
1. 11c Erlotinib
2. 11c-erlotinib
3. 358,774, Cp
4. 358774, Cp
5. Cp 358,774
6. Cp 358774
7. Cp-358,774
8. Cp-358774
9. Cp358,774
10. Cp358774
11. Erlotinib Hcl
12. Erlotinib Hydrochloride
13. Hcl, Erlotinib
14. Hydrochloride, Erlotinib
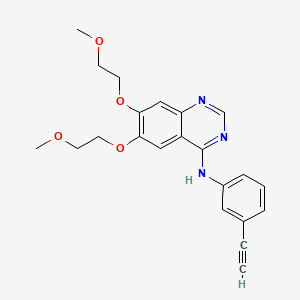
15. N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
16. Osi 774
17. Osi-774
18. Osi774
19. Tarceva
1. 183321-74-6
2. N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
3. Tarceva
4. Erlotinib Free Base
5. 4-[(3-ethynylphenyl)amino]-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazoline
6. Osi-774
7. 4-quinazolinamine, N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-
8. Erlotinib, Free Base
9. N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine
10. 183321-74-6 (free Base)
11. Nsc 718781
12. Chembl553
13. J4t82ndh7e
14. [6,7-bis(2-methoxy-ethoxy)quinazoline-4-yl]-(3-ethynylphenyl)amine
15. Cp358774
16. Cp-358,774
17. Chebi:114785
18. Mfcd02089651
19. Rg-1415
20. Ncgc00164574-01
21. [6,7-bis-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-quinazolin-4-yl]-(3-ethynyl-phenyl)-amine
22. Cp-35877401
23. R-1415
24. Dsstox_cid_26454
25. Dsstox_rid_81628
26. Dsstox_gsid_46454
27. Erlotinib(tarceva)
28. Osi-744
29. Cas-183321-74-6
30. Nsc718781
31. Erlotinib [inn:ban]
32. Sr-05000001460
33. Unii-j4t82ndh7e
34. Erlotinibum
35. Erotinib
36. Hsdb 8082
37. Osi 744
38. Nchembio866-comp3
39. Kinome_3317
40. N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine Monohydrochloride
41. Erlotinib [mi]
42. Erlotinib [vandf]
43. R 1415
44. Erlotinib [who-dd]
45. Schembl8413
46. Erlotinib [ema Epar]
47. Bdbm5446
48. Cid_176870
49. Gtpl4920
50. Dtxsid8046454
51. Hms2089f05
52. Hms3244m19
53. Hms3244m20
54. Hms3244n19
55. Hms3295a19
56. Hms3713c22
57. Hms3745m05
58. Zinc1546066
59. Tox21_112202
60. Ac-399
61. Nsc800097
62. S7786
63. Stk623143
64. Akos000282911
65. Tox21_112202_1
66. Ccg-220420
67. Cs-0620
68. Db00530
69. Nsc-800097
70. Ro-508231
71. Sb16916
72. Ncgc00164574-03
73. Ncgc00164574-05
74. Ncgc00164574-06
75. Ncgc00164574-14
76. Ncgc00164574-25
77. As-35132
78. Bcb03_000783
79. Be164419
80. Hy-50896
81. Sy028059
82. Am20090621
83. Ft-0651539
84. R1415
85. K00241
86. Ab01273955-01
87. Ab01273955-02
88. Ab01273955-03
89. 321e746
90. Q418369
91. Sr-05000001460-1
92. Sr-05000001460-2
93. Sr-05000001460-3
94. Sr-05000001460-6
95. Brd-k70401845-003-04-7
96. 1429636-49-6
| Molecular Weight | 393.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H23N3O4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 393.16885622 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 393.16885622 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 74.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 525 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tarceva |
| PubMed Health | Erlotinib (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Immunological Agent |
| Drug Label | TARCEVA (erlotinib), a kinase inhibitor, is a quinazolinamine with the chemical name N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine. TARCEVA contains erlotinib as the hydrochloride salt that has the following structural formula:Erloti... |
| Active Ingredient | Erlotinib hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 100mg base; eq 150mg base; eq 25mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Osi Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tarceva |
| PubMed Health | Erlotinib (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Immunological Agent |
| Drug Label | TARCEVA (erlotinib), a kinase inhibitor, is a quinazolinamine with the chemical name N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine. TARCEVA contains erlotinib as the hydrochloride salt that has the following structural formula:Erloti... |
| Active Ingredient | Erlotinib hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 100mg base; eq 150mg base; eq 25mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Osi Pharms |
Erlotinib hydrochloride monotherapy is indicated for the maintenance treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose disease has not progressed after four cycles of platinum-based first-line chemotherapy. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TARCEVA (erlotinib hydrochloride) tablet (April 2012). Available from, as of November 10, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=57bccb29-1c47-4c64-ab6a-77960a91cc20
Erlotinib hydrochloride monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regimen. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TARCEVA (erlotinib hydrochloride) tablet (April 2012). Available from, as of November 10, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=57bccb29-1c47-4c64-ab6a-77960a91cc20
Erlotinib hydrochloride in combination with gemcitabine is indicated for the first-line treatment of patients with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic pancreatic cancer. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TARCEVA (erlotinib hydrochloride) tablet (April 2012). Available from, as of November 10, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=57bccb29-1c47-4c64-ab6a-77960a91cc20
