

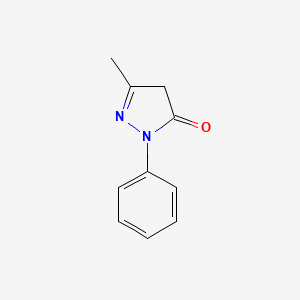

1. 1 Phenyl 3 Methyl 5 Pyrazolone
2. 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone
3. 3 Methyl 1 Phenyl 2 Pyrazolin 5 One
4. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one
5. Edarabone
6. Mci 186
7. Mci-186
8. Mci186
9. Norantipyrine
10. Norphenazone
11. Phenylmethylpyrazolone
12. Radicava
1. 89-25-8
2. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one
3. Radicut
4. Norphenazone
5. Mci-186
6. Developer Z
7. Methylphenylpyrazolone
8. Norantipyrine
9. C.i. Developer 1
10. Phenyl Methyl Pyrazolone
11. Phenylmethylpyrazolone
12. Radicava
13. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-1h-pyrazol-5(4h)-one
14. 5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3h-pyrazol-3-one
15. 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-oxo-2-pyrazoline
16. 5-methyl-2-phenyl-4h-pyrazol-3-one
17. 1-phenyl-3-methylpyrazolone
18. 3h-pyrazol-3-one, 2,4-dihydro-5-methyl-2-phenyl-
19. 1-phenyl-3-methylpyrazolone-5
20. 3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazol-5-one
21. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazoline-5-one
22. Nci-c03952
23. 2-pyrazolin-5-one, 3-methyl-1-phenyl-
24. 5-pyrazolone, 3-methyl-1-phenyl-
25. 2,4-dihydro-5-methyl-2-phenyl-3h-pyrazol-3-one
26. Edaravone (mci-186)
27. 1-fenyl-3-methyl-2-pyrazolin-5-on
28. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1h-pyrazol-5-one
29. Chebi:31530
30. Nsc-2629
31. Nsc-26139
32. Antipyrine Related Compound A
33. Mls000069602
34. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one (mci-186)
35. Ci Developer 1
36. Ncgc00164015-01
37. Smr000059020
38. Dsstox_cid_1130
39. Dsstox_rid_75961
40. Dsstox_gsid_21130
41. Monopyrazolone
42. Wln: T5nmv Dhj Br& E1
43. Cas-89-25-8
44. Ccris 512
45. Radicut (tn)
46. Hsdb 4102
47. 3h-pyrazol-3-one,4-dihydro-5-methyl-2-phenyl-
48. Sr-01000000135
49. 1-fenyl-3-methyl-2-pyrazolin-5-on [czech]
50. Einecs 201-891-0
51. Mfcd00003138
52. Unii-s798v6yjrp
53. Brn 0609575
54. Ai3-03557
55. Mci186
56. (edaravone)
57. Radicava (tn)
58. (mci-186)
59. Cds1_000986
60. Spectrum_000267
61. Tocris-0786
62. Mci-186; Edaravone
63. Edaravone [usan:inn]
64. Maybridge1_005738
65. Opera_id_1057
66. Spectrum2_001574
67. Spectrum3_000971
68. Spectrum4_001091
69. Spectrum5_001217
70. M0687
71. Ec 201-891-0
72. Schembl4704
73. Bspbio_001235
74. Bspbio_002601
75. Kbiogr_000575
76. Kbiogr_001502
77. Kbioss_000575
78. Kbioss_000747
79. Ae-641/00371017
80. Mls001146878
81. Mls002415675
82. Mls006011753
83. Divk1c_001018
84. Divk1c_002026
85. Spectrum1503635
86. Spbio_001508
87. Chembl290916
88. Edaravone (usan/jp17/inn)
89. Dtxsid9021130
90. Bcbcmap01_000127
91. Gtpl11994
92. Hms503k17
93. Hms557m18
94. Kbio1_001018
95. Kbio2_000575
96. Kbio2_000747
97. Kbio2_003143
98. Kbio2_003315
99. Kbio2_005711
100. Kbio2_005883
101. Kbio3_001029
102. Kbio3_001030
103. Kbio3_001821
104. Nsc2629
105. Ninds_001018
106. Bcpp000246
107. Bio1_000438
108. Bio1_000927
109. Bio1_001416
110. Bio2_000448
111. Bio2_000928
112. Hms1362m17
113. Hms1792m17
114. Hms1990m17
115. Hms2234m19
116. Hms3266f04
117. Hms3403m17
118. Hms3411l05
119. Hms3654l15
120. Hms3675l05
121. Hms3884a11
122. Pharmakon1600-01503635
123. Act07289
124. Bcp26336
125. Hy-b0099
126. Nsc26139
127. Tox21_112077
128. Tox21_201747
129. Tox21_302819
130. Bdbm50200541
131. Ccg-39352
132. Nsc758622
133. S1326
134. Stk201315
135. Zinc18203737
136. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5one
137. Akos000313817
138. Tox21_112077_1
139. Ac-4745
140. Bcp9000635
141. Cs-1832
142. Db12243
143. Nsc-758622
144. Sb19128
145. Idi1_001018
146. Idi1_002203
147. 1-pehnyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazalone
148. Ncgc00018218-01
149. Ncgc00018218-02
150. Ncgc00018218-03
151. Ncgc00018218-04
152. Ncgc00018218-05
153. Ncgc00018218-06
154. Ncgc00018218-07
155. Ncgc00018218-08
156. Ncgc00018218-10
157. Ncgc00018218-17
158. Ncgc00022665-02
159. Ncgc00022665-04
160. Ncgc00022665-05
161. Ncgc00022665-06
162. Ncgc00256515-01
163. Ncgc00259296-01
164. Sbi-0051836.p002
165. Db-002517
166. Am20060748
167. Ft-0608243
168. Sw148216-2
169. 5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3-pyrazolone
170. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazoline-5-one, 99%
171. 4e-901
172. 5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-pyrazol-3-one
173. D01552
174. D86209
175. 3-?methyl-?1-?phenyl-?2-?pyrazolin-?5-?one
176. Ab00375776_14
177. Ab00375776_15
178. 2 4-dihydro-5-methyl-2-phenyl-3h-pyrazol-3-one
179. 2,4-dihydro-2-phenyl-5-methyl-3h-pyrazol-3-one
180. A843105
181. Q335099
182. Q-200386
183. Sr-01000000135-2
184. Sr-01000000135-3
185. Sr-01000000135-5
186. 5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3h-pyrazol-3-one #
