


1. 141-78-6
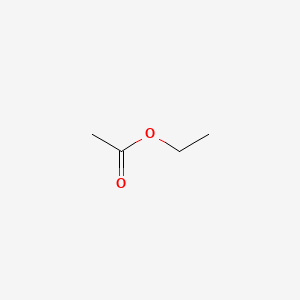
2. Ethyl Ethanoate
3. Acetic Acid Ethyl Ester
4. Acetoxyethane
5. Vinegar Naphtha
6. Acetic Ether
7. Ethyl Acetic Ester
8. Acetic Acid, Ethyl Ester
9. Acetidin
10. Ethylacetate
11. Essigester
12. Acetic Ester
13. Etoac
14. Aethylacetat
15. Ethylacetat
16. 1-acetoxyethane
17. Rcra Waste Number U112
18. Acoet
19. Ethylacetaat
20. Octan Etylu
21. Fema No. 2414
22. Etile (acetato Di)
23. Ethyle (acetate D')
24. Ethylazetat
25. Ethyl-acetate
26. Chebi:27750
27. Ethylester Kyseliny Octove
28. Acetic Acid Ethyl
29. Ethyl Ester Of Acetic Acid
30. Mfcd00009171
31. Nsc 70930
32. Essigsaeureethylester
33. Ethyl Acetate [nf]
34. Acetic-acid-ethylester
35. Ethyl Acetate Solution
36. Ethyl Acetate, Hplc
37. Nsc-70930
38. Ch3-co-o-ch3
39. 76845o8nmz
40. Ethyl Acetate (nf)
41. Ncgc00091766-01
42. E1504
43. Dsstox_cid_2001
44. Ethyl Acetate, Acs Reagent
45. Dsstox_rid_76453
46. Dsstox_gsid_22001
47. Essigester [german]
48. Ethylacetaat [dutch]
49. Aethylacetat [german]
50. Caswell No. 429
51. Octan Etylu [polish]
52. Ethyl Acetate (natural)
53. Acetate D'ethyle
54. Acetato De Etilo
55. Acetate D'ethyle [french]
56. Acetato De Etilo [spanish]
57. Ethyl Acetate, Acs Reagent, >=99.5%
58. Cas-141-78-6
59. Hsdb 83
60. Etile (acetato Di) [italian]
61. Ccris 6036
62. Ethyle (acetate D') [french]
63. Ethylester Kyseliny Octove [czech]
64. Einecs 205-500-4
65. Un1173
66. Ch3cooc2h5
67. Rcra Waste No. U112
68. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 044003
69. Ethylaceate
70. Ethylactate
71. Ethylacteate
72. Etylacetate
73. Acet-ethylester
74. Ehtyl Acetate
75. Ethanol Acetate
76. Ethly Acetate
77. Ethyl Acteate
78. Ethyl_acetate
79. Ehyl Acetate
80. Ethl Acetate
81. Ethy Acetate
82. Ethyl Aceate
83. Ethyl Actate
84. Etyl Acetate
85. Unii-76845o8nmz
86. Acetyl Ester
87. Acet-eth-ester
88. Ai3-00404
89. 1-ethyl Acetate
90. 2~ethyl Acetate
91. Acetic Ethyl Ester
92. Etile(acetato Di)
93. Nat.ethyl Acetate
94. Et-oac
95. Ethyle(acetate D')
96. Acetic Acid Ethylester
97. Ethyl Acetate Natural
98. Ch3co2et
99. Ethyl Acetate Hplc Grade
100. Ethyl Acetate, For Hplc
101. Ethyl Acetate, 99.9%
102. Ethyl Acetate, Acs Grade
103. Ch3co2ch2ch3
104. Epitope Id:116868
105. Ec 205-500-4
106. Ethyl Acetate [ii]
107. Ethyl Acetate [mi]
108. Ethyl Acetate, Hplc Grade
109. Ch3co2c2h5
110. Ethyl Acetate [fcc]
111. Ethyl Acetate [fhfi]
112. Ethyl Acetate [hsdb]
113. Ethyl Acetate [inci]
114. Ethyl Acetate 100ml
115. Ethyl Acetate, >=99.5%
116. Wln: 2ov1
117. Chembl14152
118. Acetic Acid,ethyl Ester
119. Ethyl Acetate [mart.]
120. Ethyl Acetate, Ar, >=99%
121. Ethyl Acetate, Lr, >=99%
122. Ethyl Acetate [usp-rs]
123. Ethyl Acetate [who-dd]
124. Dtxsid1022001
125. Ethyl Acetate Reagent Grade Acs
126. 2-oxo-2-ethoxyethylidyne Radical
127. Ethyl Acetate, Analytical Standard
128. Ethyl Acetate, Environmental Grade
129. Zinc895412
130. Ethyl Acetate, Anhydrous, 99.8%
