

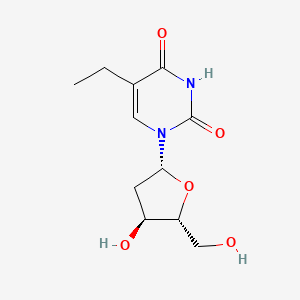

1. 1-(2'-deoxy-beta-d-ribofuranosyl)-5-ethyluracil
2. 2'-deoxy-5-ethyluridine
3. 5-ethyl-2'-deoxyuridine
4. 5-ethyl-3-(2'-deoxyribofuranosyl)uracil
5. 5-ethyldeoxyuridine
6. Edoxudin
7. Edoxudin, (alpha)-isomer
8. Edoxudin, 2-(14)c-labeled
9. Edoxudin, 2-(14)c-labeled, (alpha)-isomer
10. Edoxudin, 4-(14)c-labeled
11. Edoxudin, 4-(14)c-labeled, (alpha)-isomer
1. 5-ethyl-2'-deoxyuridine
2. 15176-29-1
3. 2'-deoxy-5-ethyluridine
4. Epoxudine
5. 5-ethyldeoxyuridine
6. Aedurid
7. Beta-5-ethyldeoxyuridine
8. Orf 15817
9. Rwj 15817
10. Eudr
11. Uridine, 2'-deoxy-5-ethyl-
12. Mls000069564
13. 15zqm81y3r
14. Chembl318153
15. Orf-15817
16. Rwj-15817
17. Nsc-758405
18. Smr000058816
19. Edoxudinum [latin]
20. Edoxudina [spanish]
21. Edoxudinum
22. Edoxudin
23. Edoxudina
24. Edoxudine [usan:inn]
25. Beta-5-ethyl-2'-deoxyuridine
26. Ccris 2349
27. Einecs 239-226-1
28. Brn 0755089
29. Unii-15zqm81y3r
30. Etudr
31. 5-ethyl-durd
32. 5-ethyl-1-(2'-deoxy-beta-d-ribofuranosyl)uracil
33. Edoxudine [inn]
34. Edoxudine [mi]
35. Edoxudine (usan/inn)
36. Edoxudine [usan]
37. Opera_id_1297
38. Edoxudine [mart.]
39. 5-ethyl-2''-deoxyuridine
40. Cid_1814
41. Edoxudine [who-dd]
42. Dsstox_cid_25890
43. Dsstox_rid_81204
44. Dsstox_gsid_45890
45. Schembl65579
46. Cid_66377
47. Mls001076558
48. Dtxsid4045890
49. Chebi:135051
50. Hms2234l05
51. Hy-b1011
52. Zinc3956771
53. Tox21_111390
54. Bdbm50132292
55. Cs-4524
56. Db13421
57. Nsc 758405
58. 5-ethyl-3-(2'-deoxyribosyl)uracil
59. Cas-15176-29-1
60. D03956
61. 5-ethyl-2 Inverted Exclamation Mark -deoxyuridine
62. Q987691
63. Brd-k86892782-001-13-9
64. 5-ethyl-1-((2r,4s,5r)-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)pyrimidine-2,4(1h,3h)-dione
65. 5-ethyl-1-((2r,4s,5r)-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)pyrimidine-2,4(1h,3h)-dione
66. 5-ethyl-1-((2r,5r)-4-hydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-tetrahydro-furan-2-yl)-1h-pyrimidine-2,4-dione
67. 5-ethyl-1-[(2r,4s,5r)-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]pyrimidine-2,4-dione
| Molecular Weight | 256.25 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H16N2O5 |
| XLogP3 | -0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 256.10592162 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 256.10592162 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 99.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 395 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Edoxudine was used in Europe, in the form of a topical antiviral, for the treatment of human herpes keratitis. Human herpes keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea in the eye caused by herpes simplex virus infection. This infection is a cause of significant morbidity whose incidence is significantly increased in the presence of recurrent infection and it can even produce corneal blindness. Edoxudine 3% cream was also indicated for the treatment of dermal herpes simplex virus. This virus can produce an infection ubiquitously and it is highly contagious. There are two types of herpes virus, type 1 that is mainly transmitted by oral-to-oral contact and type 2 that is sexually transmitted.
In reports, it has been indicated that at antivirally active doses, edoxudine is phosphorylated to a much greater extent by hepatitis-infected cells when compared to mock-infected cells. Once phosphorylated, edoxudine is more highly incorporated into viral DNA than cellular DNA. The level of incorporation into viral DNA highly seems to be correlated with the concentration of edoxudine. The suppression of viral DNA synthesis caused a shutoff of viral replication and the viral titration is significantly reduced.The effect of edoxudine is also proven to reduce significantly the lesion area produced by the viral activity to an even 44% reduction.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
D - Dermatologicals
D06 - Antibiotics and chemotherapeutics for dermatological use
D06B - Chemotherapeutics for topical use
D06BB - Antivirals
D06BB09 - Edoxudine
Absorption
Edoxudine cream is able to penetrate the skin in a very rapid manner. This easy penetration allows edoxudine to have a greater activity when compared with other topical antivirals that have better antiviral activity in vitro. In preclinical trials in mice, after intravenous administration of edoxudine, the mean residence time was 25 min. Edoxudine presented a bioavailability of 49% with a Cmax and tmax of 2.4 mcg/g and 31.1 min respectively. The AUC in plasma of edoxudine is significantly higher when administered orally when compared with intravenous administration.
Volume of Distribution
This pharmacokinetic property is not available.
Clearance
The plasma clearance of edoxudine is reported to be 85 ml/min.
In preclinical trials it has been reported that edoxudine presents a biotransformation marked by a cleavage of the glycoside bond. The degradation of edoxudine, after oral administration, seems to be processed by the activity of phosphorylases presented in the gastrointestinal tract and by pre-systemic metabolism.
In preclinical trials on mice, after intravenous administration, edoxudine presented a very short distribution half-life of 1.4 min. In the same trials, the elimination half-life was reported to be of 24.1 min.
Edoxudine is a potent inhibitor of the replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2. For the activation of this drug, the action of viral thymidine kinase is required to phosphorylate this molecule in order to form the 5'-monophosphate derivative. Then, it is needed to be further phosphorylated by cellular enzymes until the formation of the 5'-triphosphate derivative which is a competitive inhibitor of the viral-coded DNA polymerase. The advantage of edoxudine is that it is highly selective, this characteristic can be seen by its preferential phosphorylation in herpes-infected cells and its preferential incorporation into viral DNA.
