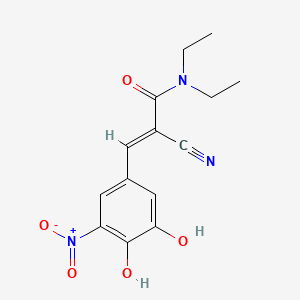

1. 2-cyano-n,n-diethyl-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)propenamide
2. Comtan
3. Comtess
4. Or 611
5. Or-611
1. 130929-57-6
2. Comtess
3. Comtan
4. Entacaponum
5. Or-611
6. Entacapona
7. (e)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethylacrylamide
8. 116314-67-1
9. Entacapone Teva
10. Entacapone Orion
11. (e)-alpha-cyano-n,n-diethyl-3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrocinnamamide
12. (e)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethylprop-2-enamide
13. (2e)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethylprop-2-enamide
14. Chembl953
15. 2-propenamide, 2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethyl-
16. Chebi:4798
17. 2-cyano-n,n-diethyl-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)propenamide
18. N,n-diethyl-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl) Acrylamide
19. 4975g9nm6t
20. (2e)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethyl-2-propenamide
21. Entacaponum [inn-latin]
22. Entacapone Sodium
23. Entacapona [inn-spanish]
24. Ncgc00164555-01
25. Entacom
26. 2-propenamide, 2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethyl-, (2e)-
27. Dsstox_cid_26439
28. Dsstox_rid_81615
29. Dsstox_gsid_46439
30. Or 611
31. (e)-entacapone
32. (~{e})-2-cyano-~{n},~{n}-diethyl-3-[3-nitro-4,5-bis(oxidanyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide
33. Comtan (tn)
34. Cas-130929-57-6
35. Sr-05000001452
36. (e)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitro-phenyl)-n,n-diethyl-prop-2-enamide
37. Unii-4975g9nm6t
38. Com-998
39. Entacapone [usan:usp:inn:ban]
40. Entacapone [mi]
41. Entacapone [inn]
42. Entacapone [jan]
43. Entacapone [usan]
44. (e)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethyl-2-propenamide
45. Entacapone [vandf]
46. Entacapone [mart.]
47. Entacapone [usp-rs]
48. Entacapone [who-dd]
49. Schembl34504
50. Schembl34505
51. Bidd:gt0026
52. Entacapone [ema Epar]
53. 2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethyl-2-propenamide
54. Entacapone (jp17/usp/inn)
55. Gtpl6647
56. Dtxsid5046439
57. Entacapone [orange Book]
58. Schembl13596593
59. Hsdb 8251
60. Entacapone [ep Monograph]
61. Entacapone [usp Monograph]
62. Hms2089o16
63. Hms3713b20
64. Hms3885k09
65. Or611
66. Stalevo Component Entacapone
67. Corbilta Component Entacapone
68. Ex-a1130
69. Tox21_112184
70. Ac-393
71. Bdbm50108879
72. Mfcd00866580
73. S3147
74. Zinc35342787
75. Akos015907685
76. Akos015965009
77. Entacapone Component Of Stalevo
78. Tox21_112184_1
79. Bcp9000645
80. Ccg-213064
81. Cs-1266
82. Db00494
83. Entacapone Component Of Corbilta
84. Ncgc00164555-02
85. Ncgc00164555-03
86. Ncgc00164555-10
87. Hy-14280
88. E0961
89. Sw199035-2
90. C07943
91. D00781
92. Ab01275450-01
93. Ab01275450_02
94. Ab01275450_03
95. 929e576
96. A806167
97. A922031
98. Q416444
99. J-005902
100. J-008069
101. Sr-05000001452-1
102. Sr-05000001452-2
103. Sr-05000001452-3
104. Brd-k83636919-001-01-4
105. Levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone Orion Component Entacapone
106. (e)-n,n-diethyl-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)acrylamide
107. Entacapone Component Of Levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone Orion
108. (e)-.alpha.-cyano-n,n-diethyl-3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrocinnamamide
109. (e)-n, N-diethyl-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)acrylamide
110. (e)-2-cyano-n,n-diethyl-3-[3-nitro-4,5-bis(oxidanyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide
111. 2-propenamide,2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-n,n-diethyl-,(2e)-
112. Pd9
| Molecular Weight | 305.29 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H15N3O5 |
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 305.10117059 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 305.10117059 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 130 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 500 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Comtan |
| PubMed Health | Entacapone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiparkinsonian |
| Drug Label | Comtan (entacapone) is available as tablets containing 200-mg entacapone.Entacapone is an inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), used in the treatment of Parkinson's Disease as an adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa therapy. It is a nitrocatec.. |
| Active Ingredient | Entacapone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Orion Pharma |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Entacapone |
| PubMed Health | Entacapone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiparkinsonian |
