


1. Elapegademase-lvlr
2. Revcovi
1. Revcovi
2. Elapegademase-lvlr
3. Elapegademase [inn]
4. Unii-9r3d3y0uhs
5. Elapegademase [usan:inn]
6. 9r3d3y0uhs
7. Schembl20670726
8. Ezn-2279
9. Q27272923
10. 1709806-75-6
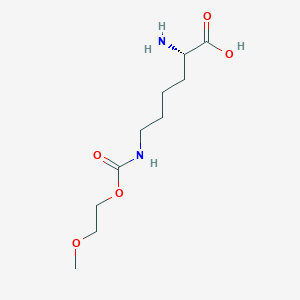
11. Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), Alpha-carboxy-omega-methoxy-, Amide With Adenosine Deaminase (synthetic)
| Molecular Weight | 248.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H20N2O5 |
| XLogP3 | -2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 248.13722174 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 248.13722174 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 111 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 235 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Elapegademase is approved for the treatment of adenosine deaminase severe combined immune deficiency (ADA-SCID) in pediatric and adult patients. This condition was previously treated by the use of bovine pegamedase as part of an enzyme replacement therapy. ADA-SCID is a genetically inherited disorder that is very rare and characterized by a deficiency in the adenosine deaminase enzyme. The patients suffering from this disease often present with a compromised immune system. This condition is characterized by very low levels of white blood cells and immunoglobulin levels which results in severe and recurring infections.
FDA Label
In clinical trials, elapegademase was shown to increase adenosine deaminase activity while reducing the concentrations of toxic metabolites which are the hallmark of ADA-SCID. As well, it was shown to improve the total lymphocyte count.
Adenosine Deaminase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit ADENOSINE DEAMINASE activity. (See all compounds classified as Adenosine Deaminase Inhibitors.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L03 - Immunostimulants
L03A - Immunostimulants
L03AX - Other immunostimulants
L03AX21 - Elapegademase
Absorption
Elapegademase is administered intramuscularly and the reported Tmax, Cmax and AUC are approximately 60 hours, 240 mmol.h/L and 33000 hr.mmol/L as reported during a week.
Route of Elimination
This pharmacokinetic property has not been fully studied.
Volume of Distribution
This pharmacokinetic property has not been fully studied.
Clearance
This pharmacokinetic property has not been fully studied.
Metabolism studies have not been performed but it is thought to be degraded by proteases to small peptides and individual amino acids.
This pharmacokinetic property has not been fully studied.
The ADA-SCID is caused by the presence of mutations in the ADA gene which is responsible for the synthesis of adenosine deaminase. This enzyme is found throughout the body but it is mainly active in lymphocytes. The normal function of adenosine deaminase is to eliminate deoxyadenosine, created when DNA is degraded, by converting it into deoxyinosine. This degradation process is very important as deoxyadenosine is cytotoxic, especially for lymphocytes. Immature lymphocytes are particularly vulnerable as deoxyadenosine kills them before maturation making them unable to produce their immune function. Therefore, based on the causes of ADA-SCID, elapegademase works by supplementing the levels of adenosine deaminase. Being a recombinant and an _E. coli_-produced molecule, the use of this drug eliminates the need to source the enzyme from animals, as it was previously.