


1. At 2266
2. At-2266
3. At2266
4. Ci 919
5. Ci-919
6. Ci919
7. Enoxacin Sesquihydrate
8. Enoxin
9. Enoxor
10. Pd 107779
11. Pd-107779
12. Pd107779
13. Penetrex
14. Sesquihydrate, Enoxacin
1. 74011-58-8
2. Penetrex
3. Enoxacine
4. Comprecin
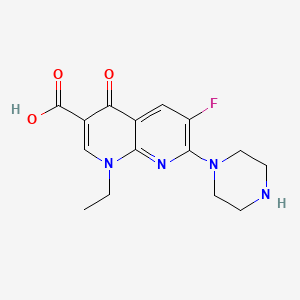
5. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
6. At-2266
7. Bactidan
8. Enoxacino
9. Enoxacinum
10. Flumark
11. Enoxor
12. Ci-919
13. Almitil
14. Pd 107779
15. Ci 919
16. Enoxacin (penetrex)
17. Pd-107779
18. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
19. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
20. Nsc 629661
21. Enoxacin (hydrate)
22. Chebi:157175
23. Chembl826
24. Nsc-629661
25. Nsc-758416
26. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-[1,8]naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
27. Enoram
28. Enoxin
29. 325ogw249p
30. Nsc629661
31. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid, 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-
32. At 2266;ci 919
33. Enoxacine [french]
34. Enoxacinum [latin]
35. Enofloxacin
36. Ncgc00016927-01
37. Enoxacino [spanish]
38. Enoksetin
39. Cas-74011-58-8
40. Dsstox_cid_2984
41. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-
42. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
43. Dsstox_rid_76818
44. Dsstox_gsid_22984
45. Enoxacin Sesquihydrate;at-2266 Hydrate;ci-919 Hydrate
46. Bactidron
47. Enoxen
48. Penetrex (tn)
49. Smr000058233
50. Ccris 5242
51. Enoxacin (usan/inn)
52. Sr-01000000202
53. Nsc 627409
54. At 2266
55. Brn 3628995
56. Pd107779
57. Abenox
58. Unii-325ogw249p
59. Enoxacin [usan:inn:ban:jan]
60. Enx
61. Prestwick_708
62. Mfcd00133308
63. Spectrum_001539
64. Enoxacin [usan]
65. Enoxacin [inn]
66. Enoxacin [mi]
67. Enoxacin [vandf]
68. Prestwick0_000353
69. Prestwick1_000353
70. Prestwick2_000353
71. Prestwick3_000353
72. Spectrum2_001731
73. Spectrum3_001570
74. Spectrum4_000166
75. Spectrum5_001044
76. E0762
77. Enoxacin [mart.]
78. Enoxacin [who-dd]
79. Epitope Id:119069
80. Oprea1_147866
81. Schembl33963
82. Bspbio_000445
83. Bspbio_003080
84. Enoxacin, Analytical Standard
85. Kbiogr_000651
86. Kbioss_002019
87. Mls000069645
88. Mls006011976
89. Bidd:gt0191
90. Divk1c_000420
91. Spectrum1503215
92. Spbio_001802
93. Spbio_002366
94. Enoxacin [orange Book]
95. Bpbio1_000491
96. Gtpl8882
97. Dtxsid5022984
98. Bcbcmap01_000009
99. Hms501e22
100. Kbio1_000420
101. Kbio2_002019
102. Kbio2_004587
103. Kbio2_007155
104. Kbio3_002580
105. Ninds_000420
106. Hms1569g07
107. Hms1922i17
108. Hms2090e10
109. Hms2092n20
110. Hms2233k20
111. Hms3372a12
112. Hms3655m08
113. Hms3715h13
114. Pharmakon1600-01503215
115. Bcp22623
116. Hy-b0268
117. Tox21_110688
118. Bdbm50296358
119. Ccg-39452
120. Enoxacin 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
121. Nsc758416
122. S1756
123. Zinc19594549
124. Akos015838626
125. Tox21_110688_1
126. Db00467
127. Ks-5190
128. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazinylhydropyridino[2,3-b]pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
129. Enoxacin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
130. Idi1_000420
131. Smp1_000113
132. Ncgc00016927-02
133. Ncgc00016927-03
134. Ncgc00016927-04
135. Ncgc00016927-05
136. Ncgc00016927-06
137. Ncgc00016927-07
138. Ncgc00016927-08
139. Ncgc00016927-10
140. Ncgc00016927-11
141. Ncgc00023864-03
142. Ncgc00023864-04
143. Ncgc00178309-01
144. Ncgc00178309-02
145. Nci60_009618
146. Sbi-0051788.p002
147. Db-055829
148. Ft-0630825
149. Sw196857-3
150. C06979
151. D00310
152. 1, 6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro- 4-oxo-7-piperazinyl
153. Ab00052328-09
154. Ab00052328_10
155. Ab00052328_11
156. 011e588
157. A837996
158. Q1639616
159. Sr-01000000202-2
160. Sr-01000000202-3
161. Brd-k78113049-001-05-5
162. Brd-k78113049-001-07-1
163. Brd-k78113049-001-12-1
164. Z1551429746
165. 1-ethyl-6-fluoranyl-4-oxidanylidene-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
166. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydro[1,8]naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
167. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
168. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid, 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)
| Molecular Weight | 320.32 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H17FN4O3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 320.12846858 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 320.12846858 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 85.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 521 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of adults (≥18 years of age) with the following infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms: (1) uncomplicated urethral or cervical gonorrhea due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae, (2) uncomplicated urinary tract infections (cystitis) due to Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus epidermidis, or Staphylococcus saprophyticus, and (3) complicated urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, or Enterobacter cloacae.
Enoxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Enoxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Enoxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Enoxacin may be active against pathogens resistant to drugs that act by different mechanisms.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Drugs and compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of CYTOCHROME P-450 CYP1A2. (See all compounds classified as Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA04 - Enoxacin
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed following oral administration, with an absolute oral bioavailability of approximately 90%.
Hepatic. Some isozymes of the cytochrome P-450 hepatic microsomal enzyme system are inhibited by enoxacin. After a single dose, greater than 40% was recovered in urine by 48 hours as unchanged drug.
Plasma half-life is 3 to 6 hours.
Enoxacin exerts its bactericidal action via the inhibition of the essential bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase (DNA Topoisomerase II).
