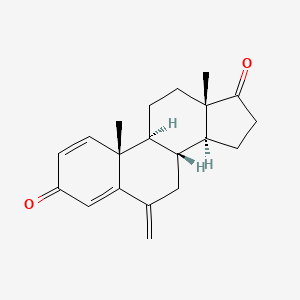

1. 6-methyleneandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione
2. Aromasil
3. Aromasin
4. Aromasine
5. Examestane
6. Fce 24304
7. Fce-24304
1. 107868-30-4
2. Aromasin
3. 6-methyleneandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione
4. Fce 24304
5. Fce-24304
6. Exemestano
7. Exemestanum
8. Exemestanum [inn-latin]
9. Exemestano [inn-spanish]
10. 6-methylene-androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione
11. Androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione, 6-methylene-
12. Fce24304
13. Pnu-155971
14. Aromasine
15. Ny22hmq4bx
16. Chebi:4953
17. (8r,9s,10r,13s,14s)-10,13-dimethyl-6-methylene-7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16-decahydro-3h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17(6h)-dione
18. (8r,9s,10r,13s,14s)-10,13-dimethyl-6-methylene-7,8,9,11,12,13,15,16-octahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17(10h,14h)-dione
19. (8r,9s,10r,13s,14s)-10,13-dimethyl-6-methylidene-7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-dione
20. Aromasil
21. Nsc713563
22. Nsc-758907
23. Exe
24. Dsstox_cid_3037
25. Dsstox_rid_76844
26. Dsstox_gsid_23037
27. 6-methylideneandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione
28. Exemestane [usan:inn:ban]
29. Nikidess
30. (8alpha,10alpha,13alpha)-6-methylideneandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione
31. Aromasin (tn)
32. Smr000466314
33. Cas-107868-30-4
34. Hsdb 7463
35. Curator_000009
36. Unii-ny22hmq4bx
37. Exemestane (jan/usp/inn)
38. Ccris 9351
39. Ncgc00095289-01
40. Exemestane [inn]
41. Exemestane; Aromasin
42. Exemestane, Aromasin
43. Pnu 155971
44. Exemestane [mi]
45. Exemestane [jan]
46. Exemestane [hsdb]
47. Exemestane [usan]
48. Exemestane [vandf]
49. Exemestane [mart.]
50. Schembl6215
51. Aromasin (pharmacia Upjohn)
52. Exemestane [usp-rs]
53. Exemestane [who-dd]
54. Exemestane(fce 24304)
55. Mls000759419
56. Mls001424062
57. Gtpl7073
58. 6-methylenandrosta-1,17-dione
59. Chembl1200374
60. Dtxsid5023037
61. Exemestane [orange Book]
62. Exemestane, >=98% (hplc)
63. Exemestane [ep Monograph]
64. Bcpp000235
65. Exemestane [usp Monograph]
66. Hms2051j04
67. Hms3713h12
68. Bcp23353
69. Zinc3973334
70. Tox21_111499
71. Bdbm50398447
72. Pnu155971
73. S1196
74. Akos015840113
75. Akos015895161
76. Tox21_111499_1
77. Ac-2171
78. Bcp9000676
79. Ccg-100995
80. Cs-1766
81. Db00990
82. Ks-5136
83. Nc00245
84. Nsc 758907
85. Nsc-713563
86. Ncgc00271596-03
87. 6-methylenandrost-1,4-dien-3,17-dione
88. As-31053
89. Cpd000466314
90. Hy-13632
91. Bcp0726000226
92. 6-methylen-androst-1,4-diene-3,17-dione
93. E0941
94. C08162
95. D00963
96. Ab00639936-06
97. Ab00639936-08
98. Ab00639936-09
99. Ab00639936-10
100. Ab00639936_11
101. 868e304
102. A801772
103. Q418819
104. Sr-01000759393
105. Sr-01000759393-4
106. Brd-k33425534-001-12-5
107. Exemestane, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
108. Exemestane, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
109. Exemestane, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
110. Exemestane For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
111. (1s,2r,10r,11s,15s)-2,15-dimethyl-8-methylidenetetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-3,6-diene-5,14-dione
112. Exm
| Molecular Weight | 296.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H24O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 296.177630004 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 296.177630004 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 34.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 653 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aromasin |
| PubMed Health | Exemestane (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | AROMASIN Tablets for oral administration contain 25 mg of exemestane, an irreversible, steroidal aromatase inactivator. Exemestane is chemically described as 6-methylenandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione. Its molecular formula is C20H24O2 and its structu... |
| Active Ingredient | Exemestane |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Exemestane |
| PubMed Health | Exemestane (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | EXEMESTANE tablets for oral administration contain 25 mg of EXEMESTANE, an irreversible, steroidal aromatase inactivator. EXEMESTANE is chemically described as 6-methylenandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione. Its molecular formula is C20H24O2 and its structu... |
| Active Ingredient | Exemestane |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alvogen; Roxane |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aromasin |
| PubMed Health | Exemestane (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | AROMASIN Tablets for oral administration contain 25 mg of exemestane, an irreversible, steroidal aromatase inactivator. Exemestane is chemically described as 6-methylenandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione. Its molecular formula is C20H24O2 and its structu... |
| Active Ingredient | Exemestane |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Exemestane |
| PubMed Health | Exemestane (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | EXEMESTANE tablets for oral administration contain 25 mg of EXEMESTANE, an irreversible, steroidal aromatase inactivator. EXEMESTANE is chemically described as 6-methylenandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione. Its molecular formula is C20H24O2 and its structu... |
| Active Ingredient | Exemestane |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alvogen; Roxane |
Antineoplastic (hormonal).
