


1. Emcyt
2. Estracyt
3. Estramustin Phosphate
4. Estramustine
5. Estramustinphosphate
6. Leo 275
7. Leo-275
8. Leo275
9. Nsc 89199
10. Nsc-89199
11. Nsc89199
12. Phosphate Sodium, Estramustine
13. Phosphate, Estramustin
1. 52205-73-9
2. Estramustine Sodium Phosphate
3. Estramustine Phosphate Disodium
4. Emcyt
5. Ro 21-8837/001
6. Chebi:31562
7. 52205-73-9 (sodium)
8. Iq856m1r16
9. Estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17-(dihydrogen Phosphate), Disodium Salt
10. Ncgc00185756-01
11. Emcyt (tn)
12. Estramustine Phosphate Sodium (usan)
13. Sodium (8r,9s,13s,14s,17s)-3-((bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamoyl)oxy)-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl Phosphate
14. Estramustine Phosphate Sodium [usan]
15. Estramustine Phosphate Sodium Hydrate
16. Ro-218837-001
17. Unii-iq856m1r16
18. Einecs 257-735-7
19. Estramustinephosphatesodium
20. Estramustine Phosphate Sodium [usan:ban:jan]
21. Dsstox_cid_28879
22. Dsstox_rid_83147
23. Dsstox_gsid_48953
24. Schembl19436
25. Chembl1200721
26. Dtxsid2048953
27. Tox21_113375
28. Mfcd00866320
29. Akos015915051
30. Ac-1612
31. Estramustine Sodium Phosphate [jan]
32. Cas-52205-73-9
33. Estramustine Sodium Phosphate [mart.]
34. Estramustine Phosphate Sodium [who-dd]
35. Estramustine Phosphate Sodium Anhydrous
36. Ro-21-8837/001
37. D02398
38. Estramustine Phosphate Sodium Anhyhdrous
39. Q27114436
40. Estramustine 17-(dihydrogenphosphate) Disodium Salt Anhydrous
41. Estramustine 17-(dihydrogenphosphate) Disodium Salt Anhydrous [mi]
42. Disodium (17beta)-3-{[bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamoyl]oxy}estra-1(10),2,4-trien-17-yl Phosphate
43. Disodium;[(8r,9s,13s,14s,17s)-3-[bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamoyloxy]-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] Phosphate
44. Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17-diol (17.beta.)-, 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17-(dihydrogen Phosphate), Disodium Salt
45. Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17-diol (17beta)-, 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17-(dihydrogen Phosphate), Disodium Salt
46. Sodium (8r,9s,13s,14s,17s)-3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamoyloxy)-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl Phosphate
1. 4891-15-0
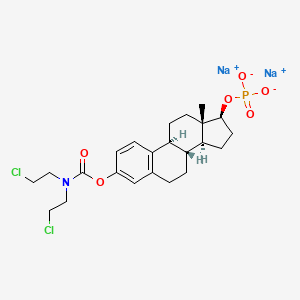
2. Estramustine Phosphate
3. Estramustina
4. Estramustine
5. Va10847
6. Estramustine Sodium Phosphate
| Molecular Weight | 564.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H30Cl2NNa2O6P |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 563.0983186 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 563.0983186 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 102 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 735 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Emcyt |
| PubMed Health | Estramustine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Estramustine phosphate sodium, an antineoplastic agent, is an off-white powder readily soluble in water. EMCYT Capsules are white and opaque, each containing estramustine phosphate sodium as the disodium salt monohydrate equivalent to 140 mg estramus... |
| Active Ingredient | Estramustine phosphate sodium |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 140mg phosphate |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Emcyt |
| PubMed Health | Estramustine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Estramustine phosphate sodium, an antineoplastic agent, is an off-white powder readily soluble in water. EMCYT Capsules are white and opaque, each containing estramustine phosphate sodium as the disodium salt monohydrate equivalent to 140 mg estramus... |
| Active Ingredient | Estramustine phosphate sodium |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 140mg phosphate |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal
Antineoplastic agents that are used to treat hormone-sensitive tumors. Hormone-sensitive tumors may be hormone-dependent, hormone-responsive, or both. A hormone-dependent tumor regresses on removal of the hormonal stimulus, by surgery or pharmacological block. Hormone-responsive tumors may regress when pharmacologic amounts of hormones are administered regardless of whether previous signs of hormone sensitivity were observed. The major hormone-responsive cancers include carcinomas of the breast, prostate, and endometrium; lymphomas; and certain leukemias. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994, p2079) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal.)
Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating
A class of drugs that differs from other alkylating agents used clinically in that they are monofunctional and thus unable to cross-link cellular macromolecules. Among their common properties are a requirement for metabolic activation to intermediates with antitumor efficacy and the presence in their chemical structures of N-methyl groups, that after metabolism, can covalently modify cellular DNA. The precise mechanisms by which each of these drugs acts to kill tumor cells are not completely understood. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2026) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating.)