| Drug Label | Entacapone is available as tablets containing 200-mg entacapone.Entacapone is an inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), used in the treatment of Parkinsons Disease as an adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa therapy. It is a nitrocatechol struc... |
| Active Ingredient | Entacapone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Wockhardt; Sun Pharma Global |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Comtan |
| PubMed Health | Entacapone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiparkinsonian |
| Drug Label | Comtan (entacapone) is available as tablets containing 200-mg entacapone.Entacapone is an inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), used in the treatment of Parkinson's Disease as an adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa therapy. It is a nitrocatec.. |
| Active Ingredient | Entacapone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Orion Pharma |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Entacapone |
| PubMed Health | Entacapone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiparkinsonian |
| Drug Label | Entacapone is available as tablets containing 200-mg entacapone.Entacapone is an inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), used in the treatment of Parkinsons Disease as an adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa therapy. It is a nitrocatechol struc... |
| Active Ingredient | Entacapone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Wockhardt; Sun Pharma Global |
Antiparkinson Agents; Enzyme Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Entacapone. Online file (MeSH, 2015). Available from, as of May 1, 2015: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health(NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Entacapone is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of July 18, 2015: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search/intervention=entacapone
Comtan is indicated as an adjunct to levodopa and carbidopa to treat end-of-dose "wearing-off" in patients with Parkinson's disease. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Comtan (Entacapone) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 4, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=b1aceb59-9be8-43b8-83d6-81e05e4b51e4
Stalevo, a combination drug consisting of levodopa, carbidopa (dopa decarboxylase inhibitor), and entacapone (catechol-O-methyltransferase-COMT inhibitor) is indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Stalevo can be used: to substitute (with equivalent strengths of each of the three components) carbidopa/levodopa and entacapone previously administered as individual products. To replace carbidopa/levodopa therapy (without entacapone) when patients experience the signs and symptoms of end-of-dose "wearing-off" and when they have been taking a total daily dose of levodopa of 600 mg or less and have not been experiencing dyskinesias. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Stalevo (Carbidopa, Levodopa and Entacapone) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2014). Available from, as of May 4, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5edfc3e7-f80d-47ee-897a-c02ff4eb3e74
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a variety of motor symptoms including freezing of gait (FOG), in which walking is transiently halted as if the patient's feet were 'glued to the ground'. Treatment of FOG is still challenging. Although L-threo-3,4-dihydroxyphenylserine (L-DOPS), a precursor of noradrenaline, has been on the market in Japan because of its beneficial effect for FOG, clinical use of L-DOPS has been far from satisfying. However, the fact that there were some responders to L-DOPS encouraged us to hypothesize that the enhancement of L-DOPS concentration in the brain by the co-administration of L-DOPS and a catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibitor, which is expected to interrupt L-DOPS metabolism in the peripheral circulation, would be beneficial for FOG. Based on our hypothesis, we conducted a preliminary study with a small number of participants with FOG. Of the 16 PD patients with FOG who completed this study, group 1 (n=6) received L-DOPS co-administered with entacapone, which is a COMT inhibitor used worldwide as an anti-parkinson drug, group 2 (n=5) received entacapone alone, and group 3 (n=5) received L-DOPS alone. Only the patients in group 1 showed a significant improvement in FOG. Moreover, the beneficial effect was observed only in patients with levodopa-resistant FOG. This result supports our hypothesis, at least in patients with levodopa-resistant FOG, and shows that the co-administration of L-DOPS and entacapone could be a new strategy for FOG treatment.
