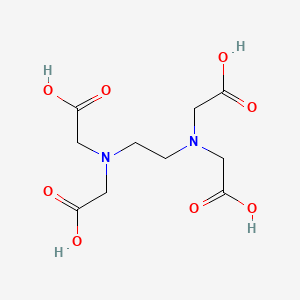

1. Acid, Edetic
2. Acid, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic
3. Acid, Ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic
4. Calcitetracemate, Disodium
5. Calcium Disodium Edetate
6. Calcium Disodium Versenate
7. Calcium Tetacine
8. Chelaton 3
9. Chromium Edta
10. Copper Edta
11. Coprin
12. Dicobalt Edta
13. Dinitrilotetraacetate, Disodium Ethylene
14. Dinitrilotetraacetate, Ethylene
15. Disodium Calcitetracemate
16. Disodium Edta
17. Disodium Ethylene Dinitrilotetraacetate
18. Disodium Versenate, Calcium
19. Distannous Edta
20. Edathamil
21. Edetate Disodium Calcium
22. Edetate, Calcium Disodium
23. Edetates
24. Edetic Acid, Calcium Salt
25. Edetic Acid, Calcium, Sodium Salt
26. Edetic Acid, Chromium Salt
27. Edetic Acid, Dipotassium Salt
28. Edetic Acid, Disodium Salt
29. Edetic Acid, Disodium Salt, Dihydrate
30. Edetic Acid, Disodium, Magnesium Salt
31. Edetic Acid, Disodium, Monopotassium Salt
32. Edetic Acid, Magnesium Salt
33. Edetic Acid, Monopotassium Salt
34. Edetic Acid, Monosodium Salt
35. Edetic Acid, Potassium Salt
36. Edetic Acid, Sodium Salt
37. Edta
38. Edta, Chromium
39. Edta, Copper
40. Edta, Dicobalt
41. Edta, Disodium
42. Edta, Distannous
43. Edta, Gallium
44. Edta, Magnesium Disodium
45. Edta, Potassium
46. Edta, Stannous
47. Ethylene Dinitrilotetraacetate
48. Ethylene Dinitrilotetraacetate, Disodium
49. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid
50. Ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic Acid
51. Gallium Edta
52. Magnesium Disodium Edta
53. N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)glycine)
54. Potassium Edta
55. Stannous Edta
56. Tetacine, Calcium
57. Tetracemate
58. Versenate
59. Versenate, Calcium Disodium
60. Versene
1. Edta
2. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid
3. 60-00-4
4. Edathamil
5. Versene
6. Endrate
7. Havidote
8. Sequestrol
9. Titriplex
10. Edta Acid
11. Versene Acid
12. Cheelox
13. Sequestric Acid
14. Warkeelate Acid
15. Gluma Cleanser
16. Sequestrene Aa
17. Komplexon Ii
18. Quastal Special
19. Tetrine Acid
20. Metaquest A
21. Trilon Bw
22. Complexon Ii
23. Hamp-ene Acid
24. Titriplex Ii
25. Cheelox Bf Acid
26. Trilon Bs
27. Celon A
28. Chelest 3a
29. Questex 4h
30. Celon Ath
31. Chemcolox 340
32. (ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetic Acid
33. Universne Acid
34. Vinkeil 100
35. Dissolvine E
36. Nullapon B Acid
37. Nullapon Bf Acid
38. Perma Kleer 50 Acid
39. Nervanaid B Acid
40. Clewat Taa
41. Edta (chelating Agent)
42. Versenate
43. Calcium Disodium Versenate
44. Acidum Edeticum
45. Edetate Disodium
46. Acide Edetique
47. Acido Edetico
48. Caswell No. 438
49. Disodium Edta
50. Chelaton 3
51. Icrf 185
52. Cheladrate
53. Seq 100
54. Edetate Calcium
55. Ethylenebisiminodiacetic Acid
56. Yd 30
57. Acide Edetique [inn-french]
58. Acido Edetico [inn-spanish]
59. Acidum Edeticum [inn-latin]
60. Ccris 946
61. Ethylenebis(iminodiacetic Acid)
62. Edetate
63. Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid
64. Glycine, N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis[n-(carboxymethyl)-
65. Hsdb 809
66. Acide Ethylenediaminetetracetique
67. Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
68. Ethylenediamine-n,n,n',n'-tetraacetic Acid
69. 2-[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl-(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic Acid
