

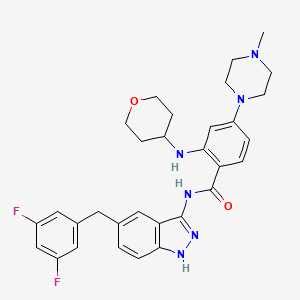

1. N-(5-(3,5-difluorobenzyl)-1h-indazol-3-yl)-4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-ylamino)benzamide
2. Nms-e628
3. Rozlytrek
4. Rxdx-101
1. 1108743-60-7
2. Rxdx-101
3. Nms-e628
4. Rozlytrek
5. Entrectinib (rxdx-101)
6. Entrectinib(rxdx-101)
7. L5orf0an1i
8. N-(5-(3,5-difluorobenzyl)-1h-indazol-3-yl)-4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-((tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)amino)benzamide
9. Benzamide, N-(5-((3,5-difluorophenyl)methyl)-1h-indazol-3-yl)-4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-((tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)amino)-
10. N-(5-(3,5-difluorobenzyl)-1h-indazol-3-yl)-4-(4-methylpiperazin-1yl)-2-(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-ylamino)benzamide
11. N-[5-[(3,5-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1h-indazol-3-yl]-4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(oxan-4-ylamino)benzamide
12. Benzamide, N-[5-[(3,5-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1h-indazol-3-yl]-4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-[(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl)amino]-
13. N-{5-[(3,5-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1h-indazol-3-yl}-4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-[(oxan-4-yl)amino]benzamide
14. Entrectinib [inn]
15. Unii-l5orf0an1i
16. Entrectinib [usan:inn]
17. Rozlytrek (tn)
18. Ymx
19. Entrectinib, 95%
20. Kinome_2659
21. Entrectinib [mi]
22. Entrectinib [jan]
23. Entrectinib; Nms-e628
24. Entrectinib [usan]
25. Entrectinib [who-dd]
26. Entrectinib (jan/usan/inn)
27. Gtpl8290
28. Schembl3512601
29. Chembl1983268
30. Nms-e-628
31. Entrectinib [orange Book]
32. Nms-e628;rxdx-101
33. Dtxsid101026450
34. Hms3886h21
35. Bcp16174
36. Ex-a2261
37. Mfcd28129099
38. Nsc774769
39. Nsc800095
40. S7998
41. Zinc43204146
42. Ccg-270048
43. Db11986
44. Nsc-774769
45. Nsc-800095
46. Sb17194
47. Ncgc00484067-01
48. Ncgc00484067-02
49. Ncgc00484067-03
50. Ac-31286
51. As-75092
52. Da-47850
53. Hy-12678
54. B5859
55. Ft-0736318
56. D10926
57. A856078
58. Q25323953
59. S900006830
60. Rxdx101; Rxdx 101; Rxdx-101; Nms E628; Nms-e628;nms E628
61. N-(5-(3,5-difluorobenzyl)-1h-indazol-3-yl)-4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-ylamino)benzamide
62. N-(5-(3,5-difluorobenzyl)-1h-indazol-3-yl)-4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(tetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-ylamino)benzamide
63. N-[5-(3,5-difluoro-benzyl)-1h-indazol-3-yl]-4-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-2-(tetrahydro-pyran-4-ylamino)-benzamide
64. N-{5-[(3,5-difluorophenyl)methyl]-3h-indazol-3-ylidene}-4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-[(oxan-4-yl)amino]benzamide
| Molecular Weight | 560.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C31H34F2N6O2 |
| XLogP3 | 5.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 560.27113067 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 560.27113067 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 85.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 847 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Entrectinib is indicated for the treatment of metastatic ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer in adults. Entrectinib is also indicated in adults and children over 12 years old for the treatment of NTRK gene fusion-positive solid tumors which have metastasized or for which surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity and for which has progressed on previous therapies or for which no comparable alternative therapies are available.
FDA Label
Rozlytrek as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adult and paediatric patients 12 years of age and older with solid tumours expressing a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion,
- who have a disease that is locally advanced, metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and
- who have not received a prior NTRK inhibitor
- who have no satisfactory treatment options.
Rozlytrek as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with ROS1 positive, advanced non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) not previously treated with ROS1 inhibitors.
Entrectinib and its active metabolite suppress several pathways which contribute to cell survival and proliferation. This suppression shifts the balance in favor of apoptosis thereby preventing cancer cell growth and shrinking tumors.
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit PROTEIN KINASES. (See all compounds classified as Protein Kinase Inhibitors.)
L01EX14
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX14 - Entrectinib
Absorption
Entrectinib has a Tmax of 4-5 h after administration of a single 600 mg dose. Food does not produce a significant effect on the extent of absorption.
Route of Elimination
After a single radio-labeled dose of entrectinib, 83% of radioactivity was present in the feces and 3% in the urine. Of the dose in the feces, 36% was present as entrectinib and 22% as M5.
Volume of Distribution
Entrectinib has an apparent volume of distribution of 551 L. The active metabolite, M5, has an apparent volume of distribution of 81.1 L. Entrectinib is known to cross the blood-brain barrier.
Clearance
The apparent clearance of entrectinib is 19.6 L/h while the apparent clearance of the active metabolite M5 is 52.4 L/h.
CYP3A4 is responsible for 76% of entrectinib metabolism in humans including metabolism to the active metabolite, M5. M5 has similar pharmacological activity to entrectinib and exists at approximately 40% of the steady state concentration of the parent drug. In rats, six in vivo metabolites have been identified including N-dealkylated, N-oxide, hydroxylated, and glucuronide conjugated metabolites.
Entrectinib has a half-life of elimination of 20 h. The active metabolite, M5, has a half-life of 40 h.
Entrectinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor which acts on several receptors. It functions as an ATP competitor to inhibit tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinases (TRK) TRKA, TRKB, TRKC, as well as proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS1 and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). TRK receptors produce cell proliferation via downstream signalling through the mitogen activated protein kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and phospholipase C-. ALK produces similar signalling with the addition of downstream JAK/STAT activation. Inhibition of these pathways suppresses cancer cell proliferation and shifts the balance in favor of apoptosis resulting in shrinking of tumor volume.
