
1. Amidazine
2. Ethioniamide
3. Trecator
4. Trecator Sc
5. Trecator-sc
1. 536-33-4
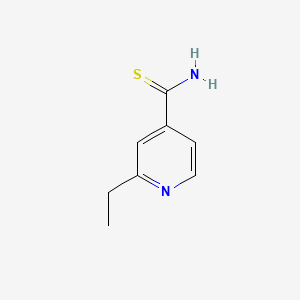
2. 2-ethylpyridine-4-carbothioamide
3. Ethioniamide
4. Trecator
5. 2-ethylthioisonicotinamide
6. Ethyonomide
7. Amidazine
8. Ethinamide
9. Etionamid
10. Etioniamid
11. Thioamide
12. Ethylisothiamide
13. Trecator-sc
14. Nizotin
15. 4-pyridinecarbothioamide, 2-ethyl-
16. Amidazin
17. Ethimide
18. Etiocidan
19. Etionizin
20. Etionizina
21. Etionizine
22. Fatoliamid
23. Iridocin
24. Iridozin
25. Isotiamida
26. Itiocide
27. Nicotion
28. Rigenicid
29. Sertinon
30. Thianide
31. Thioniden
32. Trekator
33. Trescatyl
34. Trescazide
35. Tubenamide
36. Tubermin
37. Tuberoid
38. Tuberoson
39. Aetina
40. Aetiva
41. Ethina
42. Etimid
43. Etionid
44. Isothin
45. Teberus
46. Thianid
47. Tianid
48. Atina
49. Bayer 5312
50. Ethionamid Prothionamid
51. Iridocin Bayer
52. Ethionamidum
53. Nisotin
54. Thiomid
55. Etionamide [dcit]
56. Etionamida
57. Etionamide
58. Tiomid
59. 2-ethylisothionicotinamide
60. 2-ethyl-4-pyridinecarbothioamide
61. 2-ethylisonicotinothioamide
62. Ethionamidum [inn-latin]
63. Etionamida [inn-spanish]
64. 1314 Th
65. 2-ethyl-4-thiocarbamoylpyridine
66. 2-ethyl-4-thiopyridylamide
67. 2-ethyl-thioisonicotinamide
68. 2-ethylisonicotinic Acid Thioamide
69. Th 1314
70. Nci-c01694
71. 1314-th
72. F.i. 58-30
73. 1314th
74. 2-ethyl-4-thioamidylpyridine
75. Isonicotinamide, 2-ethylthio-
76. Oay8ors3cq
77. Aethionamidum
78. Etp
79. Nsc-255115
80. Tio-mid
81. Mls000069764
82. Chebi:4885
83. .alpha.-ethylisothionicotinamide
84. .alpha.-ethylthioisonicotinamide
85. .alpha.-ethylisonicotinoylthioamide
86. Trecator Sc
87. Nsc255115
88. 1314 Tn
89. .alpha.-ethylisonicotinic Acid Thioamide
90. Ethina (van)
91. Ncgc00016497-05
92. Cas-536-33-4
93. Smr000058716
94. Dsstox_cid_577
95. Dsstox_rid_75669
96. Dsstox_gsid_20577
97. Alpha-ethylisothionicotinamide
98. Alpha-ethylthioisonicotinamide
99. Alpha-ethylisonicotinoylthioamide
100. 2-ethylisonicotinic Thioamide
101. Alpha-ethylisonicotinic Acid Thioamide
102. Ccris 287
103. Hsdb 7473
104. Bayer5312
105. Sr-01000759219
106. Unii-oay8ors3cq
107. Einecs 208-628-9
108. Nsc 255115
109. Brn 0116474
110. Thiodine
111. Trecator (tn)
112. Prestwick_842
113. Isonicotinimidic Acid, 2-ethylthio-
114. Mfcd00057361
115. Ethionamide [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
116. Spectrum_001082
117. Cpd001370750
118. Opera_id_632
119. Ethionamide [mi]
120. Prestwick0_000526
121. Prestwick1_000526
122. Prestwick2_000526
123. Prestwick3_000526
124. Spectrum2_000994
125. Spectrum3_000428
126. Spectrum4_000547
127. Spectrum5_000979
128. 2-ethylisonicotinothiamide
129. 2-ethylisonicotinthioamide
130. Ethionamide [inn]
131. Ethionamide [jan]
132. E0695
133. Ethionamide [hsdb]
134. Ethionamide [iarc]
135. Ethionamide [usan]
136. Ethionamide [vandf]
137. Chembl1441
138. Ethionamide [mart.]
139. Schembl27007
140. Bspbio_000511
141. Bspbio_002016
142. Ethionamide [usp-rs]
143. Ethionamide [who-dd]
144. Ethionamide [who-ip]
145. Kbiogr_001213
146. Kbioss_001562
147. 5-22-02-00360 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
148. Mls001074114
149. Mls002454402
150. Divk1c_000145
151. Spectrum1500292
152. Wln: T6nj B2 Dyzus
153. Spbio_001087
154. Spbio_002432
155. Bpbio1_000563
156. Ethionamide (jp17/usp/inn)
157. Dtxsid0020577
158. Aeocxxjpgcbfja-uhfffaoysa-
159. Hms500h07
160. Kbio1_000145
161. Kbio2_001562
162. Kbio2_004130
163. Kbio2_006698
164. Kbio3_001236
165. .alpha.-ethyl-thioisonicotinamide
166. Ethionamide [orange Book]
167. Isonicotinamide, 2-ethyl, Thio-
168. Ethionamide For System Suitability
169. Ninds_000145
170. Ethionamide [ep Monograph]
171. Hms1569j13
172. Hms1920m22
173. Hms2091f03
174. Hms2096j13
175. Hms2231f10
176. Hms2233j11
177. Hms3259k17
178. Hms3370i18
179. Hms3371d12
180. Hms3655m10
181. Hms3713j13