70. Acetic Acid, (ethylenedinitrilo)tetra-
71. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 039101
72. Edta Disodium
73. Disodium Edetate
74. Disodium Versene
75. Endrate Disodium
76. Kyselina Ethylendiamintetraoctova
77. Sodium Versenate
78. Edetic Acid Disodium Salt
79. Kyselina Ethylendiamintetraoctova [czech]
80. Acide Ethylenediaminetetracetique [french]
81. Metaquest B
82. Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid
83. Kiresuto B
84. Chelaplex Iii
85. Complexon Iii
86. Diso-tate
87. Titriplex Iii
88. 3,6-diazaoctanedioic Acid, 3,6-bis(carboxymethyl)-
89. Ai3-17181
90. Chelaton Iii
91. Glycine, N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)-
92. Versene Na
93. Triplex Iii
94. Disodium Versenate
95. Edathamil Disodium
96. Trilon Bd
97. Versene Na2
98. Disodium Sequestrene
99. Disodium Tetracemate
100. Edta Disodium Salt
101. F 1 (complexon)
102. Mfcd00003541
103. Edta, Ion(4-)
104. Chembl858
105. Sequestrene Sodium 2
106. Acetic Acid, 2,2',2'',2'''-(1,2-ethanediyldinitrilo)tetrakis-
107. N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)glycine)
108. {[-(bis-carboxymethyl-amino)-ethyl]-carboxymethyl-amino}-acetic Acid
109. Disodium Salt Of Edta
110. 9g34hu7rv0
111. Perma Kleer Di Crystals
112. Calcium Disodium Versenate (tn)
113. Disodium Edetate Dihydrate
114. Ethylene-diamine Tetraacetic Acid
115. 2,2',2'',2'''-(ethane-1,2-diyldinitrilo)tetraacetic Acid
116. Chebi:42191
117. 2-({2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl}(carboxymethyl)amino)acetic Acid
118. 4-04-00-02449 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
119. N,n'-1,2-ethane Diylbis-(n-(carboxymethyl)glycine)
120. 470462-56-7
121. Edt
122. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt
123. Edetate Calcium Disodium (usp)
124. Sequestrene Na2
125. Trilon B
126. Ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic Acid
127. Selekton B2
128. Disodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
129. (ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetic Acid, Ion(4-)
130. Perma Kleer 50 Crystals Disodium Salt
131. Disodium (ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetate
132. Disodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid
133. Sodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
134. Caedta
135. Cbc 50152966
136. Dr-16133
137. Ethylenediaminetetraacetate, Disodium Salt
138. Disodium Diacid Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
139. D'e.d.t.a. Disodique
140. Disodium (ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetic Acid
141. 2,2',2'',2'''-(ethane-1,2-diyldinitrilo)tetraacetate
142. Disodium Dihydrogen Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
143. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Disodium Salt
144. Disodium Dihydrogen(ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetate
145. 139-33-3
146. Nsc2760
147. N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis[n-(carboxymethyl)glycine]
148. Ncgc00159485-02
149. 6381-92-6
150. Einecs 200-449-4
151. Brn 1716295
152. Unii-9g34hu7rv0
153. Disodium-edta
154. Edetic Acid [inn:ban:nf]
155. (ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetic Acid, Disodium Salt
156. 2-[2-(bis(carboxymethyl)amino)ethyl-(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic Acid
