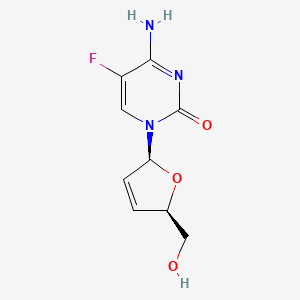

1. 2',3'-dideoxy-2',3'-didehydro-5-fluorocytidine
2. 2',3'-dideoxy-2',3'-didehydro-beta-d-5-fluorocytidine
3. 2',3'-dideoxy-2',3'-didehydro-beta-l-5-fluorocytidine
4. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1-((2s,5r)-2,5-dihydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furanyl)-5-fluoro-
5. 4-amino-5-fluoro-1-((2s,5r)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)pyrimidin-2(1h)-one
6. Ach-126-443
7. Beta-d-d4fc
8. Beta-l-fd4c
9. D-d4fc
10. Dexelvucitabine
11. Dpc 817
12. Dpc-817
13. Dpc817
14. Incb-8721
15. L-d4fc
16. Reverset
1. 181785-84-2
2. Beta-l-fd4c
3. L-fd4c
4. .beta.-l-fd4c
5. Ach-126,443
6. L-f-d4c
7. Ach-126443
8. L-d4fc
9. 4-amino-5-fluoro-1-((2s,5r)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)pyrimidin-2(1h)-one
10. 4-amino-5-fluoro-1-[(2s,5r)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one
11. M09buf90c0
12. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1-((2s,5r)-2,5-dihydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furanyl)-5-fluoro-
13. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1-[(2s,5r)-2,5-dihydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furanyl]-5-fluoro-
14. Elvucitabine [usan]
15. Elvucitabine [usan:inn]
16. Unii-m09buf90c0
17. Ach 126443
18. Ach 126,443
19. B-l-fd4c
20. Elvucitabine (usan/inn)
21. Elvucitabine [inn]
22. Chembl38700
23. (-)fd4c
24. Schembl1649928
25. Zinc7048
26. Beta-l-2',3'-dideoxy-2',3'-didehydro-5-fluorocytidine
27. Dtxsid20171185
28. Bdbm50421604
29. Db06236
30. Hy-117582
31. Cs-0066557
32. A14435
33. D03981
34. J-011630
35. Q1334337
36. .beta.-l-2',3'-didehydro-2',3'-dideoxy-5-fluorocytidine
37. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1-(2,5-dihydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furanyl)-5-fluoro-, (2s-cis)-
| Molecular Weight | 227.19 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H10FN3O3 |
| XLogP3 | -1.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 227.07061935 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 227.07061935 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 88.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 405 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in hepatitis (viral, B) and HIV infection.
Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Inhibitors of reverse transcriptase (RNA-DIRECTED DNA POLYMERASE), an enzyme that synthesizes DNA on an RNA template. (See all compounds classified as Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors.)
Anti-HIV Agents
Agents used to treat AIDS and/or stop the spread of the HIV infection. These do not include drugs used to treat symptoms or opportunistic infections associated with AIDS. (See all compounds classified as Anti-HIV Agents.)
Elvucitabine is a L-cytosine Nucleoside analog Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor (NRTIs) anti-HIV drug. NRTI's inhibit the activity of viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase (i.e., reverse transcriptase). It is believed that inhibition of reverse transcriptase interferes with the generation of DNA copies of viral RNA, which, in turn, are necessary for synthesis of new virions. Intracellular enzymes subsequently eliminate the HIV particle that previously had been uncoated, and left unprotected, during entry into the host cell. Thus, reverse transcriptase inhibitors are virustatic and do not eliminate HIV from the body.