182. Pharmakon1600-01500292
183. Ethionamide [usp Monograph]
184. Bcp29626
185. Ethionamidum [who-ip Latin]
186. Hy-b0276
187. Zinc3872520
188. Tox21_110458
189. Tox21_202409
190. Tox21_302769
191. Ccg-40212
192. Nsc757028
193. S1777
194. Akos006220662
195. Tox21_110458_1
196. Db00609
197. Fs-1770
198. Nc00508
199. Nsc-757028
200. Idi1_000145
201. Ncgc00016497-01
202. Ncgc00016497-02
203. Ncgc00016497-03
204. Ncgc00016497-04
205. Ncgc00016497-06
206. Ncgc00016497-08
207. Ncgc00016497-09
208. Ncgc00091074-01
209. Ncgc00091074-02
210. Ncgc00091074-03
211. Ncgc00091074-04
212. Ncgc00256600-01
213. Ncgc00259958-01
214. Ac-13715
215. Smr001370750
216. Sbi-0051377.p003
217. Db-049945
218. 2-ethylpyridine-4-carbothioamide;ethionamide
219. Ab00051990
220. Sw196973-3
221. C07665
222. D00591
223. F15438
224. Ab00051990-09
225. Ab00051990_10
226. Ab00051990_11
227. A829694
228. Q414767
229. Sr-01000759219-2
230. Sr-01000759219-5
231. W-105719
232. Brd-k33710385-001-05-4
233. Brd-k51207550-001-09-9
234. Ethionamide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
235. Ethionamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
236. Ethinamide; 2-ethylthioisonicotinamide; 2-ethylpyridine-4-carbothioamide
237. Ethionamide For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
238. Trecator;2-ethylthioisonicotinamide;ethinamide; Ethioniamide; Trecator Sc; Trecator-sc
| Molecular Weight | 166.25 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H10N2S |
| XLogP3 | 1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 166.05646950 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 166.05646950 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 71 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 147 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Trecator |
| PubMed Health | Ethionamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antitubercular |
| Drug Label | Trecator (ethionamide tablets, USP) is used in the treatment of tuberculosis. The chemical name for ethionamide is 2-ethylthioisonicotinamide with the following structural formula: Ethionamide is a yellow crystalline, nonhygroscopic compound with a... |
| Active Ingredient | Ethionamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Wyeth Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Trecator |
| PubMed Health | Ethionamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antitubercular |
| Drug Label | Trecator (ethionamide tablets, USP) is used in the treatment of tuberculosis. The chemical name for ethionamide is 2-ethylthioisonicotinamide with the following structural formula: Ethionamide is a yellow crystalline, nonhygroscopic compound with a... |
| Active Ingredient | Ethionamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Wyeth Pharms |
Antibacterial (tuberculostatic)
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 666
Ethionamide is indicated in combination with other antituberculosis medications in the treatment of tuberculosis, including tuberculous meningitis, after failure with the primary medications (streptomycin, isoniazid, rifampin, and ethambutol) or when these cannot be used because of toxicity or development of resistant tubercle bacilli. Ethionamide is effective only against mycobacteria. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Ethionamide is used in combination with other antileprosy agents in the treatment of Hansen's disease. /Not included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Ethionamide is used in the treatment of atypical mycobacterial infections, such as Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). /Not included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Ethionamide and prothionamide are thioamides used as second-line antituberculosis drugs for treatment of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis.
