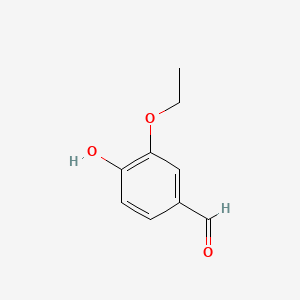

1. 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
2. Ethylvanillin
1. 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
2. Ethylvanillin
3. 121-32-4
4. Bourbonal
5. Ethylprotal
6. Ethavan
7. Ethovan
8. Vanillal
9. Vanirom
10. Vanilal
11. 4-hydroxy-3-ethoxybenzaldehyde
12. Quantrovanil
13. Rhodiarome
14. Benzaldehyde, 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxy-
15. Ethyl Protal
16. Protocatechuic Aldehyde Ethyl Ether
17. Vanillin, Ethyl-
18. Vanirome
19. 2-ethoxy-4-formylphenol
20. Ethylprotocatechuic Aldehyde
21. 3-ethoxyprotocatechualdehyde
22. Fema No. 2464
23. Arovanillon
24. Vanbeenol
25. Ethyl-vanillin
26. Ethylprotocatechualdehyde-3-ethyl Ether
27. 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde
28. Nsc 1803
29. Mfcd00006944
30. 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxy Benzaldehyde
31. Ethyl Vanillin (nf)
32. Ethyl Vanillin [nf]
33. Nsc-1803
34. Nsc-67240
35. Ethyl Protocatechuic Aldehyde
36. Yc9st449yj
37. Chebi:48408
38. Protocatechuic Aldehyde 3-ethyl Ether
39. J2.006k
40. Ncgc00091583-02
41. Dsstox_cid_1968
42. Wln: Vhr Dq Co2
43. Dsstox_rid_76432
44. Dsstox_gsid_21968
45. Quantrovanil, Vanillal
46. Cas-121-32-4
47. Ccris 1346
48. Hsdb 945
49. Einecs 204-464-7
50. Unii-yc9st449yj
51. Brn 1073761
52. Aethylvanillin
53. Vanillin,ethyl
54. Ai3-00786
55. Ethyl Vaniilin Fcc
56. Ethyl Vanillin, Usan?
57. Ethyl Protocatechualdehyde
58. Ethoxy, Hydroxybenzaldehyde
59. Ec 204-464-7
60. Ethyl Vanillin [ii]
61. Ethyl Vanillin [mi]
62. Schembl30247
63. 3ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
64. Ethyl Vanillin [fcc]
65. Mls002454403
66. Bidd:er0329
67. Ethyl Vanillin [fhfi]
68. Ethyl Vanillin [hsdb]
69. Ethyl Vanillin [inci]
70. 3-ethoxyl-4-hydroxybenzaldhyde
71. 5-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
72. Vanillin,ethyl [vandf]
73. Chembl508676
74. Ethyl Vanillin [mart.]
75. Dtxsid5021968
76. Ethyl Vanillin [usp-rs]
77. Ethyl Vanillin [who-dd]
78. Fema 2464
79. 3-ethoxy-4-oxidanyl-benzaldehyde
80. Nsc1803
81. 2-ethoxy-4-formyl Phenol
82. Hms2267d23
83. Ethyl Vanillin, Analytical Standard
84. Hy-b0940
85. Nsc67240
86. Zinc2567934
87. Tox21_113535
88. Tox21_202125
89. Tox21_302903
90. 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde,(s)
91. Bbl023011
92. S4568
93. Stk353630
94. Ethyl Vanillin, >=98%, Fcc, Fg
95. Akos000119395
96. Am84355
97. Ccg-213720
98. Cs-4409
99. Ps-4030
100. Ncgc00091583-01
101. Ncgc00091583-03
102. Ncgc00091583-04
103. Ncgc00256500-01
104. Ncgc00259674-01
105. Ac-10881
106. Ethyl Proto-catechualdehyde-3-ethyl Ether
107. Nci60_001511
108. Smr001252229
109. Sy011364
110. Db-061895
111. E0050
112. Ft-0615625
113. D01086
114. D70878
115. Ab00949623_05
116. A804713
117. Q416958
118. Sr-01000865052
119. Q-200375
120. Sr-01000865052-2
121. 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, Reagentplus(r), 99%
122. F2190-0622
123. 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 99%
124. Ethyl Vanillin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
125. Ethyl Vanillin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 166.17 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 166.062994177 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 166.062994177 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 147 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Ethyl (14C)-vanillin was administered to male and female Sprague-Dawley CD rats by gavage in polyethylene glycol solution at single doses of 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg bw. Ethyl vanillin was rapidly absorbed and peak plasma radioactivity occurred within 2 hr after dosing at all dose levels, falling rapidly to undetectable levels within 96 hr. Plasma radioactivity tended to be higher in female than male rats and it was postulated that this might reflect a lower metabolic capacity of female rats. Urinary excretion of radioactivity was rapid and more than 94% of the dose was excreted by this route within 24 hr. Only 1-5% of the dose was excreted in faeces. After 5 days, more than 99% of the administered dose was excreted. No radioactivity was detected in expired air, indicating that the aromatic ring was in a metabolically stable position.
