


1. Vumerity
1. 1577222-14-0
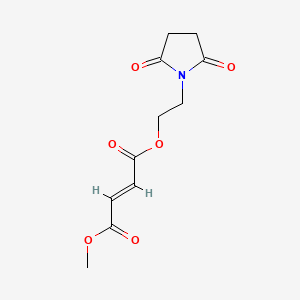
2. 2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl Methyl Fumarate
3. Alks-8700
4. Vumerity
5. Diroximel Fumarete
6. Rdc-5108
7. Biib098
8. Alks8700
9. Alks 8700
10. Diroximel Fumarate [inn]
11. Biib-098
12. K0n0z40j3w
13. Rdc5108
14. 4-o-[2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl] 1-o-methyl (e)-but-2-enedioate
15. (2e)-2-butenedioic Acid 1-[2-(2,5-dioxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl] 4-methyl Ester
16. 2-butenedioic Acid (2e)-, 1-(2-(2,5-dioxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl) 4-methyl Ester
17. Diroximel-fumarate
18. Vumerity (tn)
19. Unii-k0n0z40j3w
20. Diroximel Fumarate [mi]
21. Chembl3989944
22. Diroximel Fumarate (usan/inn)
23. Diroximel Fumarate [usan:inn]
24. Schembl15499960
25. Schembl15511916
26. Gtpl10525
27. Diroximel Fumarate [usan]
28. Diroximel Fumarete(alks-8700)
29. Dtxsid101026181
30. Bcp20867
31. Cnc22214
32. Diroximel Fumarate [who-dd]
33. Ex-a2876
34. Mfcd28502263
35. S6421
36. Zinc215286156
37. Db14783
38. Diroximel Fumarate [orange Book]
39. As-55046
40. Hy-100375
41. Cs-0018703
42. Diroximel Fumarate; Alks8700; Alks 8700
43. D11154
44. W12859
45. 2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)ethylmethylfumarate
46. Q27281786
47. 1-(2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl) 4-methyl But-2-enedioate
48. 2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl Methyl (2e)-but- 2-enedioate
49. 2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl Methyl (2e)-but-2-enedioate
| Molecular Weight | 255.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H13NO6 |
| XLogP3 | -0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 255.07428713 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 255.07428713 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 90 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 384 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Diroximel fumarate is indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults; specifically active secondary progressive disease and clinically isolated syndrome, as well as relapsing-remitting MS.
Vumerity is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (see Section 5. 1 for important information on the populations for which efficacy has been established).
Diroximel fumarate relieves the neurological symptoms of relapsing MS with less gastrointestinal effects than its bioequivalent counterpart, dimethyl fumarate. It is important to note that diroximel fumarate can cause angioedema, anaphylaxis, hepatotoxicity, flushing, lymphopenia, and Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML). Discontinue diroximel fumarate immediately if PML is suspected or if anaphylaxis or angioedema occur. Liver function and total bilirubin should be tested prior to initiating diroximel fumarate and during treatment. A complete blood count (CBC) should be obtained prior to starting diroximel fumarate, after the first 6 months of administration, and at subsequent intervals of 6 to 12 months following this period. Suspend treatment if lymphocyte counts are measured to be less than 0.5 109/L for more than 6 months.
L04AX07
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L04 - Immunosuppressants
L04A - Immunosuppressants
L04AX - Other immunosuppressants
L04AX09 - Diroximel fumarate
Absorption
Diroximel fumarate is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract following administration, like its bioequivalent drug, dimethyl fumarate. The median Tmax of monomethyl fumarate (MMF) after oral administration ranges from 2.5-3 hours with a mean Cmax of 2.11 mg/L. The bioequivalent drug, dimethyl fumarate, administered to healthy volunteers also shows a similar mean Tmax and Cmax. The average steady state concentration of this metabolite is estimated at 8.32 mg.hr/L after it is administered twice a day in patients with MS. The mean AUC0 of the active metabolite is 88mg min L1. Food appears to significantly reduce the Cmax of diroximel fumarate's active metabolite, MMF, when compared to administration in the fasted state.
Route of Elimination
Monomethyl fumarate is eliminated as carbon dioxide through expired breath. Negligible amounts, under 0.3% of the ingested dose, are measured in urine. The inactive metabolite, 2-hydroxyethyl succinimide (HES), representing 58-63% of the ingested dose, is excreted in urine.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution ranges from 72L to 83L. Monomethyl fumarate (MMF), the active metabolite of diroximel fumarate, crosses the blood brain barrier.
Clearance
No clearance information is available on the FDA label for diroximel fumarate, however, clinical study results for its active metabolite, monomethyl fumarate show a mean apparent total clearance from the plasma after oral administration of 1.54 mgL1.
Esterases heavily metabolize diroximel fumarate, as well as its bioequivalent drug, dimethyl fumarate, in the liver. These enzymes are present in high quantities in the gastrointestinal tract, tissues, and blood. Esterase metabolism of this drug produces the active metabolite, mono methyl fumarate (MMF), before it moves to the systemic circulation. In addition, the major inactive metabolite, 2-hydroxyethyl succinimide (HES) is produced along with small amounts of methanol, and another inactive metabolite, RDC-8439. Following esterase metabolism, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA)cycle further metabolizes MMF. The major metabolites of MMF in plasma include fumaric acid, citric acid, and glucose. It is important that methanol is a major metabolite of dimethyl fumarate metabolism, but a minor metabolite of diroximel fumarate metabolism, conferring its lower risk of gastrointestinal effects.
The terminal half-life of monomethyl fumarate (MMF), diroximel fumarate's active metabolite, is estimated to be 1 hour.
Currently, the mechanism of action of this drug in MS is not fully understood. Diroximel fumarate is hypothesized to regulate cell signaling pathways, causing beneficial immune and neuroprotective effects. Monomethyl fumarate (MMF) is the active metabolite of diroximel fumarate, and activates the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) pathway in humans. This pathway occurs as a response to oxidative stress in cells. In addition to the above, MMF is a nicotinic acid receptor agonist in the laboratory setting. The relevance of this finding to the treatment of MS is unknown at this time. The mechanism by which this drug leads to less gastrointestinal effects is purported to be due to its lack of a methanol leaving group in its chemical structure, and substitution with inert 2-hydroxyethyl succinimide.