PMID:23265352 Fukada K et al; Med Hypotheses 80 (2): 209-12 (2013)
Diarrhea was reported in 10% of patients receiving entacapone in clinical studies, and about 2% of patients required discontinuance of the drug because of diarrhea. Diarrhea generally was of mild to moderate intensity, but severe diarrhea, which required hospitalization, may occur rarely. Diarrhea generally occurs during the first 4-12 weeks of entacapone therapy, but may occur as early as the first week or as late as several months following initiation of entacapone therapy. Diarrhea generally resolved following discontinuance of the drug.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2649
Findings from an FDA-conducted meta-analysis suggest that patients receiving combined therapy with levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone may be at increased risk of cardiovascular events (i.e., myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular death) compared with those receiving levodopa-carbidopa. The meta-analysis combined cardiovascular-related findings from 15 clinical trials that compared the combination of levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone with levodopa-carbidopa and found a small but statistically significant increase in the risk of cardiovascular events in those receiving the levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone regimen (relative risk: 2.46). However, the increased risk was driven largely by data from a single trial (STRIDE-PD); when this trial was removed from the analysis, the results were no longer significant. Various factors make it difficult to draw firm conclusions from this meta-analysis. Many of the trials included in the analysis had a duration of less than 6 months (possibly not long enough to detect cardiovascular risk) and were not specifically designed to evaluate cardiovascular safety. In addition, the majority of patients had preexisting cardiovascular risk factors. At this time, FDA has not concluded that combined therapy with levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events and is continuing to review the available data related to this safety concern. Patients currently receiving entacapone as an adjunct to levodopa-carbidopa (either separately or as a fixed-combination preparation) should continue to take the drugs as prescribed unless otherwise instructed by a clinician. Cardiac function should be monitored regularly in such patients, particularly in those with a history of cardiovascular disease.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2648
Dopaminergic therapy in Parkinson's disease patients has been associated with orthostatic hypotension. Entacapone enhances levodopa bioavailability and, therefore, might be expected to increase the occurrence of orthostatic hypotension. In controlled studies, approximately 1.2% and 0.8% of 200 mg entacapone and placebo patients, respectively, reported at least one episode of syncope. Reports of syncope were generally more frequent in patients in both treatment groups who had an episode of documented hypotension.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Comtan (Entacapone) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 4, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=b1aceb59-9be8-43b8-83d6-81e05e4b51e4
Postmarketing reports indicate that patients may experience new or worsening mental status and behavioral changes, which may be severe, including psychotic-like behavior during Comtan treatment or after starting or increasing the dose of Comtan. Other drugs prescribed to improve the symptoms of Parkinson's disease can have similar effects on thinking and behavior. Abnormal thinking and behavior can cause paranoid ideation, delusions, hallucinations, confusion, disorientation, aggressive behavior, agitation, and delirium. Psychotic-like behaviors were also observed during the clinical development of Comtan. Patients with a major psychotic disorder should ordinarily not be treated with Comtan because of the risk of exacerbating psychosis. In addition, certain medications used to treat psychosis may exacerbate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and may decrease the effectiveness of Comtan.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Comtan (Entacapone) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 4, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=b1aceb59-9be8-43b8-83d6-81e05e4b51e4
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ENTACAPONE (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used as an adjunct to levodopa / carbidopa in the symptomatic treatment of patients with idiopathic Parkinson's Disease who experience the signs and symptoms of end-of-dose "wearing-off".
FDA Label
Entacapone is indicated as an adjunct to standard preparations of levodopa / benserazide or levodopa / carbidopa for use in adult patients with Parkinson's disease and end-of-dose motor fluctuations, who cannot be stabilised on those combinations.
Entacapone is indicated as an adjunct to standard preparations of levodopa / benserazide or levodopa / carbidopa for use in patients with Parkinson's disease and end-of-dose motor fluctuations, who cannot be stabilised on those combinations.
Entacapone is indicated as an adjunct to standard preparations of levodopa / benserazide or levodopa / carbidopa for use in adult patients with Parkinson's disease and end-of-dose motor fluctuations, who cannot be stabilised on those combinations.
Entacapone is indicated as an adjunct to standard preparations of levodopa / benserazide or levodopa / carbidopa for use in adult patients with Parkinson's disease and end-of-dose motor fluctuations, who cannot be stabilised on those combinations.
