
1. Ay 24,236
2. Ay 24236
3. Ay-24,236
4. Ay-24236
5. Etodolac, (+-)-isomer
6. Etodolac, (-)-isomer
7. Etodolac, (s)-isomer
8. Etodolac, Monosodium Salt
9. Etodolac, Monosodium Salt, (+-) Isomer
10. Etodolac, Monosodium Salt, (s)-isomer
11. Etodolic Acid
12. Lodine
13. Ramodar
14. Ultradol
1. 41340-25-4
2. Etodolic Acid
3. Lodine
4. Ultradol
5. Lodine Xl
6. Ay-24236
7. Edolan
8. Ramodar
9. Ay-24,236
10. Etodolaco
11. Etodolacum
12. Tedolan
13. Zedolac
14. Rac-etodolac
15. Ay 24236
16. Eccoxolac
17. Flancox
18. Napilac
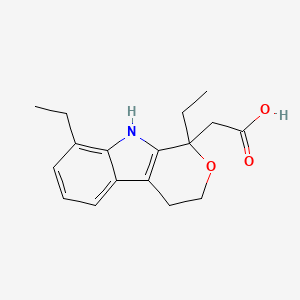
19. 2-(1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetic Acid
20. Lodin Xl
21. 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-acetic Acid
22. Pyrano[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic Acid, 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-
23. (rs)-etodolic Acid
24. 1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1,8-diethylpyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-acetic Acid
25. 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic Acid
26. 2-(1,8-diethyl-4,9-dihydro-3h-pyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetic Acid
27. Chembl622
28. Nsc-282126
29. (1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetic Acid
30. Pyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-acetic Acid, 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-
31. Mls000028474
32. Chebi:4909
33. Rak-591
34. 2-{1,8-diethyl-1h,3h,4h,9h-pyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl}acetic Acid
35. (1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-pyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)-acetic Acid
36. Nih-9918
37. Nsc282126
38. Smr000058443
39. Ay-24-236
40. Dsstox_cid_615
41. (+-)-1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-acetic Acid
42. (rs)-2-(1,8-diethyl-4,9-dihydro-3h-pyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetic Acid
43. Etodolacum [inn-latin]
44. Dsstox_rid_75691
45. Dsstox_gsid_20615
46. Etodolaco [inn-spanish]
47. 2m36281008
48. Hypen
49. 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-pyrano[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic Acid
50. 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-ylacetic Acid
51. (+/-)-1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-acetic Acid
52. Ccris 3923
53. Sr-01000000100
54. Nsc 282126
55. Etogesic
56. Osteluc
57. Etodolac O
58. Etodlic Acid
59. Lodine Sr
60. Etodolac [usan:usp:inn:ban]
61. Etodolac- Bio-x
62. Ncgc00016849-01
63. Etodolac,(s)
64. Prestwick_209
65. Cas-41340-25-4
66. Lodine (tn)
67. Mfcd00133313
68. Unii-2m36281008
69. Etodolac Assay Standard
70. Spectrum_001244
71. Etodolac [usan]
72. Etodolac [inn]
73. Etodolac [jan]
74. Etodolac [mi]
75. Etodolac [vandf]
76. Opera_id_1774
77. Prestwick0_000231
78. Prestwick1_000231
79. Prestwick2_000231
80. Prestwick3_000231
81. Spectrum2_001387
82. Spectrum3_001429
83. Spectrum4_000410
84. Spectrum5_001347
85. Etodolac [mart.]
86. Etodolac [usp-rs]
87. Etodolac [who-dd]
88. Schembl3903
89. Lopac0_000479
90. (+/-)-etodolac
91. Bspbio_000301
92. Bspbio_003138
93. Kbiogr_000680
94. Kbioss_001724
95. Mls001077315
96. Mls006011566
97. Divk1c_000147
98. Etodolac [green Book]
99. Spectrum1501005
100. Etodolac (jp17/usp/inn)
101. Spbio_001374
102. Spbio_002222
103. Etodolac [orange Book]
104. Bpbio1_000333
105. Gtpl7185
106. Etodolac [ep Monograph]
107. Etodolac For Peak Identification
108. Dtxsid9020615
109. Etodolac [usp Monograph]
110. Hms500h09
111. Kbio1_000147
112. Kbio2_001724
113. Kbio2_004292
114. Kbio2_006860
115. Kbio3_002358
116. Ninds_000147
117. Hms1568p03
118. Hms1921b09
119. Hms2092o20
120. Hms2095p03
121. Hms2231d04
122. Hms3259p10
123. Hms3261o20
124. Hms3374g09
125. Hms3712p03
126. Pharmakon1600-01501005
127. Bcp28411
128. Tox21_110644
129. Tox21_202218
130. Tox21_500479
131. Bdbm50016799
132. Ccg-39005
133. Nsc757821
134. Pyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-acetic Acid, 1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1,8-diethyl-
135. Akos015838610
136. Pyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-acetic Acid, 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-(+-)-
137. Tox21_110644_1
138. Ac-4231
139. Cs-0832
140. Db00749
141. Lp00479
142. Nc00718
143. Nsc-757821
144. Sdccgsbi-0050463.p004
145. Etodolac 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
146. Idi1_000147
147. Ncgc00015399-03
148. Ncgc00015399-04
149. Ncgc00015399-05
150. Ncgc00015399-06
151. Ncgc00015399-07
152. Ncgc00015399-08
153. Ncgc00015399-09
154. Ncgc00015399-11
155. Ncgc00015399-12
156. Ncgc00015399-13
157. Ncgc00015399-15
158. Ncgc00015399-16
159. Ncgc00015399-26
160. Ncgc00089769-02
161. Ncgc00089769-03
162. Ncgc00089769-04
163. Ncgc00089769-05
164. Ncgc00089769-06
165. Ncgc00089769-07
166. Ncgc00259767-01
167. Ncgc00261164-01
168. Br164431
169. Hy-76251
170. Sbi-0050463.p003
171. Ab00052194
172. E0858
173. Eu-0100479
174. Ft-0607046
175. Ft-0668424
176. Ft-0668425
177. C06991
178. D00315
179. E 0516
180. Pyrano[3, 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-
181. Ab00052194_17
182. 340e254
183. Q-201099
184. Q2465218
185. Sr-01000000100-2
186. Sr-01000000100-4
187. Sr-01000000100-7
188. Brd-a74667430-001-05-3
189. Brd-a74667430-001-15-2
190. 1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic Acid
191. Etodolac, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
192. F2173-0681
193. Z1820178466
194. Etodolac, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
195. 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyranol[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic Acid
196. 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano(3,4-b)indol-1-acetic Acid
197. 2-(1,8-diethyl-4,9-dihydro-3h-pyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetic Acid.
