

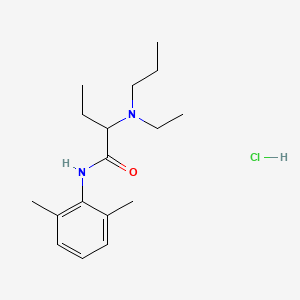

1. 2-(ethylpropylamino)-2',6'-butyroxylidide
2. Duranest
3. Etidocaine
4. W 19053
5. W-19053
6. W19053
1. 36637-19-1
2. Duranest Hydrochloride
3. Duranest
4. Etidocaine Hcl
5. Etidocaine Hydrochloride, (+)-
6. Etidocaine Hydrochloride, (-)-
7. Etidocaine (hydrochloride)
8. 38188-13-5
9. 60yd32ql30
10. Ygd0y35434
11. Duranest; Duranest Hydrochloride; W 19053
12. W-19053
13. N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-[ethyl(propyl)amino]butanamide;hydrochloride
14. (+/-)-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylpropylamino)butyramide Monohydrochloride
15. Butanamide, N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylpropylamino)-, Monohydrochloride, (+)-
16. Butanamide, N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylpropylamino)-, Monohydrochloride, (-)-
17. 38188-14-6
18. G6n3b3u8e6
19. Unii-60yd32ql30
20. Unii-ygd0y35434
21. Duranest (tn)
22. Schembl419100
23. Chebi:4905
24. Chembl1200597
25. Hy-b2080a
26. Dtxsid70957895
27. Etidocaine Hydrochloride [mi]
28. Etidocaine Hydrochloride [mart.]
29. Etidocaine Hydrochloride [vandf]
30. Etidocaine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
31. Cs-0031033
32. Ft-0696974
33. Etidocaine Hydrochloride [orange Book]
34. D00737
35. Butanamide, N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylpropylamino)-, Hydrochloride
36. Butanamide, N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylpropylamino)-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
37. Butanamide, N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylpropylamino)-, Monohydrochloride
38. N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-[ethyl(propyl)amino]butanimidic Acid--hydrogen Chloride (1/1)
39. Butanamide, N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylpropylamino)-, (+/-)-, Monohydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 312.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H29ClN2O |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 312.1968412 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 312.1968412 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 32.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 283 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Anesthetics, Local
Drugs that block nerve conduction when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentrations. They act on any part of the nervous system and on every type of nerve fiber. In contact with a nerve trunk, these anesthetics can cause both sensory and motor paralysis in the innervated area. Their action is completely reversible. (From Gilman AG, et. al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed) Nearly all local anesthetics act by reducing the tendency of voltage-dependent sodium channels to activate. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Local.)
