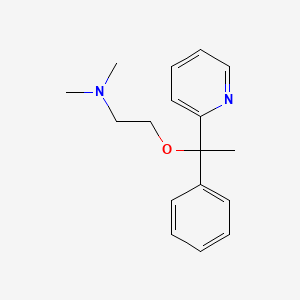

1. 469-21-6
2. Dossilamina
3. Doxylaminum
4. Doxilminio
5. (+/-)-doxylamine
6. 2-dimethylaminoethoxyphenylmethyl-2-picoline
7. N,n-dimethyl-2-(1-phenyl-1-pyridin-2-ylethoxy)ethanamine
8. N,n-dimethyl-2-(1-phenyl-1-(2-pyridinyl)ethoxy)ethanamine
9. Nci C60684
10. Doxylamine (inn)
11. Phenyl-2-pyridylmethyl-beta-n,n-dimethylaminoethyl Ether
12. 2-(alpha-(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)-alpha-methylbenzyl)pyridine
13. Ethanamine, N,n-dimethyl-2-(1-phenyl-1-(2-pyridinyl)ethoxy)-
14. Ethanamine, N,n-dimethyl-2-[1-phenyl-1-(2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]-
15. 95qb77jkpl
16. Chebi:51380
17. Dossilamina [dcit]
18. Alsadorm
19. Mereprine
20. Doxylaminum [inn-latin]
21. Doxilminio [inn-spanish]
22. Decapryn (tn)
23. Doxylamine [inn]
24. Doxylamine [inn:ban]
25. Doxilamina
26. Dimethyl({2-[1-phenyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]ethyl})amine
27. N,n-dimethyl-2-[1-phenyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]ethanamine
28. N,n-dimethyl-2-(1-phenyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethoxy)ethan-1-amine
29. Pyridine, 2-[.alpha.-[2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy]-.alpha.-methylbenzyl]-
30. Hsdb 5184
31. Einecs 207-414-2
32. Unii-95qb77jkpl
33. Brn 0230379
34. N,n-dimethyl-2-(1-phenyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethoxy)ethanamine
35. R-doxylamine
36. Pyridine, 2-(.alpha.-(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)-.alpha.-methylbenzyl)-
37. Spectrum_001014
38. Doxylamine [mi]
39. Prestwick0_000027
40. Prestwick1_000027
41. Prestwick2_000027
42. Prestwick3_000027
43. Pyridine, 2-(alpha-(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)-alpha-methylbenzyl)-
44. Spectrum2_000115
45. Spectrum3_000409
46. Spectrum4_000528
47. Spectrum5_000949
48. Doxylamine [hsdb]
49. Doxylamine [vandf]
50. Ec 207-414-2
51. Schembl4709
52. Chembl1004
53. Doxylamine [who-dd]
54. Lopac0_000348
55. Bspbio_000093
56. Bspbio_001938
57. Kbiogr_001135
58. Kbioss_001494
59. 5-21-03-00508 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
60. Divk1c_000841
61. Spbio_000130
62. Spbio_002014
63. Bpbio1_000103
64. Gtpl7171
65. Dtxsid1022970
66. Kbio1_000841
67. Kbio2_001494
68. Kbio2_004062
69. Kbio2_006630
70. Kbio3_001158
71. Ninds_000841
72. Hms3604l05
73. Bcp09058
74. N,n-dimethyl-2-[(1-phenyl-1-pyridin-2-ylethyl)oxy]ethanamine
75. Stl018676
76. Akos005657227
77. Ccg-204443
78. Db00366
79. Sdccgsbi-0050336.p005
80. Idi1_000841
81. Ncgc00021147-02
82. Ncgc00021147-03
83. Ncgc00021147-04
84. Ncgc00021147-05
85. Ncgc00021147-06
86. Ncgc00021147-08
87. Ncgc00021147-09
88. Ncgc00021147-13
89. Ncgc00021147-21
90. Ncgc00089789-02
91. Ncgc00089789-04
92. Ncgc00089789-05
93. Ac-15949
94. Sbi-0050336.p004
95. Db-051407
96. Ab00053466
97. Ft-0603401
98. D07878
99. Ab00053466-18
100. Ab00053466_19
101. Ab00053466_20
102. .alpha.-dimethylaminoethoxyphenylmethyl-2-picoline
103. 469d216
104. L001076
105. Q423390
106. Brd-a44008656-036-05-0
107. Brd-a44008656-036-15-9
108. Phenyl-2-pyridylmethyl-.beta.-n,n-dimethylaminoethyl Ether
109. N,n-dimethyl-2-[1-phenyl-1-(2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]ethanamine #
110. 2-(.alpha.-(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)-.alpha.-methylbenzyl)pyridine
111. 2-(.alpha.(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)-.alpha.-methylbenzyl)pyridine
| Molecular Weight | 270.37 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H22N2O |
