

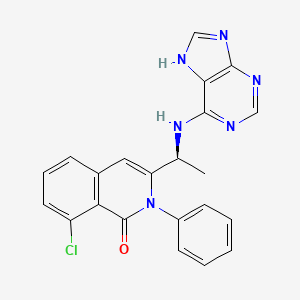

1. 8-chloro-2-phenyl-3-((1s)-1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl)-1(2h)-isoquinolinone
2. Copiktra
3. Ipi-145
1. 1201438-56-3
2. Ipi-145
3. Ink-1197
4. (s)-3-(1-((9h-purin-6-yl)amino)ethyl)-8-chloro-2-phenylisoquinolin-1(2h)-one
5. Ipi 145
6. Unii-610v23s0ji
7. Ipi145
8. (s)-3-(1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl)-8-chloro-2-phenylisoquinolin-1(2h)-one
9. Ink-1147
10. Ipi-145 (ink1197)
11. 610v23s0ji
12. 8-chloro-2-phenyl-3-[(1s)-1-(7h-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl]isoquinolin-1-one
13. Duvelisib (ipi-145, Ink1197)
14. Duvelisib Hydrate
15. Copiktra (tn)
16. 1(2h)-isoquinolinone, 8-chloro-2-phenyl-3-((1s)-1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl)-
17. Duvelisib [usan]
18. Duvelisib [usan:inn]
19. 1(2h)-isoquinolinone, 8-chloro-2-phenyl-3-[(1s)-1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl]-
20. Ink1197
21. Duvelisib [inn]
22. Duvelisib [mi]
23. Duvelisib (usan/inn)
24. Duvelisib (ipi-145)
25. Duvelisib [who-dd]
26. Schembl153543
27. Gtpl7795
28. Duvelisib [orange Book]
29. Chembl3039502
30. Schembl18343557
31. Schembl19670020
32. Schembl20580104
33. Dtxsid80152697
34. Chebi:131169
35. Amy24208
36. Bcp07042
37. Ex-a1562
38. Bdbm50193013
39. Mfcd15144635
40. Nsc772469
41. S7028
42. Zinc88346058
43. Akos022186370
44. Akos037515795
45. Ipi-145, Ink 1197, Duvelisib
46. Ccg-268854
47. Cs-0888
48. Db11952
49. Nsc-772469
50. 8-chloro-2-phenyl-3-((1s)-1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl)-1(2h)-isoquinolinone
51. Ncgc00351482-01
52. Ac-30239
53. As-16309
54. Compound 4904 [patent Us8193182]
55. Hy-17044
56. Sw219822-1
57. D10555
58. Q27077129
59. Ipi-145 Pound>>ink1197; Ipi 145; Ipi145; Ink-1197; Ink 1197
60. 8-chloro-2-phenyl-3-((1s)-1-(7h-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl)isoquinolin-1(2h)-one
| Molecular Weight | 416.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H17ClN6O |
| XLogP3 | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 416.1152369 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 416.1152369 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 668 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Duvelisib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) after at least two prior therapies. The CLL is a cancer of the blood stem cells which are the blood cells that can develop into different types of cells. In leukemia, there is an overproduction of cells that are abnormal and do not mature into blood cells and thus, they just crowd out normal cells and impair their normal function. In lymphocyte leukemia, the abnormal cell growth is observed in the lymphoid cells which are the type of blood cells that mature into lymphocytes. The CLL is the type of lymphocytic leukemia that develops slowly over months or years. The SLL is a very similar disease to the CLL and these terms are usually referred interchangeably. The only difference between these two diseases is that in CLL the cells are found mostly in the blood and bone marrow while in SLL, the cells are mainly found in the lymph nodes. As well, duvelisib obtained an accelerated approval for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma after at least two prior systemic therapies. This approval is still under the status of continued approval and it is restrained to confirmatory trials. The follicular lymphoma is a B-cell lymphoma that clusters in the lymph nodes or other tissues.
FDA Label
Treatment of mature B cell malignancies
Copiktra monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) after at least two prior therapies.
- Follicular lymphoma (FL) that is refractory to at least two prior systemic therapies.
Preclinical data showed that duvelisib presents cytotoxic actions at micromolar doses and antagonizes the activation of downstream signaling even in the presence of the mutation BTK C481S, which allows for the treatment of patients resistant to ibrutinib. In clinical trials, duvelisib was compared to ofatumumab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic leukemia. This trials reported a median progression-free survival of 16.4 months and an overall response rate of 78% which were almost 2-fold what it was reported for ofatumumab. In clinical trials of follicular lymphoma, duvelisib presented and overall response rate of 42% from which almost all the patients observed a partial response. Of the responding patients, 43% maintained the response for at least 6 months and 17% for at least 12 months.
L01EM04
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EM - Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (pi3k) inhibitors
L01EM04 - Duvelisib
Absorption
Duvelisib is rapidly absorbed and its peak plasma concentration is reached 1-2 hours after initial administration with a bioavailability of 42% and with a minimal accumulation whose rate ranges between 1.5 and 2.9. The maximal plasma concentration is reported to range in between 471 to 3294 ng/ml with a systemic exposure ranging from 2001 to 19059 ng.h/ml. Changes in the administered dose produce correspondent changes in all absorption parameters indicating a dose-response profile.
Route of Elimination
Duvelisib is eliminated after 3.5-9.5 hours when administered as a single dose and after 6.5-11.7 hours when given in multiple doses. From the administered dose, 79% os excreted in feces and 14% in urine. About 10% of the total administered dose is secreted unchanged.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of duvelisib ranges from 26 to 102 L.
Clearance
Duvelisib clearance rate is reported to be in the range of 3.6 to 11.2 L/h.
Duvelesib is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4.
The reported half-life of duvelisib is in the range of 5.2 to 10.9 hours.
Duvelisib acts as a strong reversible inhibitor of the isoform gamma and delta of the phosphoinositide3-kinase (PI3K). PI3K plays a very important role in innate and adaptative immunity and the inhibition of the form delta and gamma has been very important for the suppression of immunity. The activity of PI3K gamma and delta is restricted to hematopoietic cells and it is necessary for normal B cell development. In lymphomas, the activation of PI3K is enlarged to promote unlimited growth and survival. Hence, inhibition of PI3K can provide an inhibition of the signaling from BCR, inhibition of a cytokine signaling from the microenvironment and enhancement of anti-tumor immunity. The specific mechanism of this PI3K inhibitors are further described as follows: -BCR activates signaling pathways after antigen engagement and it is also critical for the physiologic life of the lymphocytes and neoplastic lymphomas. In CLL, BCR reacts to auto- and exo-antigens to promote clonal expansion. This sustained presence of BCR activates delta PI3K producing a pro-survival pathway of the neoplastic cells which already present a higher activity of PI3K. Thus, the blockade of PI3K will limit the activity of BCR and the driven physiology of the lymphoma. -The inhibition of PI3K can also inhibit paracrine and autocrine pro-survival signals mediated by adhesion molecules, chemokines and soluble factors. This activity is attained due to the fact that several downstream signals convey on PI3K. -It has been reported that inactivation of PI3K produces a significant resistance to tumorigenesis. This data suggests that inhibition of PI3K can facilitate recognition and elimination of tumor cells. In summary, duvelisib inhibits the isoform delta of PI3K which is necessary for cell proliferation and survival and the isoform gamma which is critical for cytokine signaling and the pro-inflammatory response.