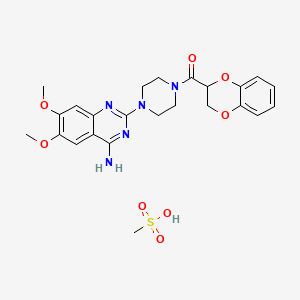

1. 1 (4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-((2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl)piperazine
2. Alfamedin
3. Apo Doxazosin
4. Apo-doxazosin
5. Cardular
6. Cardura
7. Carduran
8. Carduran Neo
9. Ct, Doxazosin Von
10. Diblocin
11. Doxa Puren
12. Doxa-puren
13. Doxacor
14. Doxagamma
15. Doxamax
16. Doxatensa
17. Doxauro
18. Doxazomerck
19. Doxazosin
20. Doxazosin Al
21. Doxazosin Apogepha
22. Doxazosin Azu
23. Doxazosin Beta
24. Doxazosin Findusfit
25. Doxazosin Heumann
26. Doxazosin Klast
27. Doxazosin Monohydrochloride
28. Doxazosin Ratiopharm
29. Doxazosin Stada
30. Doxazosin Von Ct
31. Doxazosin Wolff
32. Doxazosin-ratiopharm
33. Doxazosin-wolff
34. Doxazosina Alter
35. Doxazosina Cinfa
36. Doxazosina Combino Pharm
37. Doxazosina Geminis
38. Doxazosina Normon
39. Doxazosina Pharmagenus
40. Doxazosina Ratiopharm
41. Doxazosina Ur
42. Gen Doxazosin
43. Gen-doxazosin
44. Jutalar
45. Mesylate, Doxazosin
46. Monohydrochloride, Doxazosin
47. Mtw Doxazosin
48. Mtw-doxazosin
49. Neo, Carduran
50. Novo Doxazosin
51. Novo-doxazosin
52. Progandol Neo
53. Ratio Doxazosin
54. Ratio-doxazosin
55. Ratiopharm, Doxazosina
56. Uk 33274
57. Uk-33274
58. Uk33274
59. Uriduct
60. Von Ct, Doxazosin
61. Zoxan
1. 77883-43-3
2. Cardura
3. Carduran
4. Alfadil
5. Cardular
6. Cardura Xl
7. Doxazosin Mesilate
8. Cardenalin
9. Dedralen
10. Progandol
11. Tensiobas
12. Doxazosin (mesylate)
13. Uk 33274 Mesylate
14. Doxazosin (as Mesilate)
15. Doxazosin Methanesulfonate
16. (4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)methanone Methanesulfonate
17. Nsc-759284
18. 86p6pqk0mu
19. Mls000028455
20. Doxazomerck
21. Diblocin
22. Uk-33,274-27
23. Doxazosin Azu
24. Prostadilat
25. Cardoral
26. Cardoxan
27. Doksura
28. Doxaben
29. Doxolbran
30. Kaltensif
31. Normathen
32. Smr000058441
33. Supressin
34. Tonocardin
35. Benur
36. Cardular Uro
37. Diblocin Uro
38. Cardular Pp
39. Diblocin Pp
40. Uk-33274-27
41. Dsstox_cid_25598
42. Dsstox_rid_80991
43. Dsstox_gsid_45598
44. Piperazine, 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-((2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl)-, Monomethanesulfonate
45. Uk 33274
46. Doxazocine
47. Duracin
48. Dosin
49. 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazine Monomethanesulfonate
50. Carduran Neo
51. Chebi:4709
52. Doxazosin Mesylate [usan]
53. [4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-3-yl)methanone;methanesulfonic Acid
54. 2-{4-[(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl]piperazin-1-yl}-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine; Methanesulfonic Acid
55. Hsdb 7082
56. Sr-01000003045
57. Unii-86p6pqk0mu
58. Doxazosin Mesylate [usan:usp]
59. Uk 33,274-27
60. Ncgc00017136-01
61. Cardura (tn)
62. Cas-77883-43-3
63. Mfcd00216023
64. Prestwick_1026
65. Doxazosin Mesylate Salt
66. Doxazosin Mesylate,(s)
67. Opera_id_1881
68. Doxazosin Mesylate (usp)
69. Doxazosin Mesilate (jp17)
70. Schembl42621
71. 2-[4-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine; Methanesulfonic Acid