| XLogP3 | 2.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 270.173213330 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 270.173213330 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 25.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 276 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Allergic Agents; Antiemetics; Antitussive Agents; Histamine H1 Antagonists; Sedatives, Nonbarbiturate
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
ANTIHISTAMINIC AGENT PROBABLY EFFECTIVE FOR SYMPTOMATIC TREATMENT OF... ALLERGIC RHINITIS, VASOMOTOR RHINITIS, ALLERGIC CONJUNCTIVITIS DUE TO INHALANT ALLERGENS & FOODS, MILD, UNCOMPLICATED ALLERGIC SKIN MANIFESTATIONS OF URTICARIA & ANGIOEDEMA, AMELIORATION & PREVENTION OF...REACTIONS TO BLOOD OR PLASMA... /SUCCINATE/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1061
VET USE: AS ARE OTHER ANTIHISTAMINES IN STOMATITIS, LAMINITIS, URTICARIA, RESPIRATORY DISORDERS, BLOAT, & INDIGESTION IN CATTLE; IN URTICARIA & LAMINITIS IN HORSES; IN DERMATITIS, URTICARIA, MOTION SICKNESS, & IN PREVENTION OF DEPIGMENTATION IN BLUE NOSED DOGS. /SUCCINATE/
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 190
Antihistamines are indicated in the prophylactic and symptomatic treatment of perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis, vasomotor rhinitis, and allergic conjunctivitis due to inhalant allergens and foods. /Antihistamines; Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 324
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DOXYLAMINE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
PERSONS TAKING ANTIHISTAMINES SHOULD BE ALERTED TO THEIR SEDATIVE EFFECTS & SHOULD BE CAUTIONED NOT TO DRIVE AUTOMOBILE, FLY AIRPLANE, OR OPERATE HAZARDOUS MACHINERY... /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1057
VET: USE OF ANTIHISTAMINES IN STOMATITIS, GANGRENOUS MASTITIS, METRITIS, & TOXIC ENGORGEMENTS HAVE BEEN QUESTIONED. /SUCCINATE/
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 190
Like other antihistamines, doxylamine should not be used in premature or full-term neonates. Safety and efficacy of doxylamine as a nighttime sleep aid in children younger than 12 years of age have not been established. In addition, children may be more prone than adults to paradoxically experience CNS stimulation rather than sedation when antihistamines are used as nighttime sleep aids. Because doxylamine may cause marked drowsiness that may be potentiated by other CNS depressants (e.g., sedatives, tranquilizers), the antihistamine should be used in children receiving one of these drugs only under the direction of a physician. As an antihistamine, doxylamine should be used in children 2 to younger than 6 years of age only under the direction of a physician; use of the drug in children younger than 2 years of age is not recommended.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 23
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions to antihistamines in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or doxylamine, taking into account the importance of the drug to the woman.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 23
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DOXYLAMINE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
4. 4= VERY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 50-500 MG/KG, BETWEEN 1 TEASPOON & 1 OZ FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /SUCCINATE/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-232
Used alone as a short-term sleep aid, in combination with other drugs as a night-time cold and allergy relief drug. Also used in combination with Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) to prevent morning sickness in pregnant women.