WHO; Guidelines for the Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (WHO/TB/96.210 REV.1) 1997. Available from, as of November 26, 2006: https://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/1997/WHO_TB_96.210_(Rev.1).pdf
Adverse GI effects, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, excessive salivation, metallic taste, stomatitis, anorexia, and weight loss, are the most common adverse effects reported with ethionamide. Nausea and vomiting may be severe enough to necessitate discontinuance of ethionamide. GI effects appear to be dose related, and approximately 50% of patients are unable to tolerate a single 1-g dose of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 567
Psychotic disturbances, mental depression, restlessness, drowsiness, dizziness, headache, postural hypotension, and asthenia occur occasionally with ethionamide. Rarely, peripheral neuritis, paresthesia, seizures, tremors, a pellagra-like syndrome, hallucinations, diplopia, optic neuritis, blurred vision, and olfactory disturbances have been reported.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 567
The manufacturer of ethionamide recommends concomitant use of pyridoxine to prevent or relieve neurotoxic effects during ethionamide treatment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 568
Transient increases in serum bilirubin, AST (SGOT), and ALT (SGPT) concentrations have been reported in patients receiving ethionamide. Hepatitis (with or without jaundice) also has been reported. Hepatotoxicity generally is reversible following discontinuance of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 568
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ETHIONAMIDE (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For use in the treatment of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis when other antitubercular drugs have failed.
FDA Label
Ethinamate is bacteriostatic against M. tuberculosis. In a study examining ethionamide resistance, ethionamide administered orally initially decreased the number of culturable Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms from the lungs of H37Rv infected mice. Drug resistance developed with continued ethionamide monotherapy, but did not occur when mice received ethionamide in combination with streptomycin or isoniazid.
Antitubercular Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of tuberculosis. They are divided into two main classes: "first-line" agents, those with the greatest efficacy and acceptable degrees of toxicity used successfully in the great majority of cases; and "second-line" drugs used in drug-resistant cases or those in which some other patient-related condition has compromised the effectiveness of primary therapy. (See all compounds classified as Antitubercular Agents.)
Fatty Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds that interfere with FATTY ACID SYNTHASE resulting in a reduction of FATTY ACIDS. This is a target mechanism in humans of some ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS and ANTI-OBESITY AGENTS and of some ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS which interfere with CELL WALL and CELL MEMBRANE formation. (See all compounds classified as Fatty Acid Synthesis Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J04 - Antimycobacterials
J04A - Drugs for treatment of tuberculosis
J04AD - Thiocarbamide derivatives
J04AD03 - Ethionamide
Absorption
Essentially completely absorbed following oral administration and not subjected to any appreciable first pass metabolism. Bioavailability approximately 100%.
Route of Elimination
Less than 1% of the oral dose is excreted as ethionamide in urine. Ethionamide is extensively metabolized to active and inactive metabolites.
Volume of Distribution
93.5 L [healthy volunteers]
Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. Bioavailability approximately 100%.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Ethionamide is essentially completely absorbed following oral administration and does not undergo any appreciable first-pass metabolism.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 568
Following a single 250-mg oral dose of ethionamide given as film-coated tablets in fasting adults, peak plasma concentrations of ethionamide average 2.16 mcg/mL and are attained within 1 hour. When a single 250-mg oral dose of ethionamide is given as sugar-coated tablets (Trecator-SC; no longer commercially available in the US) in healthy adults, peak plasma concentrations average 1.48 mcg/mL and are attained within 1.5 hours.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 568
Time to peak concentration: Approximately 1.8 hours; Peak serum concentration: Approximately 2.2 mcg/mL after a single oral 500-mg dose.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ETHIONAMIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic and extensive. Metabolized to the active metabolite sulfoxide, and several inactive metabolites. The sulphoxide metabolite has been demonstrated to have antimicrobial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Ethionamide is extensively metabolized to active and inactive metabolites. Metabolism is presumed to occur in the liver and thus far 6 metabolites have been isolated: 2-ethylisonicotinamide, carbonyl-dihydropyridine, thiocarbonyl-dihydropyridine, S-oxocarbamoyl dihydropyridine, 2-ethylthioiso-nicotinamide, and ethionamide sulphoxide. The sulphoxide metabolite has been demonstrated to have antimicrobial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis .
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 3482
2 to 3 hours
The plasma half-life of ethionamide following a 250-mg oral dose given as film-coated tablets is 1.92 hours.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 568
Half-life: Approximately 2 to 3 hours.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Ethionamide may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in action, depending on the concentration of the drug attained at the site of infection and the susceptibility of the infecting organism. Ethionamide, like prothionamide and pyrazinamide, is a nicotinic acid derivative related to isoniazid. It is thought that ethionamide undergoes intracellular modification and acts in a similar fashion to isoniazid. Isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycoloic acids, an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. Specifically isoniazid inhibits InhA, the enoyl reductase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, by forming a covalent adduct with the NAD cofactor. It is the INH-NAD adduct that acts as a slow, tight-binding competitive inhibitor of InhA.
Ethionamide may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in action, depending on the concentration of the drug attained at the site of infection and the susceptibility of the infecting organism. The exact mechanism of action of ethionamide has not been fully elucidated, but the drug appears to inhibit peptide synthesis in susceptible organisms.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 568