157. Tricon Bw
158. ([2-(bis-carboxymethyl-amino)-ethyl]-carboxymethyl-amino)-acetic Acid
159. {[2-(bis-carboxymethyl-amino)-ethyl]-carboxymethyl-amino}-acetic Acid
160. Calcium Disodium Edetate (jan)
161. Techrun Do
162. Edta, Anhydrous
163. Zonon Ao
164. Edta, Free Acid
165. Edta, Free Base
166. Acetic Acid, (ethylenedinitrilo)tetra-, Disodium Salt
167. Versene Acid (tn)
168. Acroma Dh 700
169. Spectrum_001018
170. Edetic Acid (nf/inn)
171. Edta [vandf]
172. 53632-26-1
173. Spectrum2_000003
174. Spectrum3_000412
175. Spectrum4_000531
176. Spectrum5_000955
177. Edta [inci]
178. Edetic Acid [ban:inn]
179. Dsstox_cid_2977
180. Edetic Acid [ii]
181. Edetic Acid [inn]
182. Edta [mi]
183. Ec 200-449-4
184. Edetic Acid [hsdb]
185. Edta, Anhydrous Acs Grade
186. Dsstox_rid_76814
187. Dsstox_gsid_22977
188. Ethylenediaminetetracetic Acid
189. Bspbio_001964
190. Diaminoethanetetra-acetic Acid
191. Edetic Acid [mart.]
192. Ethylenediamineteraacetic Acid
193. Kbiogr_001161
194. Kbioss_001498
195. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic-acid
196. Mls001249457
197. Bidd:er0565
198. Divk1c_000777
199. Edetic Acid [usp-rs]
200. Edetic Acid [who-dd]
201. Ethylenediamine Tetracetic Acid
202. Spbio_000005
203. Ethylenediamine-tetraacetic Acid
204. Dtxsid6022977
205. Kbio1_000777
206. Kbio2_001498
207. Kbio2_004066
208. Kbio2_006634
209. Kbio3_001184
210. (ethylenedintrilo)tetraacetic Acid
211. Ethylen-ediamine Tetra-acetic Acid
212. Ninds_000777
213. Edetic Acid [ep Monograph]
214. Cs-b1827
215. Hy-y0682
216. Str08855
217. Tox21_202736
218. Bdbm50330325
219. S6350
220. Stk386291
221. Zinc19364242
222. Akos001574475
223. Glycine, (n,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)-, Labeled With Carbon-14
224. (ethane-1,2-diyldinitrilo)tetraacetate
225. Db00974
226. Cas-60-00-4
227. Idi1_000777
228. Ncgc00159485-03
229. Ncgc00159485-04
230. Ncgc00260284-01
231. 688-55-1
232. Ac-10615
233. Smr000058776
234. Sbi-0051360.p003
235. Db-084840
236. Ds-003836
237. B7197
238. E0084
239. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, 2na (edta)
240. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Lr, >=98%
241. Ft-0626319
242. Ft-0668253
243. Ft-0668254
244. C00284
245. D00052
246. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, P.a., 98.0%
247. Ab00053468_03
248. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Solution, 0.02 N
249. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, >=98.0% (kt)
250. A832566
251. N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis[n-(carboxymethyl)]glycine
252. Q408032
253. Sr-01000883946
254. Anticoagulant Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid
255. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Sodium Salt Solution
256. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Cell Culture Reagent
257. J-610078
258. Sr-01000883946-1
259. 37c3c5e7-d921-445f-82d6-febf1ae5aef5
260. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Electrophoresis Grade
261. Z2688689169
262. Anticoagulant Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid (edta)
263. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Bioultra, >=99.0% (kt)
264. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, 0.5m Aq. Solution, Ph 8.0
265. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, 99.995% Trace Metals Basis
266. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Saj Special Grade, >=99.0%
267. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
268. [{2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl}(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic Acid
269. 2,2',2'',2'''-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanetriyl))tetraacetic Acid
270. Edetic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
271. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Acs Reagent, 99.4-100.6%, Powder
272. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Purified Grade, >=98.5%, Powder
273. 2,2'',2'''',2''''''-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanetriyl))tetraacetic Acid
274. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, 0.5m Aqueous Solution, Ph 8.0, Autoclaved
275. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Bioultra, Anhydrous, >=99% (titration)
276. Glycine, N,n'-1, {2-ethanediylbis[n-(carboxymethyl)-,} Disodium Salt
277. {[2-(bis-carboxymethyl-amino)-ethyl]-carboxymethyl-amino}-acetic Acid(edta)
278. 2-[2-[bis(2-hydroxy-2-oxoethyl)amino]ethyl-(2-hydroxy-2-oxoethyl)amino]ethanoic Acid
279. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Anhydrous, Free-flowing, Redi-dri(tm), >=98%
280. 124949-23-1
281. Ethylenediamine-n,n,n Inverted Exclamation Mark ,n Inverted Exclamation Mark -tetraacetic Acid-13c4 (
282. A-labels)
283. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Solution, 0.02% In Dpbs (0.5 Mm), Sterile-filtered, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture
284. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Solution, Bioultra, For Molecular Biology, Ph 8.0, ~0.5 M In H2o
285. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Anhydrous, Crystalline, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture
286. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Anhydrous, Free-flowing, Powder, Redi-dri(tm), Acs Reagent, 99.4-100.6%
| Molecular Weight | 292.24 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N2O8 |
| XLogP3 | -5.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 292.09066547 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 292.09066547 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 156 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 316 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 1 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | CALCIUM DISODIUM VERSENATE |
| Active Ingredient | EDETATE CALCIUM DISODIUM |
| Company | MEDICIS (Application Number: N008922) |
Anticoagulants; Antidotes; Chelating Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
EDTA has been used to treat alkali, particularly lime, burns of the cornea.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
(51)Cr-EDTA has been used since 1966 as a radiotracer for the assessment of glomerular filtration rate.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
Chelation therapy using EDTA has been used since 1955 to treat atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, but its efficacy has been disputed in recent years. /Former use/
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ETHYLENEDIAMINE TETRAACETIC ACID (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Anticoagulants; Chelating Agents; Food Additives
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Endrate (Edetate Disodium Injection, USP) is indicated in selected patients for the emergency treatment of hypercalcemia and for the control of ventricular arrhythmias associated with digitalis toxicity. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Disodium edentate is also used therapeutically as an anticoagulant as it will chelate calcium and prevent the coagulation of blood in vitro. Concentrations of 0.1% w/v are used in small volumes for hematological testing and 0.3% w/v in transfusions.
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 243
Disodium EDTA is used occasionally to terminate the effects of injected calcium, to antagonize digitalis toxicity, or to suppress tachyarrhythmias. /Former/
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Disodium EDTA (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
... direct contact with EDTA may cause dermal sensitization (eczema) or allergic conjunctivitis.
Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker (GDCh) - Advisory Committee on Existing Chemicals of Environmental Relevance (BUA); S. Hirzel Verlag, P.O. Box 10 10 61, 70009 Stuttgart, Germany, 1997. xxi, 223p. Bibl.ref.
/BOXED WARNING/ The use of this drug in any particular patient is recommended only when the severity of the clinical condition justifies the aggressive measures associated with this type of therapy.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Clinical studies of edetate disodium did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Fatal medication errors have occurred that involve confusion between edetate calcium disodium (calcium EDTA) and edetate disodium (no longer commercially available in the US). Children and adults have mistakenly received edetate disodium instead of edetate calcium disodium; at least 5 deaths have occurred as a result of inadvertent administration of edetate disodium. Although both edetate calcium disodium and edetate disodium are heavy metal antagonists, the 2 drugs were originally approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for different uses and have different effects; edetate disodium was formerly FDA approved for use in selected patients for the emergency treatment of hypercalcemia or for the control of ventricular arrhythmias associated with cardiac glycoside toxicity. Use of edetate disodium may result in a substantial, and sometimes fatal, decrease in serum calcium concentrations. In June 2008, FDA withdrew its prior approval for edetate disodium because of safety concerns following a review of the risk-benefit profile of the drug. FDA stated that it was not considering additional action regarding edetate calcium disodium at that time; most of the fatalities following administration of an EDTA drug have involved medication errors in which edetate disodium was administered instead of edetate calcium disodium. FDA has not received reports of any fatalities resulting from the administration of edetate calcium disodium that involve a medication error.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Edetate Disodium Injection is contraindicated in anuric patients. It is not indicated for the treatment of generalized arteriosclerosis associated with advancing age.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Disodium EDTA (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the reduction of blood levels and depot stores of lead in lead poisoning (acute and chronic) and lead encephalopathy, in both pediatric populations and adults.