72. Mls000120399
73. Mls001148153
74. Mls002222292
75. Mls006011977
76. Chembl1200561
77. Doxazosin Mesilate [jan]
78. Dtxsid5045598
79. Hy-b0098a
80. Doxazosin Mesylate [hsdb]
81. Doxazosin Mesylate [vandf]
82. Hms1570l17
83. Hms2093j14
84. Hms2097l17
85. Hms2230l18
86. Hms3261o10
87. Hms3372c03
88. Hms3654j15
89. Hms3714l17
90. Hms3884o09
91. Pharmakon1600-01505976
92. Doxazosin Mesilate [mart.]
93. Bcp12163
94. Doxazosin Mesilate [who-dd]
95. Doxazosin Mesylate [usp-rs]
96. Tox21_110796
97. Tox21_500474
98. Nsc759284
99. S1324
100. Akos015895371
101. Piperazin-1-yl)(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b]
102. Tox21_110796_1
103. Ac-6848
104. Ccg-213583
105. Cs-1830
106. Ks-1052
107. Lp00474
108. Nsc 759284
109. Doxazosin Mesylate [orange Book]
110. Doxazosin Mesilate [ep Monograph]
111. Doxazosin Mesylate [usp Impurity]
112. Ncgc00016146-02
113. Ncgc00018158-09
114. Ncgc00093884-01
115. Ncgc00261159-01
116. 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-[4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-yl)carpiperazin-1-yl)]-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline Mesylate
117. 2-[4-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxine-2-carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine; Methanesulfonic Acid
118. Bd164387
119. Doxazosin Mesylate [usp Monograph]
120. [1,4]dioxin-2-yl)methanone Methanesulfonate
121. D4126
122. Doxazosin Mesylate, >=97% (hplc), Powder
123. Eu-0100474
124. Ft-0625592
125. Sw197099-3
126. En300-53021
127. 91d858
128. C76492
129. D 9815
130. D00608
131. A839262
132. Sr-01000003045-2
133. Sr-01000003045-4
134. Sr-01000003045-8
135. Q27106443
136. Z1259084903
137. Doxazosin Mesilate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
138. Doxazosin Mesylate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
139. (4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)methanonemethanesulfonate
140. 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazine Methanesulphonate
141. 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-[(1,4-benzodioxan-2-yl)carbonyl]piperazine Methanesulfonate
142. 2,3,4a,8a-tetrahydro-1,4-benzodioxin-3-yl-[4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-quinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]methanone; Methanesulfonate;doxazosin Mesylate
143. 4-amino-2-[4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline Methanesulfonate
144. Methanone, (4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl)(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)-, Methanesulfonate (1:1)
145. Piperazine, 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-((2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl)-, Monomethanesulphonate
| Molecular Weight | 547.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H29N5O8S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 547.17368407 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 547.17368407 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 175 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 770 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cardura |
| Drug Label | CARDURA (doxazosin mesylate) is a quinazoline compound that is a selective inhibitor of the alpha1 subtype of alpha-adrenergic receptors. The chemical name of doxazosin mesylate is 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcar... |
| Active Ingredient | Doxazosin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 2mg base; eq 1mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cardura xl |
| Drug Label | CARDURA XL contains doxazosin mesylate which is a quinazoline compound with the chemical name 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl) piperazine methanesulfonate. The empirical formula for doxazosin mesylate is C23H2... |
| Active Ingredient | Doxazosin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Doxazosin mesylate |
| PubMed Health | Doxazosin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive, Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Agent, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Doxazosin mesylate is a quinazoline compound that is a selective inhibitor of the alpha1 subtype of alpha adrenergic receptors. The chemical name of doxazosin mesylate is 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl) piper... |
| Active Ingredient | Doxazosin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 2mg base; eq 1mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva; Apotex; Accord Hlthcare; Pliva; Mylan; Dava Pharms |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cardura |
| Drug Label | CARDURA (doxazosin mesylate) is a quinazoline compound that is a selective inhibitor of the alpha1 subtype of alpha-adrenergic receptors. The chemical name of doxazosin mesylate is 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcar... |
| Active Ingredient | Doxazosin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 2mg base; eq 1mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cardura xl |
| Drug Label | CARDURA XL contains doxazosin mesylate which is a quinazoline compound with the chemical name 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl) piperazine methanesulfonate. The empirical formula for doxazosin mesylate is C23H2... |
| Active Ingredient | Doxazosin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Doxazosin mesylate |
| PubMed Health | Doxazosin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive, Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Agent, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Doxazosin mesylate is a quinazoline compound that is a selective inhibitor of the alpha1 subtype of alpha adrenergic receptors. The chemical name of doxazosin mesylate is 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl) piper... |
