

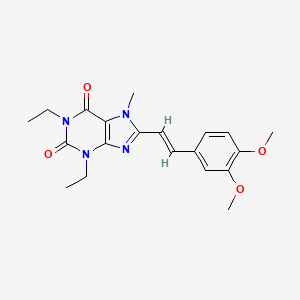

1. 8-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl)-1,3-diethyl-3,7-dihydro-7-methyl-1h-purine-2,6-dione
2. Kw 6002
3. Kw-6002
4. Kw6002
1. 155270-99-8
2. Kw-6002
3. Kw 6002
4. Istradefylline (kw-6002)
5. Nouriast
6. Nourianz
7. 8-[(e)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-purine-2,6 -dione
8. (e)-8-(3,4-dimethoxystyryl)-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-1h-purine-2,6(3h,7h)-dione
9. 8-[(e)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]-1,3-diethyl-7-methylpurine-2,6-dione
10. (e)-8-(3,4-dimethoxystyryl)-1,3-diethyl-7-methylxanthine
11. 2gz0lik7t4
12. Chembl431770
13. (e)-8-(3,4-dimethoxystyryl)-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
14. 8-((1e)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl)-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
15. 8-[(e)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)vinyl]-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
16. Kw6002
17. Unii-2gz0lik7t4
18. Istradefyline
19. Istradefylline (jan/usan/inn)
20. Istradefylline [usan:inn:jan]
21. Ncgc00253737-01
22. Nourianz (tn)
23. Nouriast (tn)
24. Istradefylline [usan]
25. Istradefylline [mi]
26. Dsstox_cid_31441
27. Dsstox_rid_97327
28. Istradefylline [inn]
29. Istradefylline [jan]
30. Dsstox_gsid_57652
31. Mls006010633
32. Schembl633262
33. Schembl633263
34. Gtpl5608
35. Istradefylline [who-dd]
36. Dtxsid7057652
37. Chebi:134726
38. Hms3884p16
39. Istradefylline, >=98% (hplc)
40. Bcp02194
41. Zinc3803921
42. Istradefylline [orange Book]
43. Tox21_113855
44. Bdbm50176050
45. Mfcd00928421
46. S2790
47. Akos015966268
48. Am84508
49. Bcp9000824
50. Ccg-268457
51. Cs-0737
52. Db11757
53. 1h-purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1,3-diethyl-8-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl)-7-methyl-, (e)-
54. Ac-30957
55. Hy-10888
56. Ls-14789
57. Smr004701638
58. Cas-155270-99-8
59. I1100
60. Sw220139-1
61. D04641
62. Kw 6002;kw-6002;kw6002
63. 270i998
64. L001483
65. Q905783
66. Sr-01000945278
67. J-009183
68. J-519355
69. Sr-01000945278-1
70. Brd-k40096621-001-01-2
71. 1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-8-(3,4-dimethoxystyryl)xanthine
72. (e)- 8-(3,4-dimethoxystyryl)-1,3-diethyl-7-methylxanthine
73. 8-(3,4-dimethoxystyryl)-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-1h-purine-2,6(3h,7h)-dione
74. 8-[2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-vinyl]-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione
75. 8-[2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-vinyl]-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-3,9-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione
76. (e)-8-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]-1,3-diethyl-3,7-dihydro-7-methyl-1h-purine-2,6-dione
77. 8-[(1e)-2-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]-1,3-diethyl-3,7-dihydro-7-methyl-1h-purine-2,6-dione
78. 8-[(e)-2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-vinyl]-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione
| Molecular Weight | 384.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H24N4O4 |
| XLogP3 | 2.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 384.17975526 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 384.17975526 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 76.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 613 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Istradefylline is indicated in adjunct to levodopa and carbidopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
Istradefylline is indicated in adults as an adjunctive treatment to levodopa based regimens in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) experiencing OFF time.
Istradefylline is a selective adenosine A2A receptor inhibitor. It has a long duration of action as it is given once daily and has a half life of 64-69 hours. Patients taking this medication should be monitored for dyskinesia, hallucinations, and lack of impulse control. Consider dose reductions for these patients.
Adenosine A2 Receptor Antagonists
Compounds that selectively bind to and block the activation of ADENOSINE A2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adenosine A2 Receptor Antagonists.)
N04
N - Nervous system
N04 - Anti-parkinson drugs
N04C - Other antiparkinson drugs
N04CX - Other antiparkinson drugs
N04CX01 - Istradefylline
Absorption
Istradefylline reaches a Cmax of 181.1ng/mL with a Tmax of 2.0h and an AUC of 11,100ng\*h/mL. M1, the primary active metabolite, reaches a Cmax of 4.34ng/mL with a Tmax of 3.5h. The M8 metabolite reaches a Cmax of 12.6ng/mL with a Tmax of 3.0h and an AUC of 610ng\*h/mL.
Route of Elimination
A 3mg/kg oral dose given to male rats was 17.6% elminated in the urine and 68.3% eliminated in the feces. In urine, 5.31% of the total dose was the M3 metabolite and 1.96% of the total dose was the M1 metabolite. In feces, 30.60% of the total dose was the M3 metabolite, 9.34% of the total dose was the M1 metabolite, 8.33% of the total dose was the M10 metabolite, and 1.62% of the total dose was unchanged istradefylline.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of istradefylline is 448-557L.
Clearance
The apparent clearance of istradefylline is 4.1-6.0L/h.
The primary metabolite found in urine is the active 4'-O-monodesmethyl istradefylline (M1). Istradefylline is metabolized mainly by CYP1A1, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5. CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C18, and CYP2D6 also partly contribute the the metabolism of istradefylline. Other identified metabolites are 1--hydroxylated-4-O-demethyl istradefylline (M2), 3,4-O-didemethyl istradefylline (M3), M1 sulfate conjugate (M4), M1 glucuronide (M5), 1--hydroxylated istradefylline (M8) and hydrogenated M3 (M10).
The terminal elimination half life of istradefylline was 64-69 hours.
Istradefylline is a selective adenosine A2A receptor inhibitor. These receptors are found in the basal ganglia, a region of the brain that suffers degeneration in Parkinson's disease, and is also significantly involved in motor control. A2A receptors are also expressed on GABAergic medium spiny neurons within the indirect striato-pallidal pathway. The GABAergic action of this pathway is thereby reduced. Istradefylline has 56 times the affinity for A2A receptors than A1 receptors.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?