131. Nsc70930
132. Ethyl Acetate, 99.9% Low Benzene
133. Tox21_111166
134. Tox21_202512
135. Bdbm50128823
136. C0036
137. Ethyl Acetate [ep Monograph]
138. Stl282717
139. Ethyl Acetate, >=99%, Fcc, Fg
140. Ethyl Acetate, Hplc Grade, 99.8%
141. Akos000121947
142. Ethyl Acetate Ethanol Solution (3:1)
143. Ethyl Acetate Gc, For Residue Analysis
144. Ethyl Acetate, Spectrophotometric Grade
145. Un 1173
146. Ethyl Acetate, For Hplc, >=99.5%
147. Ethyl Acetate, For Hplc, >=99.7%
148. Ethyl Acetate, For Hplc, >=99.8%
149. Ethyl Acetate, Pra Grade, >=99.5%
150. Ncgc00260061-01
151. Ethyl Acetate 100 Microg/ml In N-hexane
152. Ethyl Acetate 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
153. Ethyl Acetate, Biotech. Grade, >=99.8%
154. Ethyl Acetate, Reagentplus(r), >=99.5%
155. Ethyl Acetate, Reagentplus(r), >=99.8%
156. Ethyl Acetate, Tested According To Ph.eur.
157. A0030
158. Ethyl Acetate 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
159. Ethyl Acetate, Natural, >=99%, Fcc, Fg
160. Ethyl Acetate, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%
161. Ft-0621744
162. Ft-0693343
163. Q0040
164. Ethyl Acetate [un1173] [flammable Liquid]
165. Ethyl Acetate, For Hplc, >=99.8% (gc)
166. Ethyl Acetate, Jis Special Grade, >=99.5%
167. J3.639.860d
168. C00849
169. D02319
170. Ethyl Acetate, Capillary Gc Grade, >=99.5%
171. A807811
172. Q407153
173. Ethyl Acetate, Laboratory Reagent, >=99.0% (gc)
174. Ethyl Acetate, Uv-ir Min. 99.8%, Isocratic Grade
175. J-007556
176. J-521240
177. F0001-0489
178. Ethyl Acetate, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, >=99.5% (gc)
179. Ethyl Acetate, For Residue Analysis, Suitable For 5000 Per Jis
180. Ethyl Acetate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
181. Ethylacetate, Pure, Meets The Analytical Specifications Of Ph. Eur.
182. Ethyl Acetate, Hplc Plus, For Hplc, Gc, And Residue Analysis, 99.9%
183. Ethyl Acetate, Suitable For 1000 Per Jis, >=99.5%, For Residue Analysis
184. Ethyl Acetate, Suitable For 300 Per Jis, >=99.5%, For Residue Analysis
185. Ethyl Acetate, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
186. Ethyl Acetate, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, Reag. Ph. Eur., >=99.5% (gc)
187. Ethyl Acetate, Puriss. P.a., Free Of Higher Boiling Impurities, >=99.9% (gc)
188. Ethyl Acetate, Puriss., Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Nf, >=99.5% (gc)
| Molecular Weight | 88.11 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H8O2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 88.052429494 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 88.052429494 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 26.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 49.5 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
... It has been used internally in a dose of 1 to 2 cc as carminative & antispasmodic, also externally as counterirritant ... .
