

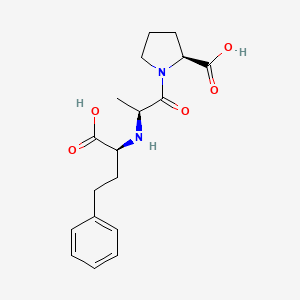

1. 1-(n-((s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-l-alanyl)-l-proline Dihydrate
2. Enalaprilat Anhydrous
3. Enalaprilat Citrate, Anhydrous
4. Enalaprilat Dihydrate
5. Enalaprilat, (r)-isomer, Anhydrous
6. Enalaprilic Acid
7. Mk 422
8. Mk-422
9. Mk422
10. Pres Iv
11. Vasotec
12. Xanef
1. 76420-72-9
2. Enalapril Acid
3. Enalaprilate
4. Enalaprilatum
5. Enalaprilic Acid
6. Enalaprilat Anhydrous
7. Enalapril Diacid
8. Enalaprilat (anhydrous)
9. (s)-1-((s)-2-(((s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)amino)propanoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid
10. N-[(1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-l-alanyl-l-proline
11. Mk-422
12. Enalaprilat [inn]
13. Chebi:4786
14. Q508q118jm
15. 1-((2s)-2-{[(1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino}propanoyl)-l-proline
16. ((s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-l-alanyl-l-proline
17. Eal
18. L-proline, N-((1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-l-alanyl-
19. L-proline, N-[(1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-l-alanyl-
20. Enalaprilat Inhibitor
21. (2s)-1-[(2s)-2-[[(1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid
22. Smr000466359
23. Enalaprilat [spanish]
24. Mk 421 Diacid
25. Chembl577
26. Enalaprilate [french]
27. Enalaprilatum [latin]
28. Mk 422
29. Unii-q508q118jm
30. Enalaprilat,(s)
31. (s)-1-((s)-2-((s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropylamino)propanoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid
32. (2s)-1-((2s)-2-(((1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)amino)propanoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid
33. (2s)-1-[(2s)-2-{[(1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino}propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid
34. Einecs 278-459-3
35. Mfcd00865786
36. Schembl37289
37. (2s)-1-[(2s)-2-[[(2s)-1-hydroxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid
38. Mls000759476
39. Mls001424138
40. Bidd:gt0752
41. Gtpl6332
42. N-(1(s)-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-l-alanyl-l-proline
43. Enalaprilat, Analytical Standard
44. Dtxsid0048975
45. Hy-b0231a
46. Hms2051h16
47. Hms2089p04
48. Hms2232b19
49. Hms3263o13
50. Pharmakon1600-01503833
51. Zinc3812851
52. Tox21_501036
53. Bdbm50367254
54. Nsc760053
55. Akos015840130
56. Akos015892570
57. Ccg-101042
58. Db09477
59. Lp01036
60. Nc00292
61. Sdccgsbi-0633781.p001
62. Ncgc00164593-01
63. Ncgc00164593-11
64. Ncgc00261721-01
65. As-13013
66. Cs-0012359
67. E1302
68. Ab00698268-05
69. Ab00698268-07
70. Ab00698268-08
71. Ab00698268_09
72. Ab00698268_10
73. Enalapril Diacid Dihydrate Anhydrous [mi]
74. 420e729
75. Enalapril Maleate Impurity C [ep Impurity]
76. Sr-01000763426
77. Q5375179
78. Sr-01000763426-3
79. W-104365
80. N-[(s)-1-carboxy-3-phenyl-propyl]-l-alanyl-l-proline
81. 1-(n-((s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-l-alanyl)-l-proline
82. L-proline, 1-(n-(1-carboxt-3-phenylpropyl)-l-alanyl)-, (s)-
83. L-proline, 1-(n-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-l-alanyl)-, (s)-
84. (s)-1-((s)-2-(((s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)amino)propanoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylicacid
85. (2s)-1-[(2s)-2-[[(1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid (enalaprilat)
| Molecular Weight | 348.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H24N2O5 |
| XLogP3 | -0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 348.16852187 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 348.16852187 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 107 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 490 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Enalaprilat |
| PubMed Health | Enalaprilat (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent, Renal Protective Agent |
| Drug Label | Enalaprilat injection USP is a sterile aqueous solution for intravenous administration. Enalaprilat is an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. It is chemically described as (S)-1-[N-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-alanyl]-L-proline dihydrate. Its st... |
| Active Ingredient | Enalaprilat |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1.25mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bedford; Hospira; Hikma Farmaceutica; Teva Pharms Usa |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Enalaprilat |
| PubMed Health | Enalaprilat (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent, Renal Protective Agent |
| Drug Label | Enalaprilat injection USP is a sterile aqueous solution for intravenous administration. Enalaprilat is an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. It is chemically described as (S)-1-[N-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-alanyl]-L-proline dihydrate. Its st... |
| Active Ingredient | Enalaprilat |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1.25mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bedford; Hospira; Hikma Farmaceutica; Teva Pharms Usa |
Enalaprilat injection is indicated for the treatment of hypertension when oral therapy is not practical.
FDA Label
Enalaprilat injection results in the reduction of both supine and standing systolic and diastolic blood pressure, usually with no orthostatic component. Symptomatic postural hypotension is therefore infrequent, although it might be anticipated in volume-depleted patients. The onset of action usually occurs within fifteen minutes of administration with the maximum effect occurring within one to four hours. The abrupt withdrawal of enalaprilat has not been associated with a rapid increase in blood pressure. The duration of hemodynamic effects appears to be dose-related. However, for the recommended dose, the duration of action in most patients is approximately six hours. Following administration of enalapril, there is an increase in renal blood flow; glomerular filtration rate is usually unchanged. The effects appear to be similar in patients with renovascular hypertension.
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
A class of drugs whose main indications are the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. They exert their hemodynamic effect mainly by inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system. They also modulate sympathetic nervous system activity and increase prostaglandin synthesis. They cause mainly vasodilation and mild natriuresis without affecting heart rate and contractility. (See all compounds classified as Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Absorption
Enalaprilat is poorly absorbed following oral administration, and is therefore only available as an intravenous injection.
Route of Elimination
Excretion of enalaprilat is primarily renal with more than 90 percent of an administered dose recovered in the urine as unchanged drug within 24 hours.
Clearance
The disposition of enalaprilat in patients with renal insufficiency is similar to that in patients with normal renal function until the glomerular filtration rate is 30 mL/min or less. Renal clearance was 158 47 ml/min.
Both enalapril and enalaprilat undergo renal excretion without further metabolism.
11 hr
Enalaprilat is the active metabolite of the orally available pro-drug, enalapril. Used in the treatment of hypertension, enalapril is an ACE inhibitor that prevents Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) from transforming angiotensin I into angiotensin II. As angiotensin II is responsible for vasoconstriction and sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the kidney, down-regulation of this protein results in reduced blood pressure and blood fluid volume