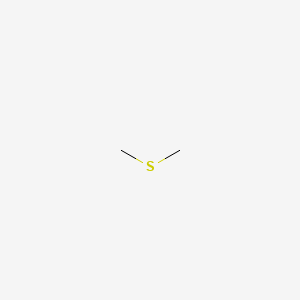

1. Dimethylsulphide
1. Methyl Sulfide
2. 75-18-3
3. Methane, Thiobis-
4. Dimethyl Sulphide
5. Dimethylsulfide
6. Methyl Thioether
7. Dimethyl Thioether
8. Dimethylsulphide
9. 2-thiapropane
10. Methyl Sulphide
11. Methylthiomethane
12. Dimethylsulfid
13. (methylsulfanyl)methane
14. Methylsulfanylmethane
15. Methyl Monosulfide
16. Dimethyl Monosulfide
17. Thiobismethane
18. 2-thiopropane
19. Methanethiomethane
20. Thiobis(methane)
21. Exact-s
22. Sulfure De Methyle
23. Dimethyl Sulfide (natural)
24. Dimethylsulfane
25. Fema No. 2746
26. Methylthiomethyl Radical
27. Methane, 1,1'-thiobis-
28. [sme2]
29. Qs3j7o7l3u
30. Chebi:17437
31. (ch3)2s
32. Methylsulfide
33. Dimethylsulfid [czech]
34. Sulfure De Methyle [french]
35. Hsdb 356
36. Einecs 200-846-2
37. Mfcd00008562
38. Un1164
39. Unii-qs3j7o7l3u
40. Brn 1696847
41. Methylsulphide
42. Thiopropane
43. Thiobis-methane
44. Di-methylsulfide
45. Ai3-25274
46. Dimethyl Sulfane
47. Sulfide, Methyl-
48. (methylthio)methane
49. Me2s
50. Reduced-dmso
51. Sme2
52. Nat. Dimethyl Sulfide
53. Dimethyl Sulfide, 98%
54. Reduced Dimethyl Sulfoxide
55. (methylsulfanyl)methane #
56. Dimethyl Sulfide [un1164] [flammable Liquid]
57. Dimethyl Sulfide-[13c2]
58. Dimethyl Sulfoxide(reduced)
59. Ec 200-846-2
60. (me)2s
61. Dimethyl Sulfide, >=99%
62. (methylthiomethylidyne)radical
63. 4-01-00-01275 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
64. Chembl15580
65. Dimethyl Sulfide [mi]
66. Methyl Sulfide [fhfi]
67. Dimethyl Sulfide [fcc]
68. Dimethyl Sulfide [hsdb]
69. Dtxsid9026398
70. S(ch3)2
71. Dimethyl Sulfide, >=99%, Fcc
72. Dimethyl Sulfide, Analytical Standard
73. Stl481894
74. Dimethyl Sulfide, >=95.0% (gc)
75. Akos009031411
76. Un 1164
77. Dimethyl Sulfide, Anhydrous, >=99.0%
78. 31533-72-9
79. M0431
80. Dimethyl Sulfide, Puriss., >=99.0% (gc)
81. C00580
82. Dimethyl Sulfide, Natural, >=99%, Fcc, Fg
83. Dimethyl Sulfide [un1164] [flammable Liquid]
84. A838342
85. Dimethyl Sulfide, Redistilled, >=99%, Fcc, Fg
86. Q423133
87. Q-100810
88. Methyl Sulphide, Dimethyl Sulphide, Exact-s, Thiobismethane
| Molecular Weight | 62.14 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2H6S |
| XLogP3 | 0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 62.01902136 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 62.01902136 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 25.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 3 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 2.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Dimethyl sulfide is excreted by the lungs and the kidneys. Rats given oral or parenteral doses showed dimethyl sulfide in the breath. Dimethyl sulfide is also found in the breath of cats and mice given dimethylsulfoxide.
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Documentation of the TLV's and BEI's with Other World Wide Occupational Exposure Values. CD-ROM Cincinnati, OH 45240-1634 2007.
Dimethyl sulfide was detected in milk from mature cows in late lactation following ingestion of capsules containing either 60 or 80 g of D,L-methionine or 1,2,or 4 mL of dimethyl sulfide; no dimethyl sulfide was detected in the cows dosed with lower doses of D,L-methionine.
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Documentation of the TLV's and BEI's with Other World Wide Occupational Exposure Values. CD-ROM Cincinnati, OH 45240-1634 2007.
Excess methyl sulfide is exhaled with carbon dioxide, if it occurs in excess and in free form.