Edetate calcium is a heavy metal chelating agent. The calcium in edetate calcium can be displaced by divalent or trivalent metals to form a stable water soluble complex that can be excreted in the urine. In theory, 1 g of edetate calcium can theoretically bind 620 mg of lead, but in reality only about 5 mg per gram is actually excreted into the urine in lead poisoned patients. In addition to chelating lead, edetate calcium also chelates and eliminates zinc from the body. Edetate calcium also binds cadmium, copper, iron and manganese, but to a much lesser extent than either lead or zinc. Edetate calcium is relatively ineffective for use in treating mercury, gold or arsenic poisoning.
Calcium Chelating Agents
Substances that bind to and sequester CALCIUM ions. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Chelating Agents.)
Food Additives
Substances used in the processing or storage of foods or animal feed including ANTIOXIDANTS; FOOD PRESERVATIVES; FOOD COLORING AGENTS; FLAVORING AGENTS; ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS; EXCIPIENTS and other similarly used substances. Many of the same substances are used as PHARMACEUTIC AIDS. (See all compounds classified as Food Additives.)
Anticoagulants
Agents that prevent BLOOD CLOTTING. (See all compounds classified as Anticoagulants.)
Absorption
Poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Well absorbed following intramuscular injection.
Route of Elimination
It is excreted primarily by the kidney, with about 50% excreted in one hour and over 95% within 24 hours.2 Almost none of the compound is metabolized.
Studies with (14)C-EDTA were performed in a similar manner to studies with (14)C-Diethylenetriamine Pentaacetic Acid (DTPA). (14)C-DTFA, 10 to 15mg with a (14)C activity of 15 to 20 pCi, was administered IV to 4 patients. Oral doses of (14)C-EDTA, either 3 mg with a 14C activity of 5 to 10 pCi or 50 mg (14)C-EDTA with a (14)C activity of 75 to 100 pCi, were administered to two patients. The urinary excretion pattern for (14)C-EDTA was similar to that of (14)C-DTPA. The kidneys were the major route of excretion for (14)C-DTPA after IV injection. At the end of 24 hours, 90% to 100% of the dose of (14)C-DTPA was excreted in the urine. Oral doses of (14)C-DTPA passed through the intestine and 95% to 100% of the dose was recovered in the stool within 2 to 5 days. The urinary excretion was < 8% in the seven patients who received (14)C-DTPA orally. Results for (14)C-EDTA were similar, although it was administered orally to two patients. Additionally, blood samples taken from 1 hour to 3 days after oral administration of (14)C-DTPA did not have any (14)C activity. Similar results were obtained for (14)C-EDTA.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
/Investigatos/ found that increasing concentrations of EDTA increases its binding per milligram of albumin. This binding action increases as the pH values increase from 5.1 to 8.2 and the beta-globulin fraction binds more EDTA than other plasma proteins.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
/Investigators/ reported that (51)Cr-EDTA moved passively across the epithelium of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract of dogs. The investigators treated muscle-stripped segments of the stomach, ileum, and colon with 0.5 mL of the chelate at a concentration of 9.0 mM. The rate of flux of the chelate was greatest in the ileum, less in the colon, and least in the stomach. No net accumulation of the probe was observed. In addition, the movement of the chelate across the ileum was not affected by neuronal blockade with tetrodotoxin. The investigators suggested that (51)Cr-EDTA moved from the gut lumen via a shunt pathway.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
/Investigators/ instilled a solution containing 5 MBq (51)Cr-EDTA (in 14 mL of isotonic saline) in the nasal cavity of 6 smokers and 12 nonsmokers, and maintained the exposure for 15 minutes. Urine was collected for 24 hours after instillation. The median recovered amount of the chelate in smokers was 0.07 mL, and the median amount in nonsmokers was 0.16 mL. After instillation was repeated with the addition of 0.6% dioctylsodium sulfosuccinate to the solution, the median amount recovered for six nonsmokers increased to 1.13 mL. The investigators concluded that nasal airway absorption was not increased in smokers compared to nonsmokers. The investigators also administered 5 MBq (51)Cr-EDTA and 0.6% dioctylsodium sulfosuccinate in 2.0 mL saline to four separate subjects to determine the GI absorption of EDTA. The mean amount of the chelate recovered in the urine corresponded to 1.4% of the dose.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ETHYLENEDIAMINE TETRAACETIC ACID (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
After intravenous administration, the chelate formed is excreted in the urine with 50% appearing in 1 hour and over 95% in 24 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Disodium edentate ... /is/ poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and /is/ associated with few adverse effects when used as an excipient in pharmaceutical preparations.
