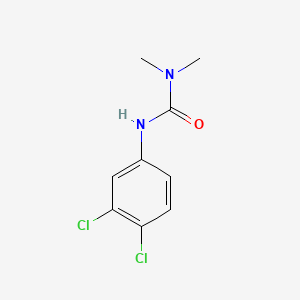

1. 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
2. Dcmu
1. 330-54-1
2. 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
3. Dcmu
4. Duran
5. Dynex
6. Dichlorfenidim
7. Herbatox
8. Vonduron
9. Dailon
10. Karmex
11. Marmer
12. Karmex Dw
13. Di-on
14. Cekiuron
15. Crisuron
16. Lucenit
17. Unidron
18. 1,1-dimethyl-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea
19. Diuron Nortox
20. Karmex D
21. Karmex Diuron Herbicide
22. 1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,3-dimethylurea
23. N'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethylurea
24. Preventol A 6
25. Urox D
26. Diuron 4l
27. Direx 4l
28. Dp Hardener 95
29. Telvar Diuron Weed Killer
30. Urea, N'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-
31. N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-n',n'-dimethylurea
32. Dcmu 99
33. Hw 920
34. Karamex
35. N,n,-dimethyl-n'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea
36. Urea, 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethyl-
37. 3-(3,4-dichlor-phenyl)-1,1-dimethyl-harnstoff
38. 1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,3-dimethyluree
39. Chebi:116509
40. 9i3sds92wy
41. 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethyl-urea
42. 3-(3,4-dicloro-fenyl)-1,1-dimetil-urea
43. 3-(3,4-dichloor-fenyl)-1,1-dimethylureum
44. Dtxsid0020446
45. Nsc-8950
46. Ncgc00094525-01
47. Anduron
48. Ansaron
49. Dirurol
50. Durashield
51. Herburon
52. Seduron
53. Bioron
54. Drexel
55. Farmco Diuron
56. Dsstox_cid_446
57. 3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-1,1-dimethyl-urea
58. Sup'r Flo
59. Dsstox_rid_75595
60. Dsstox_gsid_20446
61. Diuron 900
62. Caswell No. 410
63. Ditox-800
64. Aguron
65. Diater
66. Diuron Solution
67. Dichlorfenidim [russian]
68. Usaf P-7
69. Diuron [ansi:bsi:iso]
70. Usaf Xr-42
71. Cas-330-54-1
72. Diuron [iso]
73. Ccris 1012
74. Hsdb 382
75. Direx 80w
76. Nsc 8950
77. Einecs 206-354-4
78. Af 101
79. Unii-9i3sds92wy
80. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 035505
81. Brn 2215168
82. Xarmex
83. N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethylurea
84. Ai3-61438
85. Karmex Dl
86. 1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,3-dimethyluree [french]
87. 3-(3,4-dichloor-fenyl)-1,1-dimethylureum [dutch]
88. 3-(3,4-dicloro-fenyl)-1,1-dimetil-urea [italian]
89. Karmex 80w
90. Mfcd00018136
91. 3-(3,4-dichlor-phenyl)-1,1-dimethyl-harnstoff [german]
92. Spectrum_001823
93. 1-(3,3-dimethylurea
94. 3-(3,1-dimethylurea
95. Specplus_000424
96. N'-(3,n-dimethylurea
97. N-(3,n'-dimethylurea
98. 1,4-dichlorophenyl)urea
99. 3-(3,1-dimethylureum
100. Diuron [hsdb]
101. N,n-dimethyl-n'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea
102. 3-(3,1-dimetil-urea
103. Spectrum2_001229
104. Spectrum3_000822
105. Spectrum4_000662
106. Spectrum5_001956
107. Diuron [mi]
108. Diuron, >=98%
109. Ec 206-354-4
110. Cambridge Id 5104305
111. Schembl7279
112. 3-(3,1-dimethyl-harnstoff
113. Bspbio_002343
114. Kbiogr_001063
115. Kbioss_002328
116. Spectrum330030
117. Mls002207110
118. Divk1c_006520
119. Spbio_001078
120. Chembl278489
121. Kbio1_001464
122. Kbio2_002325
123. Kbio2_004893
124. Kbio2_007461
125. Kbio3_001843
126. Zinc57287
127. Nsc8950
128. Wln: Gr Bg Dmvn1 & 1
129. Diuron 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
130. Hy-b0860
131. Tox21_111292
132. Tox21_201438
133. Tox21_301016