Clayton, G. D. and F. E. Clayton (eds.). Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume 2A, 2B, 2C: Toxicology. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1981-1982., p. 2084
... The ip administration of dimethyl disulfide resulted in its appearance in the expired breath of mice and much smaller amounts of both methanethiol and dimethyl sulfide. The ip administration of methanethiol resulted in its pulmonary excretion and that of dimethyl sulfide. Administration of dimethyl sulfide led to its appearance alone in expired breath. Mice pretreated with ammonium acetate and then injected with dimethyl disulfide excreted the same 3 compounds via the lungs as above, but there were complex changes in the proportions and in the time sequence of their appearance. The absolute amounts of all 3 were increased, and the peak excretion for each was delayed. The amount excreted as dimethyl sulfide was particularly increased.
Susman JL et al; Drug Chem Toxicol 1 (4): 327-338 (1978). Available from, as of November 18, 2009: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/f?./temp/~3rHMi5:1
... To identify breath sulfur compounds causing halitosis induced by cysteamine therapy in patients with cystinosis. After the ingestion of 15 mg/kg cysteamine, whole blood (n = 4), urine (n = 4) and breath (n = 8) volatile sulfur compounds levels were measured every 60 min over a 360 min period by gas chromatography and the cysteamine plasma concentrations (n = 4) were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. The expired air of cystinotic patients contained elevated concentrations of methanethiol (MT, median maximum value 0.5 (range 0-11) nmol/L) and, in particular, dimethyl sulfide (DMS, median maximum value 15 (range 2-83) nmol/L). DMS concentrations higher than 0.65 nmol/L are known to cause halitosis. Maximal plasma values of cysteamine (median 46 (range 30-52) umol/L) preceded those of MT and DMS, confirming that cysteamine is converted to MT and DMS. Less than 3% of the amount of cysteamine ingested was excreted as MT and DMS via expired air and 0.002% via urine. Halitosis induced by cysteamine intake is caused by DMS and to a lesser extent by MT, excreted via the expired air ...
PMID:17513151 Besouw M et al; Mol Genet Metab. 2007 Jul;91(3):228-33 (2007).
Dimethylsulfoxide and dimethylsulfdioxide were found in rabbit urine following dimethyl sulfide administration.
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Documentation of the TLV's and BEI's with Other World Wide Occupational Exposure Values. CD-ROM Cincinnati, OH 45240-1634 2007.
The ip admin of dimethyl disulfide resulted in the appearance of dimethyl sulfide in expired breath of mice. Ip admin of methanethiol resulted in pulmonary excretion of dimethyl sulfide.
Susman JL et al; Drug Chem Toxicol 1 (4): 327-38 (1979)
Methyl sulfide introduced into the mammalian system by ingestion or inhalation at low quantities can readily be metabolized. ... Methyl sulfide can also be formed as a degradation product from dimethyl sulfoxide. ... It is also formed from S-methylcysteine sulfoxide by intestinal bacteria.
Clayton, G. D. and F. E. Clayton (eds.). Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume 2A, 2B, 2C: Toxicology. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1981-1982., p. 2084
A single ip injection of 275 mg of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to rats effectively uncouples oxidative phosphorylation in liver mitochondria during the period from 2 hr to 5 days postinjection. Higher doses of DMSO are inhibitory to mitochondrial respiration. DMSO has, however, no uncoupling action on oxidative phosphorylation in vitro. Dimethyl sulfide, a known metabolite of DMSO, brings about the uncoupling effect in vitro. The uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation by normal mitochondria could also be achieved if these are preincubated with postmitochondrial liver supernatant derived from rat injected with DMSO, 2-24 hr prior to sacrifice. These results provide an explanation for the observed uncoupling effect exerted by DMSO in vivo.
PMID:6838520 Mhatre SS et al; Biochem Biophys Res Commun 110 (1): 325-31 (1983)
After overnight fasting, the concn of dimethyl sulfide in expired alveolar gas (ALV-DMS) was determined serially following ingestion of 2 g of dl-methionine in normal subjects and pt with liver diseases. ALV-DMS peaked in 30-90 min, declined markedly in 3 hr. Cirrhotics had t/2 longer than any other group.
PMID:445853 Kaji H et al; Clin Chim Acta 93 (3): 377-80 (1979)
A single ip injection of 275 mg of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to rats effectively uncouples oxidative phosphorylation in liver mitochondria during the period from 2 hr to 5 days postinjection. Higher doses of DMSO are inhibitory to mitochondrial respiration. DMSO has, however, no uncoupling action on oxidative phosphorylation in vitro. Dimethyl sulfide, a known metabolite of DMSO, brings about the uncoupling effect in vitro. The uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation by normal mitochondria could also be achieved if these are preincubated with postmitochondrial liver supernatant derived from rat injected with DMSO, 2-24 hr prior to sacrifice. These results provide an explanation for the observed uncoupling effect exerted by DMSO in vivo.
PMID:6838520 Mhatre SS et al; Biochem Biophys Res Commun 110 (1): 325-31 (1983)