Doxylamine is an antihistamine commonly used as a sleep aid. This drug is also used to relieve symptoms of hay fever (allergic rhinitis), hives (rash or itching), and other allergic reactions. Doxylamine is a member of the ethanolamine class of antihistamines and has anti-allergy power far superior to virtually every other antihistamine on the market, with the exception of diphenhydramine (Benadryl). It is also the most powerful over-the-counter sedative available in the United States, and more sedating than many prescription hypnotics. In a study, it was found to be superior to even the barbiturate, phenobarbital for use as a sedative. Doxylamine is also a potent anticholinergic.
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
Antiemetics
Drugs used to prevent NAUSEA or VOMITING. (See all compounds classified as Antiemetics.)
R - Respiratory system
R06 - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06A - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06AA - Aminoalkyl ethers
R06AA09 - Doxylamine
Absorption
Readily absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract.
H1 antagonists are eliminated more rapidly by children than by adults and more slowly in those with severe liver disease. /H1 Receptor Antagonists/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 590
The H1 antagonists are well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Following oral administration, peak plasma concentrations are achieved in 2 to 3 hours ... . /H1 Receptor Antagonists/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 588
Elimination and metabolic profiles of the glucuronide products of doxylamine and its N-demethylated metabolites were determined after the oral admin of (14)C-doxylamine succinate (13.3 and 133 mg/kg doses) to male and female Fischer 344 rats. The cumulative urinary and fecal eliminations of these conjugated doxylamine metaboites at the 13.3 mg/kg dose were 44.4 + or - 4.2% and 47.3 + or - 8.1% of the total recoverd dose for male and female rats, respectively. The cumulative urinary and fecal eliminations of conjugated doxylamine metabolites at the 133 mg/kg dose were 55.2 + or - 2.6% and 47.9 + or - 2.5% of the total recovered dose for male and female rats, respectively. The conjugated doxylamine metabolites that were isolated, quantitiated, and identified are doxylamine O-glucuronide, N-desmethyl-doxylamine O-glucuronide, and N,N-didesmethyldoxylamine O-glucuronide.
PMID:1975634 Holder CL et al; J Anal Toxicol 14 (4): 247-51 (1990)
The elimination of doxylamine and metabolites was determined after iv admin of (14)C-doxylamine succinate at 0.7 and 13.3 mg/kg to the adult female rhesus monkey. Although the total recovery of radioactivity was the same for the low- and high-dose studies (90.2%), the rate of plasma elimination of doxylamine and its demethylated metabolite (desmethyldoxylamine) was slower for the high dose group. The 24 hr urinary excretion of doxylamine metabolites, desmethyl- and didesmethyldoxylamine, was significantly incr and the polar doxylamine metabolites were significantly decr as the iv doxylamine succinate dose was incr. The plasma elimination of GC-detected doxylamine was determined after po admin of Bendectin (doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride) /also contains dicyclomine hydrochloride/ at 7, 13.3, and 27 mg/kg to adult female rhesus monkeys. As the dose incr, the clearance of doxylamine decr. A statistically evaluated fit of the po data to a single-compartment, parallel first-order elimination model and a single-compartment, parallel first- and second-order (Michaelis-Menten) elimination model indicated that the more complex model containing the second-order process was most consistent with the observed elimination data. /Doxylamine succinate/
PMID:2520522 Slikker W Jr et al; Reprod Toxicol 3 (3): 187-96 (1989)
Hepatic.
The conjugated doxylamine metabolites that were isolated, quantitiated, and identified are doxylamine O-glucuronide, N-desmethyl-doxylamine O-glucuronide, and N,N-didesmethyldoxylamine O-glucuronide.
PMID:1975634 Holder CL et al; J Anal Toxicol 14 (4): 247-51 (1990)
Analysis of doxylamine N-oxide and pyrilamine N-oxide as synthetic standards and biologically derived metabolites by thermospray mass spectrometry (TSP/MS) provided (M + H) + ions for each metabolite. ... In addition, TSP/MS and TSP/MS/MS analysis of ring-hydroxylated N-desmethyldoxylamine ... is also reported.
PMID:3382805 Korfmacher WA et al; Biomed Environ Mass Spectrom 15 (9): 501-8 (1988)
10 hours
The drug has an elimination half-life of about 10 hours in healthy adults.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 22
Like other antihistamines, doxylamine acts by competitively inhibiting histamine at H1 receptors. It also has substantial sedative and anticholinergic effects.