WHO/JECFA; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives monograph 683. Ethyl vanillin (WHO Food Additives Series 26). Available from, as of June 9, 2015: https://inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
A healthy adult male volunteer drank a 235 ml aliquot of a liquid dietary supplement containing an unknown quantity of ethyl vanillin. A concentration of 13 mg ethyl vanillic acid/g creatinine was found in a 12-hour urine sample. The compound was not present in urine collected before exposure.
WHO/JECFA; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives monograph 683. Ethyl vanillin (WHO Food Additives Series 26). Available from, as of June 9, 2015: https://inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Ethyl vanillic acid was identified by GC/MS in the urine of a 9-year old female patient who had received liquid dietary supplementation flavored with vanilla. Other patients excreting this acid were also known to have consumed foodstuffs flavored with ethyl vanillin. Eight different urine samples containing more than 50 mg ethyl vanillic acid/g creatinine were also found to contain small amounts of vanillylmandelic acid. Unchanged ethyl vanillin was not detected in any of the urine samples.
WHO/JECFA; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives monograph 683. Ethyl vanillin (WHO Food Additives Series 26). Available from, as of June 9, 2015: https://inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
During urinary organic acid profiling in human subjects, several patients excreted high concentrations of ethyl vanillic acid (3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid) and traces of 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxy- mandelic acid.
WHO/JECFA; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives monograph 683. Ethyl vanillin (WHO Food Additives Series 26). Available from, as of June 9, 2015: https://inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Ethyl (14C)-vanillin was administered to male and female Sprague Dawley CD rats at single oral doses of 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg bw. Rapid metabolism occurred and the principal metabolite at all dose levels was ethyl vanillic acid. Analysis of urine after hydrolysis with glucuronidase and/or sulfatase indicated that the major metabolites were glucuronide or sulfate conjugates of ethyl vanillic acid (56-62%), ethyl vanillyl alcohol (15-20%), and ethyl vanillin (7-12%). A minor proportion of the dose (2-8%) was excreted as the glycine conjugate of vanillic acid (ethyl vanilloyl glycine).
WHO/JECFA; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives monograph 683. Ethyl vanillin (WHO Food Additives Series 26). Available from, as of June 9, 2015: https://inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Early reports indicated that ethyl vanillin was probably metabolized to glucuroethyl vanillin and ethyl vanillic acid, of which some was conjugated with glucuronic and sulfuric acids.
WHO/JECFA; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives monograph 683. Ethyl vanillin (WHO Food Additives Series 26). Available from, as of June 9, 2015: https://inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html