Entacapone is structurally and pharmacologically related to tolcapone, but unlike tolcapone, is not associated with hepatotoxicity. Entacapone is used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease as an adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa therapy. Entacapone selectively and reversiblly inhibits catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). In mammals, COMT is distributed throughout various organs with the highest activities in the liver and kidney. COMT also occurs in the heart, lung, smooth and skeletal muscles, intestinal tract, reproductive organs, various glands, adipose tissue, skin, blood cells and neuronal tissues, especially in glial cells. COMT catalyzes the transfer of the methyl group of S-adenosyl-L-methionine to the phenolic group of substrates that contain a catechol structure. Physiological substrates of COMT include dopa, catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine) and their hydroxylated metabolites. The function of COMT is the elimination of biologically active catechols and some other hydroxylated metabolites. COMT is responsible for the elimination of biologically active catechols and some other hydroxylated metabolites. In the presence of a decarboxylase inhibitor, COMT becomes the major metabolizing enzyme for levodopa, catalyzing the it to 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-L-phenylalanine (3-OMD) in the brain and periphery.
Catechol O-Methyltransferase Inhibitors
Compounds and drugs that inhibit or block the activity of CATECHOL O-METHYLTRANSFERASE enzymes. Drugs in this class are used in management of central nervous system disorders such as PARKINSON DISEASE. (See all compounds classified as Catechol O-Methyltransferase Inhibitors.)
Antiparkinson Agents
Agents used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The most commonly used drugs act on the dopaminergic system in the striatum and basal ganglia or are centrally acting muscarinic antagonists. (See all compounds classified as Antiparkinson Agents.)
N04BX02
N04BX02
N04BX02
N04BX02
N - Nervous system
N04 - Anti-parkinson drugs
N04B - Dopaminergic agents
N04BX - Other dopaminergic agents
N04BX02 - Entacapone
Absorption
Entacapone is rapidly absorbed (approximately 1 hour). The absolute bioavailability following oral administration is 35%.
Route of Elimination
Entacapone is almost completely metabolized prior to excretion, with only a very small amount (0.2% of dose) found unchanged in urine. As only about 10% of the entacapone dose is excreted in urine as parent compound and conjugated glucuronide, biliary excretion appears to be the major route of excretion of this drug.
Volume of Distribution
20 L
Clearance
850 mL/min
In rats and in humans, the absolute bioavailability was dose-dependent and ranged from 20% to 55%, following single dose of 10, 65 and 400 mg/kg, in rats and from 29% to 49%, following single dose of 5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 and 800 mg, in humans.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Comtan (Entacapone), Scientific Discussion p.4 (2005). Available from, as of June 5, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000171/WC500033075.pdf
Absorption of unchanged entacapone after single oral administration is quite rapid both in rats and in dogs. Two peaks in plasma concentrations, occurring at 5-15 minutes and at 3-5 hours post dose, were found in rats indicating that entacapone is subject to enterohepatic circulation and a single peak at 3 hours was found in dogs. A transformation of entacapone to its (Z)-isomer took place in both species studied, the transformation being minimal in rats but quite noticeable in dogs.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Comtan (Entacapone), Scientific Discussion p.4 (2005). Available from, as of June 5, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000171/WC500033075.pdf
/MILK/ In animal studies, entacapone was excreted into maternal rat milk.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Comtan (Entacapone) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 4, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=b1aceb59-9be8-43b8-83d6-81e05e4b51e4
In rats and dogs, entacapone metabolites are predominantly excreted in the feces (two thirds as glucuronide or sulfate conjugates) and one third in the urine with less than 1.5% of the dose as unchanged entacapone. After the first hour 30-45% of the dose was recovered in the bile, with an enterohepatic circulation accounting for about 10% of the given radioactivity.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Comtan (Entacapone), Scientific Discussion p.4 (2005). Available from, as of June 5, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000171/WC500033075.pdf
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ENTACAPONE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Metabolized via isomerization to the cis-isomer, followed by direct glucuronidation of the parent and cis-isomer.
