

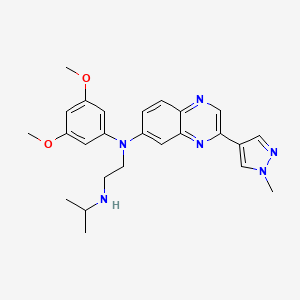

1. Balversa
2. Jnj-42756493
1. 1346242-81-6
2. Jnj-42756493
3. Balversa
4. 890e37nhmv
5. Jnj42756493
6. 1,2-ethanediamine, N1-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-n2-(1-methylethyl)-n1-(3-(1-methyl-1h-pyrazol-4-yl)-6-quinoxalinyl)-
7. N'-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-n'-[3-(1-methylpyrazol-4-yl)quinoxalin-6-yl]-n-propan-2-ylethane-1,2-diamine
8. N1-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-n2-isopropyl-n1-(3-(1-methyl-1h-pyrazol-4-yl)quinoxalin-6-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine
9. Erdafitinib [inn]
10. Erdafitinib [usan:inn]
11. Unii-890e37nhmv
12. Balversa (tn)
13. Erdafitinib [mi]
14. Erdafitinib [jan]
15. Erdafitinib (usan/inn)
16. Erdafitinib [usan]
17. Erdafitinib [who-dd]
18. Gtpl9039
19. Schembl2583760
20. Chembl3545376
21. Erdafitinib [orange Book]
22. Erdafitinib(jnj-42756493)
23. Erdafitinib; Jnj-42756493
24. Dtxsid001027936
25. Jnj-42756493 (erdafitinib)
26. Amy31119
27. Bcp20346
28. Ex-a2564
29. Bdbm50525939
30. Mfcd28502040
31. Nsc781556
32. S8401
33. Compound 4 [wo2011135376]
34. Zinc168520308
35. Ccg-269200
36. Cs-4988
37. Db12147
38. Nsc-781556
39. Sb16854
40. Ncgc00475735-01
41. Ac-30222
42. As-35040
43. Hy-18708
44. Jnj 42756493
45. N-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-n'-(1-methylethyl)-n-[3-(1-methyl-1h-pyrazol-4-yl)quinoxalin-6-yl]ethane-1,2-diamine
46. D10927
47. A857165
48. Q27077213
49. B0084-470835
50. Pan-fgfr Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Jnj-42756493
51. 5sf
52. N-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-n'-(1-methylethyl)-n-[3-(1-methyl-1h-pyrazol-4-yl)quinoxalin-6-yl]ethane-1,2-diamine;erdafitinib
| Molecular Weight | 446.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H30N6O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 446.24302422 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 446.24302422 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 583 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Erdafitinib is a pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma that has: i) susceptible FGFR3 or FGFR2 genetic alterations and has, ii) progressed during or following at least one line of prior platinum-containing chemotherapy including within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant platinum-containing chemotherapy. The selection of patients for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with erdafitinib should be based on the presence of susceptible FGFR genetic alterations in tumor specimens as detected by an FDA-approved companion diagnostic like the FDA approved therascreen FGFR RGQ RT-PCR Kit as developed by QIAGEN. This above indication is approved under accelerated approval by the US FDA based on tumor response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
FDA Label
Treatment of urothelial carcinoma
Treatment of all conditions included in the category of malignant neoplasms (except urothelial carcinoma, haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue neoplasms)
Upon administration, it was observed that erdafitinib increased serum phosphate level as a consequence of FGFR inhibition. Erdafitinib should be increased to the maximum recommended dose to achieve target serum phosphate levels of 5.5 7.0 mg/dL in early cycles with continuous daily dosing. Subsequently, in erfatinib clinical trials, the use of drugs which could increase serum phosphate levels, such as potassium phosphate supplements, vitamin D supplements, antacids, phosphate-containing enemas or laxatives, and medications known to have phosphate as an excipient were prohibited unless no alternatives existed. To manage phosphate elevation, phosphate binders were utilized. Additionally, the concomitant use of agents that can alter serum phosphate levels before the initial erfatinib dose increase period based on serum phosphate levels was also avoided. Furthermore, based on the evaluation of QTc interval in an open-label, dose escalation, and dose expansion study in 187 patients with cancer, erdafitinib had no large effect (i.e., > 20 ms) on the QTc interval.
