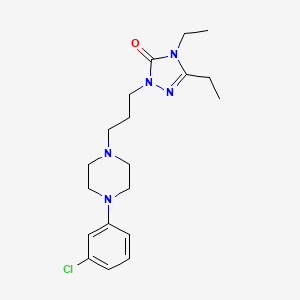

1. (1,3-(4-m-chlorophenyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-3,4-diethyl-delta(2)-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
2. Etoperidone Monohydrochloride
1. 52942-31-1
2. Etoperidone [inn]
3. Kai6mvo39z
4. 2-[3-[4-(3-chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl]-4,5-diethyl-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
5. Etoperidona
6. Etoperidonum
7. Etoperidona [spanish]
8. Unii-kai6mvo39z
9. Etoperidonum [inn-latin]
10. Etoperidona [inn-spanish]
11. Etoperidone [mi]
12. Schembl49314
13. Etoperidone [who-dd]
14. Chembl1743259
15. Dtxsid0023034
16. Bdbm82438
17. Chebi:135589
18. Zinc3830815
19. Nsc_40589
20. Pdsp1_000523
21. Pdsp2_000521
22. Db09194
23. Cas_52942-31-1
24. L001188
25. Q5404839
26. 1,2,4-triazol-3-one, 2-(3-(4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-4,5-diethyl-2,4-dihydro-
27. 1-(3-(4-(m-chlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-3,4-diethyl-d2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
28. 2-{3-[4-(3-chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl}-4,5-diethyl-2,4-dihydro-3h-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
| Molecular Weight | 377.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H28ClN5O |
| XLogP3 | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 377.1982382 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 377.1982382 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 42.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 506 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Etoperidone has been studied for the treatment of depression, tremors in Parkinson, extrapyramidal symptoms and male impotence. It is not certain if it was ever approved and marketed but its current status is withdrawn.
Etoperidone has a biphasic effect on the central transmission of serotonin. It presents the capacity to inhibit serotonin receptor but also to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine. As part of its actions, etoperidone also inhibits the -adrenergic receptors which directly corresponds to the sedative and cardiovascular effects. The presence of both effects caused that the effective dose of etoperidone was poorly tolerated thus, efforts have been made to separate the serotonergic and adrenergic functions in order to generate etoperidone-derivatives like nefazodone.
N - Nervous system
N06 - Psychoanaleptics
N06A - Antidepressants
N06AB - Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
N06AB09 - Etoperidone
Absorption
The absorption and bioavailability is highly variable between individuals and can be as low as 12%. The lower bioavailability is explained due to its high metabolism. The mean time to peak plasma concentration is ranged from 1.4-4.8 hours.
Route of Elimination
The elimination of an oral dose of etoperidone presents a division of 78.8% found in urine and 9.6% found in faeces. On the elimination route, less than 0.01% of the etoperidone dose is represented by the unchanged drug while the rest is formed by 21 different metabolites.
Volume of Distribution
The high protein binding presented in etoperidone modulates its volume of distribution to a range of 0.23 to 0.69 L/kg.
Clearance
The apparent clearance of etoperidone was 1.01 ml/min.
Etoperidone is highly metabolized and it forms 21 different metabolites that can be found in plasma, urine and faeces. The metabolism of etoperidone is thought to be related to 5 different reaction pathways that are alkyl oxidation, piperazinyl oxidation, N-dealkylation, phenyl hydroxylation and conjugation.
Etoperidone has known human metabolites that include 1-(3-Chlorophenyl)piperazine, 2-[3-[4-(3-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl]-4-ethyl-5-(1-hydroxyethyl)-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, 2-[3-[4-(3-chloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl]-4,5-diethyl-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, and 4,5-diethyl-2-propyl-1,2,4-triazol-3-one.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
After oral administration of etoperidone the terminal half-life was 21.7 hours.
The activity of etoperidone is made mainly by its major metabolite 1-(3'-chlorophenyl)piperazine (mCPP). mCPP binds with different affinity to most of the serotonergic receptors and adrenergic receptors. This metabolite is an agonist of 5-HT2c and an antagonist of 5-HT2a. Part of etoperidone structure contibutes to the activity in the -adrenergic receptors.