198. Pyrano(3,4,b)indole-1-acetic Acid, 1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1,8-diethyl-
199. Ay 24,236; Ay 24236;ay-24,236; Ay-24236; Ay24,236; Ay24236
200. Etodolac For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
201. Pyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-acetic Acid, 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-(+/-)-
| Molecular Weight | 287.35 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H21NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 287.15214353 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 287.15214353 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 62.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 400 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Etodolac |
| PubMed Health | Etodolac (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Antirheumatic, Central Nervous System Agent, Musculoskeletal Agent |
| Drug Label | Etodolac capsules and tablets, USP are members of the pyranocarboxylic acid group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Each tablet and capsule contains etodolac for oral administration. Etodolac is a racemic mixture of [+]S and [-]R-enan... |
| Active Ingredient | Etodolac |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Tablet; Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 200mg; 600mg; 500mg; 400mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ani Pharms; Teva; Apotex; Taro; Taro Pharm Inds; Zydus Pharms Usa; Sandoz; Mylan |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Etodolac |
| PubMed Health | Etodolac (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Antirheumatic, Central Nervous System Agent, Musculoskeletal Agent |
| Drug Label | Etodolac capsules and tablets, USP are members of the pyranocarboxylic acid group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Each tablet and capsule contains etodolac for oral administration. Etodolac is a racemic mixture of [+]S and [-]R-enan... |
| Active Ingredient | Etodolac |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Tablet; Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 200mg; 600mg; 500mg; 400mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ani Pharms; Teva; Apotex; Taro; Taro Pharm Inds; Zydus Pharms Usa; Sandoz; Mylan |
For acute and long-term management of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for the management of pain.
FDA Label
Etodolac is an anti-inflammatory agent with analgesic and antipyretic properties. It is used to treat osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and control acute pain. The therapeutic effects of etodolac are achieved via inhibition of the synthesis of prostaglandins involved in fever, pain, swelling and inflammation. Etodolac is administered as a racemate. As with other NSAIDs, the S-form has been shown to be active while the R-form is inactive. Both enantiomers are stable and there is no evidence of R- to S- conversion _in vivo_.
Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors
A subclass of cyclooxygenase inhibitors with specificity for CYCLOOXYGENASE-2. (See all compounds classified as Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors.)
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AB - Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
M01AB08 - Etodolac
Absorption
Based on mass balance studies, the systemic bioavailability of etodolac from either the tablet or capsule formulation is at least 80%.
Route of Elimination
It is not known whether etodolac is excreted in human milk; however, based on its physical-chemical properties, excretion into breast milk is expected. Etodolac is extensively metabolized in the liver. The hydroxylated-etodolac metabolites undergo further glucuronidation followed by renal excretion and partial elimination in the feces (16% of dose). Approximately 1% of a etodolac dose is excreted unchanged in the urine with 72% of the dose excreted into urine as parent drug plus metabolite.
Volume of Distribution
390 mL/kg
Clearance
Oral cl=49.1 mL/h/kg [Normal healthy adults]
Oral cl=49.4 mL/h/kg [Healthy males (18-65 years)]
Oral cl=35.7 mL/h/kg [Healthy females (27-65 years)]
Oral cl=45.7 mL/h/kg [Eldery (>65 years)]
Oral cl=58.3 mL/h/kg [Renal impairement (46-73 years)]
Oral cl=42.0 mL/h/kg [Hepatic impairement (34-60 years)]
Etodolac is extensively metabolized in the liver. Renal elimination of etodolac and its metabolites is the primary route of excretion (72%). Metabolites found in urine (with percents of the administered dose) are: unchanged etodolac (1%), etodolac glucuronide (13%), hydroxylated metabolites (6-, 7-, and 8-OH; 5%), hydroxylated metabolite glucuronides (20%), and unidentified metabolites (33%). Fecal excretion accounts for 16% of its elimination.
Etodolac has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[2-(1,8-Diethyl-4,9-dihydro-3H-pyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetyl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Terminal t1/2, 7.3 ± 4.0 hours. Distribution t1/2, 0.71 ± 0.50 hours
Similar to other NSAIDs, the anti-inflammatory effects of etodolac result from inhibition of the enzyme cycooxygenase (COX). This decreases the synthesis of peripheral prostaglandins involved in mediating inflammation. Etodolac binds to the upper portion of the COX enzyme active site and prevents its substrate, arachidonic acid, from entering the active site. Etodolac was previously thought to be a non-selective COX inhibitor, but it is now known to be 5 50 times more selective for COX-2 than COX-1. Antipyresis may occur by central action on the hypothalamus, resulting in peripheral dilation, increased cutaneous blood flow, and subsequent heat loss.