The manufacturer states that there are no known contraindications to the use of erlotinib.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 1040
Serious, sometimes fatal, interstitial lung disease-like events have occurred in patients receiving erlotinib. Interstitial lung disease-like events have been reported in approximately 0.7% of about 4900 patients receiving erlotinib in controlled and uncontrolled studies. In the principal efficacy study for non-small cell lung cancer, the reported incidence of interstitial lung disease-like events (0.8%) was similar among patients receiving erlotinib and those receiving placebo. In the principal efficacy study for pancreatic cancer, interstitial lung disease-like events occurred in 2.5% of patients receiving erlotinib and gemcitabine versus 0.4% of those receiving placebo and gemcitabine. Onset of manifestations occurred from 5 days to more than 9 months (median: 39 days) after initiating erlotinib therapy. Reported diagnoses in patients suspected of having interstitial lung disease-like events included pneumonitis, radiation pneumonitis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, interstitial pneumonia, interstitial lung disease, obliterative bronchiolitis, pulmonary fibrosis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and lung infiltration. Among patients receiving erlotinib for non-small cell lung cancer, most of these cases were associated with confounding or contributing factors, including concomitant or prior chemotherapy, prior radiotherapy, preexisting parenchymal lung disease, metastatic lung disease, or pulmonary infections.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 1040
Interruption or discontinuance of erlotinib therapy may be required in patients experiencing pulmonary toxicity.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 1040
Hepatorenal syndrome or acute renal failure, sometimes fatal, and renal insufficiency, with or without hypokalemia, have been reported in patients receiving erlotinib. Factors contributing to these adverse renal effects included baseline hepatic impairment; severe dehydration caused by diarrhea, vomiting, and/or anorexia; and concurrent chemotherapy. If dehydration occurs, erlotinib therapy should be interrupted and rehydration measures should be initiated. Periodic monitoring of renal function and serum electrolytes is recommended in patients at risk of dehydration.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 1040
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Erlotinib (27 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Erlotinib is indicated for: - The treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with tumors showing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations. - In combination with first-line treatment for patients diagnosed with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic pancreatic cancer. The safety and efficacy of erlotinib have not been established for patients with NSCLC whose tumors show other EGFR mutations. Additionally it is not recommended for use in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy.
FDA Label
* Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
Tarceva is also indicated for switch maintenance treatment in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR activating mutations and stable disease after first-line chemotherapy.
Tarceva is also indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regimen.
In patients with tumours without EGFR activating mutations, Tarceva is indicated when other treatment options are not considered suitable.
When prescribing Tarceva, factors associated with prolonged survival should be taken into account.
No survival benefit or other clinically relevant effects of the treatment have been demonstrated in patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-IHC - negative tumours.
* Pancreatic cancer :
Tarceva in combination with gemcitabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer .
When prescribing Tarceva, factors associated with prolonged survival should be taken into account.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit PROTEIN KINASES. (See all compounds classified as Protein Kinase Inhibitors.)
L01EB02
L01XE03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EB - Epidermal growth factor receptor (egfr) tyrosine kinase inhibitors
L01EB02 - Erlotinib
Absorption
Erlotinib is about 60% absorbed after oral administration and its bioavailability is substantially increased by food to almost 100%. Peak plasma levels occur 4 hours after dosing. The solubility of erlotinib is pH dependent. Solubility decreases pH increases. Smoking also decrease the exposure of erlotinib.
Route of Elimination
Following a 100 mg oral dose, 91% of the dose was recovered in which 83% was in feces (1% of the dose as unchanged parent compound) and 8% in urine (0.3% of the dose as unchanged parent compound).
Volume of Distribution
Apparent volume of distribution = 232 L
Clearance
Smokers have a 24% higher rate of erlotinib clearance.