| Active Ingredient | Doxazosin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 2mg base; eq 1mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva; Apotex; Accord Hlthcare; Pliva; Mylan; Dava Pharms |
Doxazosin is indicated for the treatment of both the urinary outflow obstruction and the obstructive and irritative symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Obstructive symptoms are hesitation, intermittency, dribbling, weak urinary stream, and incomplete emptying of the bladder; while irritative symptoms include nocturia, daytime frequency, urgency, and burning. Doxaxosin may be used in nomotensive or hypertensive patients. In normotensive patients with BPH, doxazosin does not appear to significantly lower blood pressure. In hypertensive patients with BPH, both conditions are effectively treated with doxazosin. The long term effects of doxazosin on the incidence of acute urinary obstruction or other complications of BPH or on the need for surgery have not yet been determined. /Included in US product labeling/ /Salt not specified/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1278
Doxazosin is indicated in the treatment of hypertension. /Included in US product labeling/ /Salt not specified/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1278
Antihypertensive; in treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy. /Salt not specified/
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 604
Evaluation of atherosclerosis is important in the treatment of hypertension. To evaluate the preventive effects of a small amount of alpha-blockade, arterial and endothelial dysfunction were measured by noninvasive tests, i.e., pulse wave velocity, acceleration plethysmography and strain-gauge plethysmography, in patients with essential hypertension. Fifteen patients (65+/-3 years old) with essential hypertension (WHO stage I or II) were analyzed in this study. We performed noninvasive evaluations to measure aortic stiffness and endothelial dysfunction, in addition to measuring blood pressure, cholesterol profile, and levels of cells adhesion molecules and nitric oxide before and 6 and 12 months after the start of doxazosin treatment (1.0 mg/day). Blood pressure and heart rate did not significantly change during treatment. The pulse wave velocity index was significantly reduced both at 6 (7.72+/-0.23 m/s; p<0.05) and 12 (7.34+/-0.26 m/s; p<0.05) months after the start of treatment compared to the pretreatment level that at baseline. There was also a significant improvement in b/a after 12 months (-0.46+/-0.04; p<0.05) and in d/a after 6 months (-0.38+/-0.03; p<0.05) and 12 months (-0.39+/-0.03; p=0.05) compared to the pretreatment values. Moreover, reactive hyperemia evaluated by strain-gauge plethysmography after 6 months (1.34+/-0.11; p<0.05) and 12 months (1.49+/-0.16; p<0.05) was significantly improved compared to that before treatment, and NOx was significantly increased after 12 months (89.7+/-15.7 micromol/l; p<0.005). These data suggest that a low dose of doxazosin may play an important role in improving arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction without changing cardiac hemodynamics. /Salt not specified/
Komai N et al; Hypertens Res 25(1) : p.5-10 (2002)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DOXAZOSIN MESYLATE (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Adverse effects occurring most frequently during doxazosin mesylate therapy for hypertension include dizziness, headache, drowsiness, lack of energy (eg, lethargy, fatigue), nausea, edema, and rhinitis. In patients receiving the drug for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), the most frequent adverse effects are dizziness, headache, fatigue, edema, dyspnea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. The frequency of adverse effects in controlled clinical trails generally has been lower in patients receiving doxazosin for BPH than in those receiving the drug for hypertension; however, dosages employed for this condition also generally have been lower than those for hypertension. /Salt not specified/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1819
While adverse effects occur frequently in patients receiving the drug, most are mild to moderate in severity, and discontinuance of doxazosin secondary to adverse effects was required in only 7% of patients with hypertension during clinical trials. The principal reasons for discontinuance in patients with hypertension were postural effects in 2% of patients and edema, malaise/fatigue, and heart rate disturbance each in about 0.7% of patients. In controlled clinical trials in patients with hypertension, only dizziness (including postural effects), weight gain, somnolence, and malaise/fatigue occurred at rates significantly greater than those for placebo; postural effects and edema appeared to be dose related. Only dizziness, fatigue, hypotension, edema, and dyspnea occurred significantly more frequently with the drug than placebo in controlled clinical trials for BPH; dizziness and dyspnea appeared to be dose-related. /Salt not specified/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1819
Besides dizziness ..., headache is the most common adverse nervous system effect associated with doxazosin therapy, occurring in about 14 or 10% of patients receiving the drug for hypertension or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), respectively. Somnolence occurs in 5 or 3% of such patients, respectively, and pain in 2% of patients. Nervousness occurs in about 2% of patients receiving doxazosin for hypertension, and insomnia and anxiety occur in 1.2 and 1.1%, respectively, of those receiving the drug for BPH; insomnia occurs in 1% of hypertensive patients. Adverse nervous system effects occurring in 0.5-1% of patients include paresthesia, kinetic disorders, ataxia, hypertonia, hypoesthesia, agitation, depression, and decreased libido. Paresis, tremor, twitching, confusion, migraine, paroniria, amnesia, emotional lability, impaired concentration, abnormal thinking, and depresonalization have been reported in less than 0.5% of patients, but a causal relationship to the drug has not been established. /Salt not specified/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1819