134. Bdbm50487027
135. Ccg-39151
136. Diuron 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
137. Stk077954
138. Akos001303464
139. Diuron 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
140. Tox21_111292_1
141. Urea,4-dichlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-
142. Urea,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethyl-
143. Ncgc00094525-02
144. Ncgc00094525-03
145. Ncgc00094525-04
146. Ncgc00094525-05
147. Ncgc00094525-06
148. Ncgc00094525-07
149. Ncgc00094525-08
150. Ncgc00094525-09
151. Ncgc00254918-01
152. Ncgc00258989-01
153. As-15493
154. Smr000777941
155. Diuron, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
156. 3-(3,4-dichlorophenol)-1,1-dimethylurea
157. Db-048327
158. Cs-0012874
159. D1328
160. Ft-0603378
161. Ft-0667750
162. N,n-dimethyl-n'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-urea
163. N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-n',n'-dimethyl Urea
164. C18428
165. A821585
166. Q425389
167. Sr-01000195223
168. Diuron, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
169. J-018992
170. Sr-01000195223-1
171. Brd-k75330923-001-02-6
172. Diuron Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Acetonitrile, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
173. W9m
| Molecular Weight | 233.09 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H10Cl2N2O |
| XLogP3 | 2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 232.0170183 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 232.0170183 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 32.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 211 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Herbicides
Pesticides used to destroy unwanted vegetation, especially various types of weeds, grasses (POACEAE), and woody plants. Some plants develop HERBICIDE RESISTANCE. (See all compounds classified as Herbicides.)
Diuron is readily absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract in rats and dogs. Tissue level of diuron were positively correlated with dosage. No apparent storage of diuron in tissues was noted ... Diuron is also partially excreted unchanged in feces and urine.
Krieger, R. (ed.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2, 2nd ed. 2001. Academic Press, San Diego, California., p. 1522
Root uptake of (14)C-Diuron from solution was studied. ... small amount of the monomethyl and demethylated derivatives were found in nutrient solution from ... soybeans, ... oat, and corn tops.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides. U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife, Publication 127. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1969., p. 338
Diuron is most readily absorbed through the root system; less so through foliage & stems. Translocation is primarily upward in xylem.
Weed Science Society of America. Herbicide Handbook. 5th ed. Champaign, Illinois: Weed Science Society of America, 1983., p. 205
Diuron was fed to five dairy cows at 0-550 ppm concentration levels. About 50% of the diuron was detected in the urine, 10% in the feces and 5% in the blood. Milk samples did not contain diuron. A positive correlation was noted between the concn of diuron products in urine and blood and a negative correlation between urine and feces. It is suggested that the remaining diuron is absorbed in the body or degraded into undetectable metabolites.