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EN - Fibroblast growth factor receptor (fgfr) tyrosine kinase inhibitors
L01EN01 - Erdafitinib
Absorption
Following administration of erdafitinib 8 mg once daily, the mean (coefficient of variation [CV%]) steady-state maximum observed plasma concentration (Cmax), area under the curve (AUCtau), and minimum observed plasma concentration (Cmin) were 1,399 ng/mL (51%), 29,268 ngh/mL (60%), and 936 ng/mL (65%), respectively. Following single and repeat once daily dosing, erdafitinib exposure (maximum observed plasma concentration [Cmax] and area under the plasma concentration time curve [AUC]) increased proportionally across the dose range of 0.5 to 12 mg (0.06 to 1.3 times the maximum approved recommended dose). Steady state was achieved after 2 weeks with once daily dosing and the mean accumulation ratio was 4-fold. The median time to achieve peak plasma concentration (tmax) was 2.5 hours (range: 2 to 6 hours). And finally, no clinically meaningful differences with erdafitinib pharmacokinetics were observed following administration of a high-fat and high-calorie meal (800 calories to 1,000 calories with approximately 50% of total caloric content of the meal from fat) in healthy subjects.
Route of Elimination
After administering a single oral dose of radiolabeled erdafitinib, about 69% of the dose was recovered in feces (19% as unchanged) and 19% in urine (13% as unchanged).
Volume of Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution determined for erdafitinib is about 26 to 29 L in patients.
Clearance
The mean total apparent clearance (CL/F) documented for erdafitinib is about 0.362 L/h, while the oral clearance has been observed to be approximately 0.26 L/h.
It has been determined that erdafitinib is primarily metabolized by the cytochrome CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes. The contribution of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 in the total clearance of erdafitinib is estimated to be 39% and 20% respectively. Unchanged erdafitinib was ultimately the predominant drug-related moiety found in the plasma - there were no circulating metabolites observed.
The mean effective half-life documented for erdafitinib is 59 hours, although it has also been observed between 50 to 60 hours.
Urothelial cancer is statistically the fourth most common kind of cancer in the world. In general, such urothelial cancers originate in the urothelium - or the transitional epithelium - a membrane that covers the renal pelvis to the ureter, the bladder, and the proximal two-thirds of the urethra. While 90 to 95% of urothelial cancers are bladder cancers and the other 5 to 10% are upper tract urothelial cancers, the bladder cancers can also be either superficial or invasive (either not having or having invaded the deeper layers of the bladder). Moreover, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) is a transmembrane protein that is expressed ubiquitously in normal tissues and is involved in various endogenous bio-physiological processes including the homeostasis of phosphate and vitamin D, cell proliferation, cell anti-apoptotic signaling, and cell migration in a variety of cell types. Concurrently, genetic mutations or changes like deregulation of FGFR pathways and FGFR aberrations such as gene amplification, point mutations, and chromosomal translocations have been implicated in the pathogenesis of urothelial cancer, including the possibility of such changes to all four FGFR genes (FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4). Changes to the FGFR genes are consequently thought to promote cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, and anti-apoptosis in many cancers including urothelial cancer. Erdafitinib is subsequently an oral selective pan-FGFR kinase inhibitor that binds to and inhibits the enzymatic activity of expressed FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4 based on in vitro data. In particular, erdafitinib demonstrates inhibition of FGFR phosphorylation and signaling as well as decreased cell viability in cell lines expressing FGFR genetic alterations, including point mutations, amplifications, and fusions. Erdafitinib demonstrated antitumor activity in FGFR-expressing cell lines and xenograft models derived from tumor types, including bladder cancer.