Nausea, diarrhea, and dry mouth are the most common adverse GI effects of doxazosin in hypertensive patients, occurring in 3, 2, and 2% of such patients, respectively, and abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia, nausea, and dry mouth are the most common in those with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), occurring in 2.4, 2.3, 1.7, 1.5, and 1.4% of such patients, respectively; dyspepsia occurs in 1% of hypertensive patients. Constipation and flatulence occur in 1% of patients receiving the drug for hypertension. Increased appetite, anorexia, fecal incontinence, and gastroenteritis have been reported in less than 0.5% of hypertensive patients but not directly attributed to the drug. Vomiting has been reported during postmarketing experience with doxazosin. /Salt not specified/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1820
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DOXAZOSIN MESYLATE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Adrenergic alpha-1 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to and block the activation of ADRENERGIC ALPHA-1 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-1 Receptor Antagonists.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Most doxazosin metabolites are eliminated in the feces. /Salt not specified/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 246
Well absorbed from gastrointestinal tract; bioavailability is about 65%. /Salt not specified/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1278
Elimination: Fecal: Unchanged drug, about 5%; metabolites, 63 to 65%. Renal: 9%. /Salt not specified/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1278
Metabolized extensively in the liver. Although several active and inactive metabolites have been identified (2-piperazinyl, 6' and 7'-hydroxy,6' and 7'-O-desmethyl, and 2-amino), there is no evidence that they are present in substantial amounts. /Salt not specified/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1278
The half-life of doxazosin is approximately 20 hours ... /Salt not specified/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 246
Elimination /half life/: 19 to 22 hours; does not appear to be significantly influenced by age or mild to moderate renal impairment. /Salt not specified/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1278
Selective alpha1-adrenergic blocker related to prazosin, q.v. /Salt not specified/
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 604
Blocks postsynaptic alpha 1 receptors and cause vasodilation /Salt not specified/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 552
Hypertension: Blockade of alpha1-adrenergic receptors by doxazosin results in peripheral vasodilation, which produces a fall in blood pressure because of decreased peripheral vascular resistance. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: Relaxation of smooth muscle in the bladder neck, prostate, and prostate capsule produced by alpha1-adrenergic blockade results in a reduction in urethral resistance and pressure, bladder outlet resistance, and urinary symptoms. /Salt not specified/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1278
Previous studies have demonstrated that the alpha(1)-adrenergic receptor antagonist doxazosin (Dox) inhibits multiple mitogenic signaling pathways in human vascular smooth muscle cells. This broad antiproliferative activity of Dox occurs through a novel mechanism unrelated to its blocking the alpha(1)-adrenergic receptor. Flow cytometry demonstrated that Dox prevents mitogen-induced G(1)-->S progression of human coronary artery smooth muscle cells (CASMCs) in a dose-dependent manner, with a maximal reduction of S-phase transition by 88+/-10.5% in 20 ng/mL platelet-derived growth factor and 1 micromol/L insulin (P+I)-stimulated cells (P<0.01 for 10 micromol/L Dox versus P+I alone) and 52+/-18.7% for 10% FBS-induced mitogenesis (P<0.05 for 10 micromol/L Dox versus 10% FBS alone). Inhibition of G(1) exit by Dox was accompanied by a significant blockade of retinoblastoma protein (Rb) phospstimulated quiescent CASMCs to progress through G(1) and enter the S phase. E2F-mediated G(1) exit was not affected by Dox, suggesting that it targets events upstream from Rb hyperphosphorylation. Downregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory protein p27 is important for maximal activation of G(1) cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase holoenzymes to overcome the cell cycle inhibitory activity of Rb. In Western blot analysis, p27 levels decreased after mitogenic stimulation (after P+I, 43+/-1.8% of quiescent cells [P<0.01 versus quiescent cells]; after 10% FBS, 55+/-7.7% of quiescent cells [P<0. 05 versus quiescent cells]), whereas the addition of Dox (10 micromol/L) markedly attenuated its downregulation (after P+I, 90+/-8.3% of quiescent cells [P<0.05 versus P+I alone]; after 10% FBS, 78+/-8.3% of quiescent cells [P<0.05 versus 10% FBS alone]). Furthermore, Dox inhibited cyclin A expression, an E2F regulated gene that is essential for cell cycle progression into the S phase. The present study demonstrates that Dox inhibits CASMC proliferation by blocking cell cycle progression from the G(0)/G(1) phase to the S phase. This G(1)-->S blockade likely results from an inhibition of mitogen-induced Rb hyperphosphorylation through prevention of p27 downregulation. /Salt not specified/
Kintscher U et al; Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(5): p.1216-1224 (2002)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for DOXAZOSIN MESYLATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.