Erlotinib is about 60% absorbed after oral administration and its bioavailability is substantially increased by food to almost 100%. Peak plasma levels occur 4 hours after dosing. The solubility of erlotinib is pH dependent. Erlotinib solubility decreases as pH increases.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TARCEVA (erlotinib hydrochloride) tablet (April 2012). Available from, as of November 10, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=57bccb29-1c47-4c64-ab6a-77960a91cc20
Following absorption, erlotinib is approximately 93% protein bound to plasma albumin and alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. Erlotinib has an apparent volume of distribution of 232 liters.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TARCEVA (erlotinib hydrochloride) tablet (April 2012). Available from, as of November 10, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=57bccb29-1c47-4c64-ab6a-77960a91cc20
Time to reach steady state plasma concentration /is/ 7 - 8 days. No significant relationships of clearance to covariates of patient age, body weight or gender were observed. Smokers had a 24% higher rate of erlotinib clearance.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TARCEVA (erlotinib hydrochloride) tablet (April 2012). Available from, as of November 10, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=57bccb29-1c47-4c64-ab6a-77960a91cc20
Following a 100 mg oral dose, 91% of the dose was recovered: 83% in feces (1% of the dose as intact parent) and 8% in urine (0.3% of the dose as intact parent).
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TARCEVA (erlotinib hydrochloride) tablet (April 2012). Available from, as of November 10, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=57bccb29-1c47-4c64-ab6a-77960a91cc20
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Erlotinib (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Metabolism occurs in the liver. In vitro assays of cytochrome P450 metabolism showed that erlotinib is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP1A2, and the extrahepatic isoform CYP1A1.
Metabolism and excretion of erlotinib, an orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, were studied in healthy male volunteers after a single oral dose of (14)C-erlotinib hydrochloride (100-mg free base equivalent, approximately 91 microCi/subject)... In plasma, unchanged erlotinib represented the major circulating component, with the pharmacologically active metabolite M14 accounting for approximately 5% of the total circulating radioactivity. Three major biotransformation pathways of erlotinib are O-demethylation of the side chains followed by oxidation to a carboxylic acid, M11 (29.4% of dose); oxidation of the acetylene moiety to a carboxylic acid, M6 (21.0%); and hydroxylation of the aromatic ring to M16 (9.6%). In addition, O-demethylation of M6 to M2, O-demethylation of the side chains to M13 and M14, and conjugation of the oxidative metabolites with glucuronic acid (M3, M8, and M18) and sulfuric acid (M9) play a minor role in the metabolism of erlotinib. The identified metabolites accounted for >90% of the total radioactivity recovered in urine and feces. The metabolites observed in humans were similar to those found in the toxicity species, rats and dogs.
PMID:16381666 Ling J et al; Drug Metab Dispos 34 (3): 420-6 (2006)
Erlotinib has known human metabolites that include Erlotinib M14.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Median half-life of 36.2 hours.
A population pharmacokinetic analysis in 591 patients receiving the single-agent erlotinib hydrochloride 2nd/3rd line regimen showed a median half-life of 36.2 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TARCEVA (erlotinib hydrochloride) tablet (April 2012). Available from, as of November 10, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=57bccb29-1c47-4c64-ab6a-77960a91cc20
The mechanism of clinical antitumor action of erlotinib is not fully characterized. Erlotinib inhibits the intracellular phosphorylation of tyrosine kinase associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Specificity of inhibition with regard to other tyrosine kinase receptors has not been fully characterized. EGFR is expressed on the cell surface of normal cells and cancer cells.
Although the exact mechanism of antineoplastic activity of erlotinib has not been fully elucidated, erlotinib appears to inhibit the intracellular phosphorylation of tyrosine kinase associated with EGFR, which is expressed on the surface of normal and cancer cells. Specificity with regard to other tyrosine kinase receptors has not been fully characterized.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 1042
Erlotinib is a potent inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and has been demonstrated to treat advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer to prolong survival after failure of first-line or second-line chemotherapy. However, little is known about its effects on immune system. In the present study, /investigators/ aimed to investigate the immunosuppressive activity of erlotinib on T lymphocytes both in vitro and in vivo, and further explore its potential molecular mechanism. Erlotinib exerted a significant inhibition on the T cell proliferation and activation induced by concanavalin A, anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28, staphylococcal enterotoxin B or phorbol myristate acetate respectively in a concentration-dependent manner and it also inhibited the secretion of the proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-2 and IFN-gamma of activated T cells. Further study showed that erlotinib caused G0/G1 arrest and suppressed the phosphorylations of c-Raf, ERK and Akt in activated T cells. Moreover, erlotinib significantly ameliorated picryl chloride-induced ear contact dermatitis in a dose-dependent manner in vivo. In summary, these findings suggest that erlotinib may cause the impairment of T-cell-mediated immune response both in vitro and in vivo through inhibiting T cell proliferation and activation, which is closely associated with its potent down-regulation of the c-Raf/ERK cascade and Akt signaling pathway.
PMID:21195724 Luo Q et al; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251 (2): 130-6 (2011)