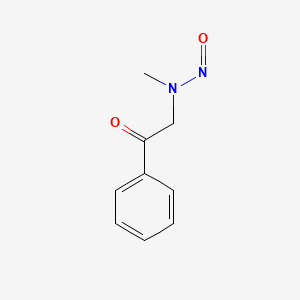

1. Endostatins
1. N-methyl-n-phenacylnitrous Amide
2. 55984-52-6
3. 187888-07-9
4. Ethanone, 2-(methylnitrosoamino)-1-phenyl-
5. 2-oxo-2-phenylethylmethylnitrosamine
6. Dtxsid10204557
7. Zinc5965474
| Molecular Weight | 178.19 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H10N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 178.074227566 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 178.074227566 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 188 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in cancer/tumors (unspecified), macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy.
Angiogenesis Inhibitors
Agents and endogenous substances that antagonize or inhibit the development of new blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Angiogenesis Inhibitors.)
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Endostatin is an endogenous antitumor protein. Endostatin is a 20-kDa C-terminal fragment derived from type XVIII collagen which inhibits cell proliferation and migration, and induces endothelial cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. It is proposed that endostatin's effects are due to inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) tyrosine phosphorylation of KDR/F1k-1 (VEGF receptor 2), the cell surface receptor for VEGF. VEGF is an important mediator of angiogensis. Endostatin additionally blocks activation of extracellular signal related kinases, or ERK, protein 38 mitogen activated protein kinase, or p38 MAPK (signal transduction pathways involving kinases that couple growth factors to cell surface receptors), as well as focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK). Studies are being done to determine if endostatin has possible impact on other pathways, and may also target E-selectin and block activity of metalloproteinases 2, 9 and 13. There is further research into a possible mechanistic link involving endostatin's angiogenic and zinc binding ability.