PMID:535556 Kalra SK, Chahal KS; Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 3 (4): 362-8 (1979)
Diuron is carcinogenic to the rat urinary bladder at high dietary levels. The proposed mode of action (MOA) for diuron is urothelial cytotoxicity and necrosis followed by regenerative urothelial hyperplasia. Diuron-induced urothelial cytotoxicity is not due to urinary solids. Diuron is extensively metabolized, and in rats, N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea (DCPU) and 4,5-dichloro-2-hydroxyphenyl urea (2-OH-DCPU) were the predominant urinary metabolites; lesser metabolites included N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-methylurea (DCPMU) and trace levels of 3,4-dichloroaniline (DCA). In humans, DCPMU and DCPU have been found in the urine after a case of product abuse. To aid in elucidating the MOA of diuronand to evaluate the metabolites that are responsible for the diuron toxicity in the bladder epithelium, we investigated the urinary concentrations of metabolites in male Wistar rats treated with 2500 ppm of diuron, the urothelial cytotoxicity in vitro of the metabolites and their gene expression profiles. DCPU was found in rat urine at concentrations substantially greater than the in vitro IC50 and induced more gene expression alterations than the other metabolites tested. 2-OH-DCPU was present in urine at a concentration approximately half of the in vitro IC50, whereas DCPMU and DCA were present in urine at concentrations well below the IC50. For the diuron-induced MOA for the rat bladder, we suggest that DCPU is the primary metabolite responsible for the urothelial cytotoxicity with some contribution also by 2-OH-DCPU. This study supports a MOA for diuron-induced bladder effects in rats consisting of metabolism to DCPU (and 2-OH-DCPU to a lesser extent), concentration and excretion in urine, urothelial cytotoxicity, and regenerative proliferation.
PMID:24172598 Da Rocha MS et al; Toxicology 314 (2-3): 238-46 (2013)
This study was designed to investigate diuron biotransformation and disposition ... . The only metabolic pathway detected by liquid chromatography/mass spectometry in human liver homogenates and seven types of mammalian liver microsomes including human was demethylation at the terminal nitrogen atom. No other phase I or phase II metabolites were observed. The rank order of N-demethyldiuron formation in liver microsomes based on intrinsic clearance (V(max)/K(m)) was dog > monkey > rabbit > mouse > human > minipig > rat. All tested recombinant human cytochrome P450s (P450s) catalyzed diuron N-demethylation and the highest activities were possessed by CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6. Relative contributions of human CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4 to hepatic diuron N-demethylation, based on average abundances of P450 enzymes in human liver microsomes, were approximately 60, 14, and 13%, respectively. Diuron inhibited relatively potently only CYP1A1/2 (IC(50) 4 uM)...
PMID:17576805 Abass K et al; Drug Metab Dispos 35 (9): 1634-41 (2007)
3,4-dichloroaniline (3,4-DCA) is a metabolite of diuron as well as two other pesticides, linuron and propanil. However, EPA's Metabolism Assessment Review Committee (MARC) concluded that residues of 3,4-DCA should not be aggregated for the diuron, linuron, and propanil risk assessments because 3,4-DCA is significant residue of concern for propanil, but is not a residue of concern per se for diuron or linuron. Although the analytical method for quantifying residues of concern from diuron converts all residues to 3,4-DCA as a convenience, 3,4-DCA was not a significant residue in any metabolism or hydrolysis study.
USEPA/Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document for Diuron p.15 List A Case 0046 (September 2003). Available from, as of July 11, 2018: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
... In ... a woman poisoned with Diuron, 1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,3-dimethylurea, plus 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, 1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-methylurea, and 1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea were isolated from urine. The urine probably contained small amt of 3,4-dichloroaniline, but no unchanged herbicide.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 312
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for Diuron (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Diuron has known human metabolites that include N-demethyldiuron.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
/Chlorophyll/ fluorescence measurements indicated significant electron transport inhibition in /intact soybean/ leaves 1 hr after treatment with 40 mM solutions of ... diuron.
Richard EP Jr et al; Weed Sci 31 (3): 361-7 (1983)
The potent inhibitory effect of substituted ureas on the photosynthetic mechanism of ... plants ... /is exerted through inhibition of/ Hill reaction, ie, evolution of oxygen in presence of living chloroplasts & suitable hydrogen acceptor. /Substituted ureas/
Kearney, P.C., and D. D. Kaufman (eds.) Herbicides: Chemistry, Degredation and Mode of Action. Volumes 1 and 2. 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1975., p. 262