


1. Dihydrochloride, Emetine
2. Emetine
3. Emetine Dihydrochloride
4. Hydrochloride, Emetine
5. Ipecine
6. Methylcephaeline
1. 14198-59-5
2. Mls000028478
3. Cephaeline Methyl Ether Hydrochloride
4. Emetine (hydrochloride)
5. Smr000058444
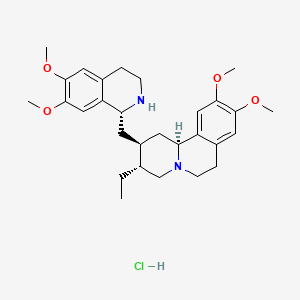
6. (2s,3r,11bs)-2-[[(1r)-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-1-yl]methyl]-3-ethyl-9,10-dimethoxy-2,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-1h-benzo[a]quinolizine;hydrochloride
7. Nsc33669
8. Nsc-33669
9. Emetinal
10. Erketin
11. Encol
12. Emetinehydrochloride
13. Emetine, Hydrochloride
14. Emetine Monohydrochloride
15. Opera_id_1460
16. Cephaeline Methyl Ether Hcl
17. Schembl636599
18. Chembl513000
19. Niosh/jy5800000
20. Hy-b1479c
21. Dtxsid80424947
22. Nsc752340
23. S3233
24. Akos024374935
25. Nsc-752340
26. Cs-0103259
27. Jy58000000
28. Emetan,7',10,11-tetramethoxy-, Dihydrochloride
29. Q-100155
30. 2h-benzo[a]quinolizine,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-9,10-dimethoxy-2-[(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-1-isoquinolyl)methyl]-, Dihydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 517.1 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H41ClN2O4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 516.2754855 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 516.2754855 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 52.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 679 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Amebicides
Agents which are destructive to amebae, especially the parasitic species causing AMEBIASIS in man and animal. (See all compounds classified as Amebicides.)
Antinematodal Agents
Substances used in the treatment or control of nematode infestations. They are used also in veterinary practice. (See all compounds classified as Antinematodal Agents.)
Cathartics
Agents that are used to stimulate evacuation of the bowels. (See all compounds classified as Cathartics.)
Emetics
Agents that cause vomiting. They may act directly on the gastrointestinal tract, bringing about emesis through local irritant effects, or indirectly, through their effects on the chemoreceptor trigger zone in the postremal area near the medulla. (See all compounds classified as Emetics.)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds which inhibit the synthesis of proteins. They are usually ANTI-BACTERIAL AGENTS or toxins. Mechanism of the action of inhibition includes the interruption of peptide-chain elongation, the blocking the A site of ribosomes, the misreading of the genetic code or the prevention of the attachment of oligosaccharide side chains to glycoproteins. (See all compounds classified as Protein Synthesis Inhibitors.)