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 692
Exemestane is indicated for the treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women whose disease has progressed following tamoxifen therapy. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1434
Use of exemestane in premenopausal women is not accepted. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1434
Adverse events of any cause observed in the overall clinical trials program (N=1058) in 5% or greater of patients treated with exemestane 25 mg once daily but not in the comparative study included pain at tumor sites (8%), asthenia (6%) and fever (5%). Adverse events of any cause reported in 2% to 5% of all patients treated with exemestane 25 mg in the overall clinical trials program but not in the comparative study included chest pain, hypoesthesia, confusion, dyspepsia, arthralgia, back pain, skeletal pain, infection, upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, rhinitis, and alopecia.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2602
Less frequent adverse events of any cause (from 2% to 5%) reported in the comparative study for patients receiving /exemestane/ 25 mg once daily were fever, generalized weakness, paresthesia, pathological fracture, bronchitis, sinusitis, rash, itching, urinary tract infection, and lymphedema.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2601
Other adverse effects occurring in at least 5%, regardless of causality, include mental depression, pain, insomnia, anxiety, dyspnea, dizziness, headache, edema, vomiting, abdominal pain, anorexia, cough, flu-like symptoms, hypertension, and constipation.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1044
Lymphocytopenia grade 3 or 4 was also reported in 20% of patients; however, 89% of these patients had a preexisting lower-grade lymphopenia, and 40% either recovered or improved to a lesser severity lymphopenia during exemestane. Patients did not experience a significant increase in viral infections, and no opportunistic infections were observed.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1044
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for EXEMESTANE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women whose disease has progressed following tamoxifen therapy.
FDA Label
Aromatase is an enzyme that converts hormones to estrogen in the body's adrenal glands. The aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are drugs that reduce estrogen levels by blocking the action of aromatase in the adrenal glands. The selective AIs (SAIs) selectively reduce levels of estrogen without interfering with levels of other steroid hormones that are produced by the adrenal gland. Drugs in this class include anastrozole (Arimidex ™), letrozole (Femara ™) and exemestane (Aromasin ™).
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Aromatase Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit AROMATASE in order to reduce production of estrogenic steroid hormones. (See all compounds classified as Aromatase Inhibitors.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L02 - Endocrine therapy
L02B - Hormone antagonists and related agents
L02BG - Aromatase inhibitors
L02BG06 - Exemestane
Absorption
42%
Following oral administration of radiolabeled exemestane, at least 42% of radioactivity was absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Exemestane plasma levels increased by approximately 40% after a high-fat breakfast.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2600
The pharmacokinetics of exemestane are dose proportional after single (10 to 200 mg) or repeated oral doses (0.5 to 50 mg). Following repeated daily doses of exemestane 25 mg, plasma concentrations of unchanged drug are similar to levels measured after a single dose.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2600
Pharmacokinetic parameters in postmenopausal women with advanced breast cancer following single or repeated doses have been compared with those in healthy, postmenopausal women. Exemestane appeared to be more rapidly absorbed in the women with breast cancer than in the healthy women, with a mean tmax of 1.2 hours in the women with breast cancer and 2.9 hours in the healthy women. After repeated dosing, the average oral clearance in women with advanced breast cancer was 45% lower than the oral clearance in healthy postmenopausal women, with corresponding higher systemic exposure. Mean AUC values following repeated doses in women with breast cancer (75.4 nghr/mL) were about twice those in healthy women (41.4 nghr/mL).
