR OPERATE HAZARDOUS MACHINERY... /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1057
Dimenhydrinate is indicated for the prevention and treatment of nausea, vomiting, or vertigo of motion sickness.
Dimenhydrinate is indicated for the prevention and treatment of nausea, vomiting, or vertigo of motion sickness. It has a short duration of action of 4-8 hours. Patients should be counselled regarding pronounced drowsiness, avoiding alcohol and other sedatives, and exercising caution when operating a motor vehicle or heavy machinery.
Antiemetics
Drugs used to prevent NAUSEA or VOMITING. (See all compounds classified as Antiemetics.)
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
R - Respiratory system
R06 - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06A - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06AA - Aminoalkyl ethers
R06AA11 - Dimenhydrinate
Absorption
A 50 mg oral film coated tablet reaches a Cmax of 72.6 ng/mL with a Tmax of 2.7 hours. A 100 mg suppository reaches a Cmax of 112.2 ng/mL with a Tmax of 5.3 hours.
Route of Elimination
Dimenhydrinate is predominantly eliminated in the urine. 1-3% of the dissociated diphenhydramine is eliminated in the urine unchanged, while 64% of diphenhydramine is eliminated in the urine as metabolites. The elimination of dimenhydrinate has not been fully studied.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of dimenhydrinate is 3-4 L/kg.
DIMENHYDRINATE (ETHANOLAMINES): DURATION OF ACTION (HR) 4-6. /FROM TABLE/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 609
H1 ANTAGONISTS ARE READILY ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT & PARENTERAL SITES OF ADMIN. FOLLOWING ORAL ADMIN, EFFECTS START WITHIN 15 TO 30 MIN, ARE FULLY DEVELOPED WITHIN 1 HR, & LAST ABOUT 3 TO 6 HR, ALTHOUGH SOME...ACT LONGER. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 607
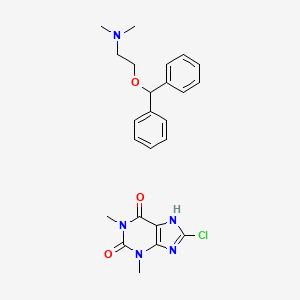
Dimenhydrinate is a theoclate salt that separates into [diphenhydramine] and [8-chlorotheophylline]. diphenhydramine can either be N-glucuronidated by UGTs to diphenhydramine N-glucuronide or N-demethylated by CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 to N-desmethyldiphenhydramine. N-desmethyldiphenhydramine can be N-demethylated again by the same enzymes to N,N-didesmethyldiphenhydramine, which undergoes oxidative deamination to form diphenylmethoxyacetic acid.
EXTENSIVE STUDIES OF METABOLIC FATE OF ANTIHISTAMINES HAVE BEEN LIMITED TO A FEW COMPD. ... MAIN SITE OF METABOLIC TRANSFORMATION IS LIVER. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 607
The plasma elimination half life of dimenhydrinate is 5-8 hours.
Dimenhydrinate is a theoclate salt that separates into [diphenhydramine] and [8-chlorotheophylline]. While the exact mechanism of action is unknown, diphenhydramine is theorized to reduce disturbances to equilibrium through antimuscarinic effects or histamine H1 antagonism. 8-chlorotheophylline may produce excitation through blocking adenosine receptors, reducing the drowsiness produced by diphenhydramine.
IT IS ESSENTIAL TO NOTE THAT NEITHER H1...BLOCKERS INHIBIT HISTAMINE RELEASE. ...EFFECTS OF HISTAMINE ANTAGONISTS...FACILITATE RELEASE. BENEFICIAL EFFECTS OF HISTAMINE ANTAGONISTS ARE THUS CONFINED TO ANTAGONISM OF RESPONSES TO HISTAMINE THAT IS RELEASED. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 605
DRUGS USED TO BLOCK HISTAMINE RECEPTORS FALL INTO THAT LARGE GROUP OF PHARMACOLOGICAL ANTAGONISTS THAT APPEAR TO ACT BY OCCUPYING "RECEPTIVE SITES" ON EFFECTOR CELL, TO EXCLUSION OF AGONIST MOLECULES, WITHOUT THEMSELVES INITIATING RESPONSE. TYPICALLY...COMPETITIVE & REVERSIBLE. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 603
...ANTIHISTAMINES EFFECTIVE IN MOTION SICKNESS ACT BY VIRTUE OF CENTRAL ANTAGONISM OF ACH... ACT BY BLOCKING EXCITATORY LABYRINTHINE IMPULSES @ CHOLINERGIC SYNAPSES IN REGION OF VESTIBULAR NUCLEI. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 606
...MOTION SICKNESS. ...STIMULATION OF VESTIBULAR APPARATUS...& THAT VESTIBULAR CEREBELLAR MIDBRAIN "INTEGRATIVE VOMITING CENTER" & MEDULLARY CHEMORECEPTIVE TRIGGER ZONE ARE SOMEHOW INVOLVED. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 606