

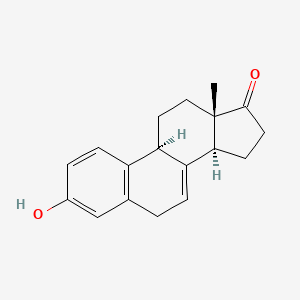

1. 474-86-2
2. 7-dehydroestrone
3. Dihydroequilenin
4. 3-hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraen-17-one
5. Estra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraen-17-one, 3-hydroxy-
6. 1,3,5,7-estratetraen-3-ol-17-one
7. Equilin [usp]
8. (9s,13s,14s)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-9,11,12,14,15,16-hexahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-one
9. Nsc-10971
10. Mls000028624
11. Chebi:42309
12. 08o86ex0j4
13. Equilin (usp)
14. Smr000058656
15. 3-hydroxy-estra-1,3,5(10),7tetraen-17-one
16. Unii-08o86ex0j4
17. Ccris 9074
18. 3-hydroxyoestra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraen-17-one
19. Cas-474-86-2
20. Prestwick_219
21. Einecs 207-488-6
22. Nsc 10971
23. Brn 2624302
24. Opera_id_780
25. Equilin [mi]
26. Equilin [mart.]
27. Prestwick0_000850
28. Prestwick1_000850
29. Prestwick2_000850
30. Prestwick3_000850
31. Equilin [usp-rs]
32. Equilin [who-dd]
33. Dsstox_cid_27433
34. Dsstox_rid_82343
35. Dsstox_gsid_47433
36. Bspbio_000839
37. 4-08-00-01366 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
38. Mls001148117
39. Schembl124758
40. Spbio_002760
41. Bpbio1_000923
42. Chembl323533
43. Equilin [usp Monograph]
44. Dtxsid7047433
45. Hms1570j21
46. Hms2097j21
47. Hms2233a16
48. Hms3714j21
49. Hy-b1176
50. Nsc10971
51. Tox21_302641
52. 1,5,7-estratetraen-3-ol-17-one
53. Bdbm50423544
54. Lmst02010026
55. Akos024285096
56. Zinc100031739
57. Ccg-220850
58. Cs-4786
59. Db02187
60. Ncgc00179406-01
61. Ncgc00256728-01
62. Equilin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
63. 3-hydroxyestra-1,5(10),7-tetraen-17-one
64. Wln: L E5 B666 Fv Juttt&j E1 Oq
65. D04041
66. S00287
67. 3-hydroxy-estra-1,3,5(10), 7-tetraen-17-one
68. 3-hydroxy-estra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraen-17-one
69. Estra-1,5(10),7-tetraen-17-one, 3-hydroxy-
70. Sr-01000721841
71. Q5384492
72. Sr-01000721841-2
73. Brd-k04046242-001-03-6
74. Equilin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
75. Equilin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
76. Equilin Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
77. (9s,13s,14s)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-9,11,12,13,15,16-hexahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17(14h)-one
78. (9s,13s,14s)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-9,11,12,14,15,16-hexahydro- 6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-one
79. Equilin; 7-dehydroestrone; 3-hydroxy-1,3,5(10),7-estratetraen-17-one; 1,3,5(10),7-estratetraen-3-ol-17-one
| Molecular Weight | 268.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H20O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 268.146329876 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 268.146329876 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 466 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with the menopause, atrophic vaginitis, osteoporosis, hypoestrogenism due to hypogonadism, castration, primary ovarian failure, breast cancer (for palliation only), and Advanced androgen-dependent carcinoma of the prostate (for palliation only)
Equilin is a component of Premarin (conjugated estrogens), a mixture of the water soluble salts of sulfate esters from estrone, equilin, 17 alpha-dihydroequilin, and other related steroids, may be derived from pregnant equine urine or yam and soy plants. Estrogens are important in the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. They promote growth and development of the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes, and enlargement of the breasts. Indirectly, they contribute to the shaping of the skeleton, maintenance of tone and elasticity of urogenital structures, changes in the epiphyses of the long bones that allow for the pubertal growth spurt and its termination, growth of axillary and pubic hair, and pigmentation of the nipples and genitals. Decline of estrogenic activity at the end of the menstrual cycle can bring on menstruation, although the cessation of progesterone secretion is the most important factor in the mature ovulatory cycle. However, in the preovulatory or nonovulatory cycle, estrogen is the primary determinant in the onset of menstruation. Estrogens also affect the release of pituitary gonadotropins. The pharmacologic effects of conjugated estrogens are similar to those of endogenous estrogens.
Absorption
Well absorbed.
Hepatic
Estrogens enter the cells of responsive tissues (e.g., female organs, breasts, hypothalamus, pituitary) where they interact with a protein receptor, subsequently increasing the rate of synthesis of DNA, RNA, and some proteins. Estrogens decrease the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone by the hypothalamus, reducing the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary.