Grant, W.M. Toxicology of the Eye. 3rd ed. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas Publisher, 1986., p. 412
... The primary route of absorption responsible for the toxicity of ethyl acetate is inhalation.
Ryan, R.P., C.E. Terry (eds.). Toxicology Desk Reference 4th ed. Volumes 1-3. Taylor & Francis, Washington, D.C. 1997., p. 1253
... The current study was aimed at quantitating the extent of metabolism of inspired ethyl acetate in the upper respiratory tract (URT) of the F344 rat and Syrian hamster. Ethyl acetate deposition was measured in the surgically isolated URT of these species under constant velocity unidirectional flow conditions. The degree of metabolism was estimated by mathematic modeling based on a simple venous-equilibration approach and by direct comparison of deposition efficiencies in naive and carboxylesterase-inhibited animals. Ethyl acetate deposition efficiencies averaged between 10 and 35% in the rat URT and 36 and 72% in the hamster. Carboxylesterase inhibition decreased deposition in both species. Both the modeling efforts and the direct comparisons between naive and inhibited animals indicated that significant amounts of the deposited ethyl acetate were metabolized in the URT of both species with the extent of metabolism being more pronounced in the hamster. Specifically, 40-65% of the deposited ethyl acetate was metabolized in the URT of the rat compared to 63-90% in the hamster. This first-pass metabolism (i) increased URT deposition efficiencies; (ii) led to production of high metabolite levels in URT tissues; and (iii) decreased the amount of parent ethyl acetate available for absorption into the bloodstream in the URT.
PMID:2300973 Morris JB; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 102 (2): 331-345 (1990)
Because of the abundance of nonspecific esterases, one might expect the common solvent ethyl acetate (EtAc) to be hydrolyzed to ethyl alcohol (EtOH) in vivo. It would then be possible to demonstrate EtOH accumulation following exposure to EtAc vapor. Preliminary studies showed that rat blood incubated at 37 C does hydrolyze EtAc to EtOH, with a half-time of approximately 65 min. Analyses were done by gas chromatography. To study this reaction in vivo, rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital, and cannulae were inserted into the femoral arteries. EtAc was injected ip as a 25% () solution in corn oil (1.6 g/kg) and blood samples were drawn periodically. Hydrolysis was very rapid in vivo, with a half-time estimated at 5-10 min. Inhalation studies were then carried out by exposing anesthetized rats to several concentrations of EtAc vapor via an endotracheal tube. When EtAc concentrations were increased above 2000 ppm, EtAc absorption exceeded EtOH oxidation, leading to an accumulation of EtOH in the blood. Although blood EtOH concentrations increased steadily to over 0.10 g/100 mL in 5 hr, EtAc remained consistently below 0.01 g/100 mL and did not change throughout the course of the experiment, again indicating rapid hydrolysis. The data indicate that EtOH will accumulate during exposure to EtAc if the ambient concentration of EtAc is sufficiently high.
Gallaher EJ, Loomis TA; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 34 (2): 309-313 (1975)
... Ethyl acetate ... metabolism produces corresponding ethyl alcohol & is partly excreted in exhaled air & urine & partly metabolized.
Snyder, R. (ed.). Ethel Browning's Toxicity and Metabolism of Industrial Solvents. Second Edition. Volume 3 Alcohols and Esters. New York, NY: Elsevier, 1992., p. 237
Metabolic studies in the rat have revealed an approximate 2000 ppm no-effect level. At higher levels, the rate of hydrolysis of ethyl acetate appeared to exceed ethanol oxidation, leading to its accumulation in the vascular system. Also, when it was injected intraperitoneally at 1.6 g/kg, hydrolysis to acetic acid and ethanol occurred rapidly. Intraperitoneal injections of 1 mL/kg to male rats for 8 days increased the blood pyruvic and lactic acid content considerably and also elevated the glycolytic enzymatic activity.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. 567
No reports found; [TDR, p. 625]
TDR - Ryan RP, Terry CE, Leffingwell SS (eds). Toxicology Desk Reference: The Toxic Exposure and Medical Monitoring Index, 5th Ed. Washington DC: Taylor & Francis, 1999., p. 625