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 243
Twenty male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups of five animals each. Rats in group 1 received ip injections of (14)C Disodium EDTA, group 2 received this compound on depilated skin, rats in group 3 received this compound on depilated and abraded skin (abraded every 2 or 3 cm over treated area), and group 4 was the control group. The specific activity of the (14)C Disodium EDTA was 21.6 mCi/mM and it was dissolved in saline to yield a final solution of 50 pCi/mL. Animals that received ip injections got 0.5 mL of this solution, or 25 pCi of (14)C Disodium EDTA. Animals that had the compound applied to the skin received 25 pCi of (14)C Disodium EDTA in the form of an ointment (modulan, mineral oil, petrolatum, cetyl alcohol 35:21 :25:12) spread over an area of 50 sq cm spread over a sheet of thin polyethylene. This sheet was taped to the trunk of each animal. A collar was fixed around the neck of the rats. All animals were decapitated 24 hours after treatment. The tissue distribution (per 100 mg wet organ weight) of (14)C Disodium EDTA 24 hours after ip administration was as follows: liver 577+/- 13, small intestine 631 +/- 25, large intestine 696 +/- 19, and kidney 1964 +/- 220. Twenty-four hours after application on normal skin the tissue distribution was as follows: liver 6 +/- 4, small intestine 99 +/- 22, large intestine 107 +/- 24, and kidneys 29 +/- 12. Twenty-four hours after application on abraded skin the tissue distribution was as follows: liver 139 +/- 34, small intestine 214 +/- 76, large intestine 309 +/- 115, and kidneys 222 +/- 30.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
/Investigators/ reported that rats fed 0.5%, 1.0%, and 5.0% Disodium EDTA for 12 weeks excreted 82.2%, 44.5%, and 45.4%, respectively, of the ingested dose in the urine and feces. The feces contained 99.4%, 98.2%, and 97.5% of the excreted material and the urine contained 0.6%, 1.8%, and 2.5% of the material for the respective doses.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Disodium EDTA (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Almost none of the compound is metabolized.
EDTA is reportedly eliminated essentially unchanged.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 769
The half life of edetate calcium disodium is 20 to 60 minutes.
... About 50% of EDTA admin iv is excreted within 1 hr and 90% within 7 hr. ...
International Labour Office. Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety. Vols. I&II. Geneva, Switzerland: International Labour Office, 1983., p. 443
After intravenous administration, the chelate formed is excreted in the urine with 50% appearing in 1 hour and over 95% in 24 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
The pharmacologic effects of edetate calcium disodium are due to the formation of chelates with divalent and trivalent metals. A stable chelate will form with any metal that has the ability to displace calcium from the molecule, a feature shared by lead, zinc, cadmium, manganese, iron and mercury. The amounts of manganese and iron metabolized are not significant. Copper is not mobilized and mercury is unavailable for chelation because it is too tightly bound to body ligands or it is stored in inaccessible body compartments. The excretion of calcium by the body is not increased following intravenous administration of edetate calcium disodium, but the excretion of zinc is considerably increased.
Effects on rat liver glucocorticoid receptor in vitro was studied. At 4 C, 10 mmole EDTA had a stablizing effect on unbound hepatic glucocorticoid receptors. Apparently, endogenous metal ions are involved in the processes of glucocorticoid-receptor complex stabilization and transformation.
PMID:6411997 Hubbard J et al; J STEROID BIOCHEM 19 (2): 1163-7 (1983)
Edetate disodium injection forms chelates with the cations of calcium and many divalent and trivalent metals. Because of its affinity for calcium, edetate disodium will produce a lowering of the serum calcium level during intravenous infusion. Slow infusion over a protracted period may cause mobilization of extracirculatory calcium stores. Edetate disodium exerts a negative inotropic effect upon the heart.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006).
Edetate disodium likewise forms chelates with other polyvalent metals and produces increases in urinary excretion of magnesium, zinc and other trace elements. It does not form a chelate with potassium but may reduce the serum level and increase urinary loss of potassium.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77