187. Brd-k35458079-001-04-2
188. Brd-k35458079-001-12-5
189. Brd-k35458079-001-23-2
190. Z50145861
191. F0391-0021
192. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazoline-5-one, Saj Special Grade
193. 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazoline-5-one, Purum, >=98.0% (nt)
194. 5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3h-pyrazol-3-one (edaravone)
195. Phenazone Impurity A, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
196. 5-methyl-2-phenyl-1,2-dihydropyrazol-3-one;3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one
197. Antipyrine Related Compound A, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 174.20 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H10N2O |
| XLogP3 | 1.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 174.079312947 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 174.079312947 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 32.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 241 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for improving neurological symptoms and damage from acute ischemic stroke and delaying disease progression of ALS.
FDA Label
Treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Edaravone scavenges free hydroxyl radicals and peroxynitrite radicals which are highly associated with neuronal damage/death from many cerebral vascular disorders such as ischemic strokes and degenerative neurological disorders such as ALS. It exerts a neuroprotective and antioxidant effect and delays disease progression by limiting the extent of lipid peroxidation via free radical generation and cell membrane damage from oxidative stress. It reversed the reduction in regional blood flow and cerebral edema in a case of ischemic stroke.
Free Radical Scavengers
Substances that eliminate free radicals. Among other effects, they protect PANCREATIC ISLETS against damage by CYTOKINES and prevent myocardial and pulmonary REPERFUSION INJURY. (See all compounds classified as Free Radical Scavengers.)
Neuroprotective Agents
Drugs intended to prevent damage to the brain or spinal cord from ischemia, stroke, convulsions, or trauma. Some must be administered before the event, but others may be effective for some time after. They act by a variety of mechanisms, but often directly or indirectly minimize the damage produced by endogenous excitatory amino acids. (See all compounds classified as Neuroprotective Agents.)
N - Nervous system
N07 - Other nervous system drugs
N07X - Other nervous system drugs
N07XX - Other nervous system drugs
N07XX14 - Edaravone
Absorption
The peak plasma concentration of the parent drug is reached at the end of infusion, without accumulation of the drug with multiple dosing regimen. The mean Cmax value in healthy male adults is 888ng/mL for intravenous infusion. The values of AUC and Cmax are increased in a dose-proportional relationship. The oral bioavailability in mouse studies is 38% of the I.V. delivery.
Route of Elimination
About 0.7-0.9% of the dose is excreted as unchanged drug and 71.0-79.9% of the dose is excreted as metabolites (mostly as glucuronide conjugates) through mainly renal elimination.
Volume of Distribution
The mean Vd value following an intravenous infusion of a single 30mg dose is 18.5L/kg.
Clearance
The mean total plasma drug clearance following an intravenous infusion of a single 30mg dose is 0.1L/min.
Multiple renal and hepatic uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoforms catalyze glucuronidation reaction of edaravone to form glucuronide conjugates. Edaravone is also metabolized into sulfate conjugates via sulfotransferase activity, which is the main metabolite form predominantly found circulating in plasma. It is predicted that the sulfate conjugate is hydrolyzed back to edaravone, which is then converted to the glucuronide conjugate in the human kidney before excretion into the urine. These metabolites have no pharmacological activity.
The mean terminal elimination half-life of edaravone is 4.5 to 6 hours and the half-lives of its metabolites are 2 to 2.8 hours.
Nootropic and neuroprotective effects are mediated through inhibiting lipid peroxidation and scavenging free radicals. Edaravone acts to increase prostacyclin production, decrease lipoxygenase metabolism of arachidonic acid by trapping hydroxyl radicals, and inhibit alloxan-induced lipid peroxidation and quench active oxygen species. It targets various kinds of cells, including neurons, endothelial cells and myocardial cells. There is also evidence of reduction of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) levels and potentiation of SOD1 levels after transient ischemia in rabbits thus preventing spinal cord injury.