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2600
Exemestane is distributed extensively into tissues. Exemestane is 90% bound to plasma proteins and the fraction bound is independent of the total concentration. Albumin and (alpha) 1 -acid glycoprotein both contribute to the binding. The distribution of exemestane and its metabolites into blood cells is negligible.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2600
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for EXEMESTANE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic
Exemestane is extensively metabolized, with levels of the unchanged drug in plasma accounting for less than 10% of the total radioactivity. The initial steps in the metabolism of exemestane are oxidation of the methylene group in position 6 and reduction of the 17-keto group with subsequent formation of many secondary metabolites. Each metabolite accounts only for a limited amount of drug-related material. The metabolites are inactive or inhibit aromatase with decreased potency compared with the parent drug. One metabolite may have androgenic activity. Studies using human liver preparations indicate that cytochrome P-450 3A4 (CYP 3A4) is the principal isoenzyme involved in the oxidation of exemestane.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2600
24 hours
Following oral administration to healthy postmenopausal women, exemestane is rapidly absorbed. After maximum plasma concentration is reached, levels decline polyexponentially with a mean terminal half-life of about 24 hours.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2600
... The terminal half-life was 8.9 hr. Maximal estradiol suppression of 62 +/- 14% was observed at 12 hr.
PMID:14671195 Mauras N et al; J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88 (12): 5951-6 (2003)
Breast cancer cell growth may be estrogen-dependent. Aromatase (exemestane) is the principal enzyme that converts androgens to estrogens both in pre- and postmenopausal women. While the main source of estrogen (primarily estradiol) is the ovary in premenopausal women, the principal source of circulating estrogens in postmenopausal women is from conversion of adrenal and ovarian androgens (androstenedione and testosterone) to estrogens (estrone and estradiol) by the aromatase enzyme in peripheral tissues. Estrogen deprivation through aromatase inhibition is an effective and selective treatment for some postmenopausal patients with hormone-dependent breast cancer. Exemestane is an irreversible, steroidal aromatase inactivator, structurally related to the natural substrate androstenedione. It irreversibly binds to the active site causing permanent inhibition necessitating de novo synthesis to restore enzymatic function. Exemestane significantly lowers circulating estrogen concentrations in postmenopausal women, but has no detectable effect on the adrenal biosynthesis of corticosteroids or aldosterone. This reduction in serum and tumor concentrations of estrogen delays tumor growth and disease progression. Exemestane has no effect on other enzymes involved in the steroidogenic pathway up to a concentration at least 600 times higher than that inhibiting the aromatase enzyme.
... exemestane is a potent aromatase inhibitor in men and an alternative to the choice of available inhibitors...
PMID:14671195 Mauras N et al; J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88 (12): 5951-6 (2003)
Estrogen deprivation through aromatase inhibition is an effective and selective treatment for some postmenopausal patients with hormone-dependent breast cancer. Exemestane is an irreversible, steroidal aromatase inactivator, structurally related to the natural substrate androstenedione. It acts as a false substrate for the aromatase enzyme, and is processed to an intermediate that binds irreversibly to the active site of the enzyme causing its inactivation, an effect also known as "suicide inhibition." Exemestane significantly lowers circulating estrogen concentrations in postmenopausal women, but has no detectable effect on adrenal biosynthesis of corticosteroids or aldosterone. Exemestane has no effect on other enzymes involved in the steroidogenic pathway up to a concentration at least 600 times higher than that inhibiting the aromatase enzyme.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2600
... Treatment with exemestane suppressed whole body aromatization from a mean pretreatment value of 2.059% to 0.042% (mean suppression of 97.9%). Plasma levels of estrone, estradiol, and estrone sulfate were found to be suppressed by 94.5%, 92.2%, and 93.2%, respectively. This is the first study revealing near total aromatase inhibition in vivo with the use of a steroidal aromatase inhibitor. The observation that exemestane is a highly potent aromatase inhibitor, together with the fact that the drug is administered p.o. and causes limited side effects, suggests that exemestane is a promising new drug for the treatment of hormone sensitive breast cancer.
PMID:9748124 Geisler J et al; Clin Cancer Res 4 (9): 2089-93 (1998)
... Exemestane induces aromatase degradation in a dose-responsive manner (25-200 nmol/L), and the effect can be seen in as early as 2 hours. Metabolic labeling with S(35)-methionine was used to determine the half-life (t(1/2)) of aromatase protein. In the presence of 200 nmol/L exemestane, the t(1/2) of aromatase was reduced to 12.5 hours from 28.2 hours in the untreated cells. ...
PMID:17079446 Wang X et al; Cancer Res 66 (21): 10281-6 (2006)