In rats and dogs, entacapone metabolites are predominantly excreted in the feces (two thirds as glucuronide or sulfate conjugates) and one third in the urine with less than 1.5% of the dose as unchanged entacapone. After the first hour 30-45% of the dose was recovered in the bile, with an enterohepatic circulation accounting for about 10% of the given radioactivity.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Comtan (Entacapone), Scientific Discussion p.4 (2005). Available from, as of June 5, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000171/WC500033075.pdf
Entacapone is extensively metabolised in the liver in all species including humans, the main metabolic pathway being glucuronidation, sulfation and isomerisation from (E)- to (Z)-isomer (active metabolite). Similar pathways across species are the reduction of the C-C double bond of the side chain (less important in rat and in man) and the hydrolysis to 3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde. The dissimilarities consists of amide N-dealkylation, nitro reduction and O-methylation (only in rats), amide hydrolysis and nitrile hydrolysis (only in dogs) and oxidative hydrolysis of one of the ethyl groups of the diethylamide group (only in man).
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Comtan (Entacapone), Scientific Discussion p.4 (2005). Available from, as of June 5, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000171/WC500033075.pdf
Entacapone is almost completely metabolized prior to excretion, with only a very small amount (0.2% of dose) found unchanged in urine. The main metabolic pathway is isomerization to the cis-isomer, followed by direct glucuronidation of the parent and cis-isomer; the glucuronide conjugate is inactive.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Comtan (Entacapone) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 4, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=b1aceb59-9be8-43b8-83d6-81e05e4b51e4
Entacapone undergoes extensive metabolism, mainly in the liver. The main metabolic pathway of entacapone in humans is the isomerization to the cis-isomer, followed by direct glucuronidation of the parent and cis-isomer; the glucuronide conjugate is inactive.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Comtan (Entacapone), Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02243763 (Date of Revision: November 18, 2013). Available from, as of June 5, 2015: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
Entacapone has known human metabolites that include Entacapone 3-o-glucuronide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
0.4-0.7 hour
The elimination of entacapone is biphasic, with an elimination half-life of 0.4 hour to 0.7 hour based on the beta-phase and 2.4 hours based on the gamma-phase.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Comtan (Entacapone) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 4, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=b1aceb59-9be8-43b8-83d6-81e05e4b51e4
The overall elimination half-life of entacapone ranged from 30 minutes to 1 hour in dogs and from 1.5 to 3 hours in man.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Comtan (Entacapone), Scientific Discussion p.4 (2005). Available from, as of June 5, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000171/WC500033075.pdf
The mechanism of action of entacapone is believed to be through its ability to inhibit COMT in peripheral tissues, altering the plasma pharmacokinetics of levodopa. When entacapone is given in conjunction with levodopa and an aromatic amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor, such as carbidopa, plasma levels of levodopa are greater and more sustained than after administration of levodopa and an aromatic amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor alone. It is believed that at a given frequency of levodopa administration, these more sustained plasma levels of levodopa result in more constant dopaminergic stimulation in the brain, leading to a greater reduction in the manifestations of parkinsonian syndrome.
Comtan (entacapone) is a reversible, selective and mainly peripherally acting inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). Comtan has no antiparkinsonian effect of its own and is designed for concomitant administration with levodopa preparations. COMT catalyzes the transfer of the methyl group of S-adenosyl-L-methionine to the phenolic group of substrates that contain a cathecol structure. Physiological substrates of COMT include dopa, catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine) and their hydroxylated metabolites. In the presence of a dopa decarboxylase (DDC) inhibitor, COMT becomes the major enzyme which is responsible for the metabolism of levodopa to 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-l-phenylalanine (3-OMD). The mechanism of action of entacapone is believed to be related to its ability to inhibit COMT and thereby alter the plasma pharmacokinetics of levodopa. When administered with levodopa and a DDC inhibitor (carbidopa or benserazide), entacapone decreases the degradation of levodopa in the peripheral tissues further by inhibiting the metabolism of levodopa to 3-OMD through the COMT pathway. This leads to more sustained plasma concentrations of levodopa. It is believed that at a given frequency of levodopa administration, these more sustained plasma levels of levodopa result in more constant dopaminergic stimulation in the brain leading to greater effects on the signs and symptoms of Parkinson's Disease. The higher levodopa levels also lead to increased levodopa adverse effects, sometimes requiring a decrease in the dose of levodopa.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Comtan (Entacapone), Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02243763 (Date of Revision: November 18, 2013). Available from, as of June 5, 2015: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng