
1. Antara Micronized Procetofen
2. Apo Feno Micro
3. Apo Fenofibrate
4. Apo-feno-micro
5. Apo-fenofibrate
6. Azu, Fenofibrat
7. Cil
8. Controlip
9. Debat, Fnofibrate
10. Durafenat
11. Fnofibrate Debat
12. Fnofibrate Msd
13. Fenobeta
14. Fenofanton
15. Fenofibrat Abz
16. Fenofibrat Al
17. Fenofibrat Azu
18. Fenofibrat Fph
19. Fenofibrat Heumann
20. Fenofibrat Hexal
21. Fenofibrat Ratiopharm
22. Fenofibrat Stada
23. Fenofibrat Von Ct
24. Fenofibrat-ratiopharm
25. Gen Fenofibrate
26. Gen-fenofibrate
27. Heumann, Fenofibrat
28. Hexal, Fenofibrat
29. Lf 178
30. Lf-178
31. Lf178
32. Lipanthyl
33. Lipantil
34. Liparison
35. Lipidil
36. Lipidil Ter
37. Lipidil-ter
38. Livesan
39. Lofibra
40. Micronized Procetofen, Antara
41. Mtw Fenofibrat
42. Mtw-fenofibrat
43. Normalip
44. Novo Fenofibrate
45. Novo-fenofibrate
46. Nu Fenofibrate
47. Nu-fenofibrate
48. Phenofibrate
49. Pms Fenofibrate Micro
50. Pms-fenofibrate Micro
51. Procetofen
52. Procetofen, Antara Micronized
53. Procetofene
54. Secalip
55. Stada, Fenofibrat
56. Supralip
57. Tricor
1. 49562-28-9
2. Procetofen
3. Lipantil
4. Tricor
5. Lipanthyl
6. Antara
7. Lipidil
8. Fenobrate
9. Secalip
10. Triglide
11. Fenoglide
12. Finofibrate
13. Lipoclar
14. Lipofene
15. Proctofene
16. Fenogal
17. Lipirex
18. Lipofen
19. Sedufen
20. Elasterin
21. Fenotard
22. Protolipan
23. Ankebin
24. Lipidex
25. Lipifen
26. Liposit
27. Lipsin
28. Nolipax
29. Fenofibratum [inn-latin]
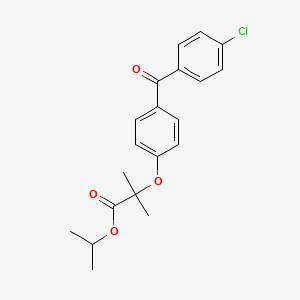
30. Propan-2-yl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate
31. Fenofibrato [inn-spanish]
32. Lipantil (tn)
33. Tricor (tn)
34. Isopropyl 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoate
35. Lf-178
36. Isopropyl 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropionate
37. 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic Acid 1-methylethyl Ester
38. Nsc 281319
39. Fenofibrate Micronized
40. Isopropyl (4'-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-2-phenoxy-2-methyl)propionate
41. Fnf
42. Propanoic Acid, 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-, 1-methylethyl Ester
43. Elasterate
44. Procetofene
45. Luxacor
46. Mfcd00133314
47. Fenofibrate Delayed Release
48. Chembl672
49. Mls000028515
50. Chebi:5001
51. Isopropyl 2-(p-(p-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropionate
52. Isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate
53. Lofibra
54. U202363uos
55. Propanoic Acid, 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methyl-, 1-methylethyl Ester
56. Nsc-281319
57. Ncgc00015437-10
58. Fenofibrato
59. Fenofibratum
60. Smr000058299
61. Supralip
62. Cas-49562-28-9
63. Dsstox_cid_9874
64. Propan-2-yl 2-{4-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]phenoxy}-2-methylpropanoate
65. Dsstox_rid_78828
66. Dsstox_gsid_29874
67. Tricor (micronized)
68. Antara (micronized)
69. Fenomax
70. Isopropyl 2-[p-(p-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropionate
71. Pharmavit
72. Fenofibrate (micronized)
73. Fulcro
74. Cip-fenofibrate
75. 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic Acid 1-methylethyl Ester
76. Lcp-fenochol
77. Lcp-feno
78. Triglide (tn)
79. Fenofibrate Idd-p
80. Lipofen (tn)
81. Antara (tn)
82. Ccris 7282
83. Sr-01000000091
84. Einecs 256-376-3
85. Lf 178
86. Brn 2062462
87. Procetoken
88. Isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropionate
89. Unii-u202363uos
90. Hsdb 7736
91. Fenofibrate,(s)
92. Grs-027
93. Fenofibrate [usan:usp:inn:ban]
94. Prestwick_217
95. Spectrum_001250
96. Opera_id_328
97. Fenofibrate [mi]
98. Prestwick0_000275
99. Prestwick1_000275
100. Prestwick2_000275
101. Prestwick3_000275
102. Spectrum2_001390
103. Spectrum3_001431
104. Spectrum4_000413
105. Spectrum5_001479
106. Fenofibrate [inn]
107. Fenofibrate [jan]
108. Lopac-f-6020
109. Fenofibrate [hsdb]
110. Fenofibrate [usan]
111. Ec 256-376-3
112. F 6020
113. Fenofibrate [vandf]
114. Schembl4670
115. Fenofibrate [mart.]
116. Lopac0_000486
117. Bspbio_000150
118. Bspbio_003162
119. Fenofibrate [usp-rs]
120. Fenofibrate [who-dd]
121. Kbiogr_000706
122. Kbioss_001730
123. Mls001148191
124. Mls002548878
125. Bidd:gt0574
126. Divk1c_000557
127. Fenofibrate (jan/usp/inn)
128. Spectrum1501010
129. Spbio_001380
130. Spbio_002369
131. Fenofibrate [ema Epar]
132. Fenofibrate, >=99%, Powder
133. Bpbio1_000166
134. Fenofibrate (tricor, Trilipix)
135. Gtpl7186
136. Dtxsid2029874
137. Hms501l19
138. Kbio1_000557
139. Kbio2_001730
140. Kbio2_004298
141. Kbio2_006866
142. Kbio3_002382
143. Fenofibrate [orange Book]
144. Ninds_000557
145. Fenofibrate [ep Monograph]
146. Fenofibrate [usp Impurity]
147. Hms1568h12
148. Hms1921b17
149. Hms2090g20
150. Hms2092b05
151. Hms2095h12
152. Hms2231b14
153. Hms3259k03
154. Hms3261b13
155. Hms3369m13
156. Hms3649d20
157. Hms3655k12
158. Hms3712h12
159. Isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoate
160. Pharmakon1600-01501010
161. Zinc584092
162. Fenofibrate [usp Monograph]
163. Albb-028958
164. Bcp21243
165. Tox21_110147
166. Tox21_300151
167. Tox21_500486
168. 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic Acid Isopropyl Ester
169. Bdbm50085042
170. Ccg-38996
171. Nsc281319
172. Nsc757822
173. S1794
174. Akos005107777
175. Tox21_110147_1
176. Ab03716
177. Ac-4227
178. Cs-0892
179. Db01039
180. Lp00486
181. Ms-2223
182. Nc00452
183. Nsc-757822
184. Sdccgsbi-0050470.p004
185. Idi1_000557
186. Ncgc00015437-01
187. Ncgc00015437-02
188. Ncgc00015437-03
189. Ncgc00015437-04
190. Ncgc00015437-05
191. Ncgc00015437-06
192. Ncgc00015437-07
193. Ncgc00015437-08
194. Ncgc00015437-09
195. Ncgc00015437-11
196. Ncgc00015437-12
197. Ncgc00015437-13
198. Ncgc00015437-14
199. Ncgc00015437-16
200. Ncgc00015437-17
201. Ncgc00015437-31
202. Ncgc00021475-03
203. Ncgc00021475-04
204. Ncgc00021475-05
205. Ncgc00021475-06
206. Ncgc00021475-07
207. Ncgc00021475-08
208. Ncgc00253945-01
209. Ncgc00261171-01
210. Fenofibrate (micronized) (fenofibrate
211. Fenofibrate, Analytical Reference Material
212. Hy-17356
213. Sy052561
214. Sbi-0050470.p003
215. Db-051642
216. Ab00052196
217. Eu-0100486
218. F0674
219. Ft-0626400
220. Ft-0654669
221. Sw196525-4
222. C07586
223. D00565
224. Ab00052196-15
225. Ab00052196-16
226. Ab00052196_17
227. Ab00052196_18
228. 562f289
229. A827746
230. Q419724
231. Q-201111
232. Sr-01000000091-2
233. Sr-01000000091-5
234. Sr-01000000091-6
235. Sr-01000000091-8
236. Brd-k50388907-001-05-6
237. Brd-k50388907-001-18-9
238. Brd-k50388907-001-20-5
239. Sr-01000000091-16
240. Z2768724415
241. Fenofibrate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
242. Isopropyl 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoate
243. 1-methylethyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate
244. 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoicacidisopropylester
245. Fenofibrate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
246. Isopropyl (4''-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-2-phenoxy-2-methyl)propionate
247. 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic Acid 1-methyl-ethyl Ester
248. 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropionic Acid Isopropyl Ester
249. Fenofibrate, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
250. Isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoate;fenofibrate
251. Propanoic Acid, 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-, 1-methylethylester
1. 42017-89-0
2. Fenofibric Acid
| Molecular Weight | 360.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H21ClO4 |
| XLogP3 | 5.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 360.1128368 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 360.1128368 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 52.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 458 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Antara |
| PubMed Health | Fenofibrate (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | Fenofibrate, is a lipid regulating agent available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 54 mg or 160 mg of fenofibrate, USP. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid, 1-methylethy... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 43mg; 130mg; 30mg; 90mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Lupin Atlantis |
| 2 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fenofibrate |
| PubMed Health | Fenofibrate (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 43mg; 200mg; 130mg; 67mg; 134mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Teva; Apotex; Dr Reddys Labs Sa; Impax Labs |
| 3 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fenofibrate |
| PubMed Health | Fenofibric acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | FENOGLIDE (fenofibrate) Tablets, is a lipid regulating agent available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 40 mg or 120 mg fenofibrate. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl) phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid,... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Capsule |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 43mg; 160mg; 54mg; 48mg; 130mg; 107mg; 145mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Ranbaxy; Valeant Intl; Teva; Lupin; Mylan; Impax Labs |
| 4 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fenoglide |
| Drug Label | LIPOFEN (fenofibrate capsules, USP), is a lipid regulating agent available as hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. Each hard gelatin capsule contains 50 or 150 mg of fenofibrate, USP. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chloroben... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 120mg; 40mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Santarus |
| 5 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fibricor |
| Drug Label | TRICOR (fenofibrate tablets), is a lipid regulating agent available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 48 mg or 145 mg of fenofibrate. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl) phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid,... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibric acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 105mg; 35mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mutual Pharm |
| 6 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lipofen |
| Drug Label | Triglide (fenofibrate) Tablets, is a lipid regulating agent available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 50 mg or 160 mg of fenofibrate. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl) phenoxy] 2-methyl-pr... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 150mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Cipher Pharms |
| 7 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tricor |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 145mg; 48mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Abbvie |
| 8 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Triglide |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 160mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Skyepharma Ag |
| 9 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Antara |
| PubMed Health | Fenofibrate (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | Fenofibrate, is a lipid regulating agent available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 54 mg or 160 mg of fenofibrate, USP. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid, 1-methylethy... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 43mg; 130mg; 30mg; 90mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Lupin Atlantis |
| 10 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fenofibrate |
| PubMed Health | Fenofibrate (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 43mg; 200mg; 130mg; 67mg; 134mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Teva; Apotex; Dr Reddys Labs Sa; Impax Labs |
| 11 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fenofibrate |
| PubMed Health | Fenofibric acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | FENOGLIDE (fenofibrate) Tablets, is a lipid regulating agent available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 40 mg or 120 mg fenofibrate. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl) phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid,... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Capsule |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 43mg; 160mg; 54mg; 48mg; 130mg; 107mg; 145mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Ranbaxy; Valeant Intl; Teva; Lupin; Mylan; Impax Labs |
| 12 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fenoglide |
| Drug Label | LIPOFEN (fenofibrate capsules, USP), is a lipid regulating agent available as hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. Each hard gelatin capsule contains 50 or 150 mg of fenofibrate, USP. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chloroben... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 120mg; 40mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Santarus |
| 13 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fibricor |
| Drug Label | TRICOR (fenofibrate tablets), is a lipid regulating agent available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 48 mg or 145 mg of fenofibrate. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl) phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid,... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibric acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 105mg; 35mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mutual Pharm |
| 14 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lipofen |
| Drug Label | Triglide (fenofibrate) Tablets, is a lipid regulating agent available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 50 mg or 160 mg of fenofibrate. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl) phenoxy] 2-methyl-pr... |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 150mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Cipher Pharms |
| 15 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tricor |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 145mg; 48mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Abbvie |
| 16 of 16 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Triglide |
| Active Ingredient | Fenofibrate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 160mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Skyepharma Ag |
Fenofibrate is used as an adjunct to dietary therapy to decrease elevated serum total and LDL-cholesterol, triglyceride, and apo B concentrations, and to increase HDL-cholesterol concentrations in the management of primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia, including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and other causes of hypercholesterolemia.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1731
Fenofibrate also is used as an adjunct to dietary therapy in the management of patients with elevated serum triglyceride concentrations. Efficacy of the drug in reducing the risk of pancreatitis in patients with marked elevations in triglyceride concentrations (i.e., greater than 2000 mg/dL) has not been established. Fenofibrate is not indicated for use in patients with type I hyperlipoproteinemia who have elevated triglyceride and chylomicron concentrations but normal VLDL-cholesterol concentrations.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1732
/EXPL THER/ Inflammation is implicated in chronic heart failure. In this study, the potential inhibitory effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha) activator fenofibrate on monocyte adhesion in chronic heart failure patients was investigated in vitro. ... Isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells were collected from 36 patients (aged 65 +/- 8 years) with symptomatic chronic heart failure and from 12 healthy control subjects. The cultured human aortic endothelial cells were stimulated with or without 2 ng mL(-1) tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and the inhibitory effects of fenofibrate at 25, 50, 100 and 200 uM on endothelial mononuclear cell adhesion were tested. Furthermore, the human aortic endothelial cells were stimulated with 70% sera obtained from chronic heart failure patients and control individuals, respectively, with or without pretreatments with fenofibrate. The endothelial expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) was then confirmed by mRNA expression and Western blot. ... The increased adhesion of peripheral blood mononuclear cells to TNF-alpha-stimulated human aortic endothelial cells in chronic heart failure patients was reduced when the human aortic endothelial cells were pretreated with fenofibrate (31% inhibition, P = 0.0121). However, pretreatment of the isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells collected from chronic heart failure patients with fenofibrate failed to suppress their adherence to TNF-alpha-stimulated human aortic endothelial cells. Furthermore, stimulation of cultured human aortic endothelial cells with chronic heart failure patient sera significantly increased VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression, which could also be inhibited by fenofibrate. The fenofibrate directly inhibits monocyte binding by TNF-alpha-activated human aortic endothelial cells, probably through preventing up-regulation of cell adhesion molecules by endothelial cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. This PPARalpha activator may have the potential to ameliorate vascular inflammation in patients with chronic heart failure.
PMID:19531154 Huang WP et al; Eur J Clin Invest. 2009 Jun 15. (Epub ahead of print)
Severe rashes requiring hospitalization and corticosteroid therapy, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported rarely with fenofibrate in clinical studies. Urticaria and rash also have been reported in approximately 1% of patients receiving fenofibrate therapy in controlled trials.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1732
Fenofibrate, like other fibric acid derivatives (e.g., gemfibrozil), may increase cholesterol excretion in bile, resulting in cholelithiasis. If gallbladder studies indicate the presence of gallstones, fenofibrate should be discontinued.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1732
Liver function tests should be performed periodically (i.e., every 3 months) during the first 12 months of therapy. If serum aminotransferase concentrations of 3 times the upper limit of normal or higher persist, fenofibrate therapy should be discontinued.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1732
Chronic active hepatitis and cholestatic hepatitis have occurred as early as several weeks and as late as several years after initiation of fenofibrate therapy; cirrhosis associated with chronic active hepatitis has been reported rarely with fenofibrate.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1732
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Fenofibrate (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Fenofibrate is indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet to reduce elevated LDL-C, Total-C, Triglycerides, and Apo B, and to increase HDL-C adults with primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia. Fenofibrate is also indicated to treat adults with severe hypertriglyceridemia.
FDA Label
Fenofibrate is a fibrate that activates peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPAR) to alter lipid metabolism and treat primary hypercholesterolemia, mixed dyslipidemia, and severe hypertriglyceridemia. Fenofibrate requires once daily dosing and has a half life of 19-27 hours so its duration of action is long. Fenofibrate capsules are given at a dose of 50-150mg daily so the therapeutic index is wide. Patients should be counselled about the risk of rhabdomyolysis, myopathy, and cholelithiasis when taking fibrates.
Hypolipidemic Agents
Substances that lower the levels of certain LIPIDS in the BLOOD. They are used to treat HYPERLIPIDEMIAS. (See all compounds classified as Hypolipidemic Agents.)
C10AB05
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C10AB05
S66 | EAWAGTPS | Parent-Transformation Product Pairs from Eawag | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3754448
C - Cardiovascular system
C10 - Lipid modifying agents
C10A - Lipid modifying agents, plain
C10AB - Fibrates
C10AB05 - Fenofibrate
Absorption
A single 300mg oral dose of fenofibrate reaches a Cmax of 6-9.5mg/L with a Tmax of 4-6h in healthy, fasting volunteers.
Route of Elimination
5-25% of a dose of fenofibrate is eliminated in the feces, while 60-88% is eliminated in the urine. 70-75% of the dose recovered in the urine is in the form of fenofibryl glucuronide and 16% as fenofibric acid.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of fenofibrate is 0.89L/kg, and can be as high as 60L.
Clearance
The oral clearance of fenofibrate is 1.1L/h in young adults and 1.2L/h in the elderly.
Upon multiple dosing of fenofibrate, fenofibric acid steady state is achieved within 9 days. Plasma concentrations of fenofibric acid at steady state are approximately double those following a single dose. Serum protein binding was approximately 99% in normal and hyperlipidemic subjects.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 521
The absolute bioavailability of fenofibrate cannot be determined as the compound is virtually insoluble in aqueous media suitable for injection. However, fenofibrate is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Following oral administration in healthy volunteers, approximately 60% of a single dose of radiolabelled fenofibrate appeared in urine, primarily as fenofibric acid and its glucuronate conjugate, and 25% was excreted in the feces. Peak plasma levels of fenofibric acid occur within 6 to 8 hours after administration.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 520
After absorption, fenofibrate is mainly excreted in the urine in the form of metabolites, primarily fenofibric acid and fenofibric acid glucuronide. After administration of radiolabelled fenofibrate, approximately 60% of the dose appeared in the urine and 25% was excreted in the feces.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 521
The metabolism and disposition of orally administered single doses of (14)C fenofibrate (isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2- methylpropionate) have been studied in rat, guinea pig, and dog. In rats, the urinary excretion of (14)C in 5 days varied from 11 to 51% of the dose and was markedly dependent upon the dose form given. The interpretation of these data in terms of factors affecting the absorption of fenofibrate from the gut is complicated by the enterohepatic recirculation of metabolites. The tissue distribution of (14)C after oral administration of an ethanolic solution of fenofibrate has been studied in the rat. The only tissues in which the concentration of (14)C exceeded that in the blood were the organs of absorption and elimination, the gut, liver, and kidneys. Guinea pigs excreted 53% of the dose in the urine in 5 days, with a further 34% in the feces, while in dogs the corresponding figures were 9% and 81%, respectively. In all three species, all the urinary metabolites were products of ester hydrolysis, and the principal excretion product was "reduced fenofibric acid" which arose by subsequent carbonyl reduction. Glucuronidation of fenofibric acid and "reduced fenofibric acid" was a very minor reaction in the rat and guinea pig and was not detected in the dog. In addition, polar unknown metabolite(s) were detected in all three species, but were not investigated further. The results are discussed in terms of the comparative disposition of fenofibrate and other hypolipidemic agents and the contribution of these findings to the safety assessment of such drugs.
PMID:2898351 Weil A et al; Drug Metab Dispos 16 (2): 302-9 (1988).
Fenofibrate is completely hydrolyzed by liver carboxylesterase 1 to fenofibric acid. Fenofibric acid is either glucuronidated or has its carbonyl group reduced to a benzhydrol that is then glucuronidated. Glucuronidation of fenofibrate metabolites is mediated by UGT1A9. Reduction of the carbonyl group is primarily mediated by CBR1 and minorly by AKR1C1, AKR1C2, AKR1C3, and AKR1B1.
... The metabolism of fenofibrate was investigated in cynomolgus monkeys by ultraperformance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOFMS)-based metabolomics. Urine samples were collected before and after oral doses of fenofibrate. The samples were analyzed in both positive-ion and negative-ion modes by UPLC-QTOFMS, and after data deconvolution, the resulting data matrices were subjected to multivariate data analysis. Pattern recognition was performed on the retention time, mass/charge ratio, and other metabolite-related variables. Synthesized or purchased authentic compounds were used for metabolite identification and structure elucidation by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Several metabolites were identified, including fenofibric acid, reduced fenofibric acid, fenofibric acid ester glucuronide, reduced fenofibric acid ester glucuronide, and compound X. Another two metabolites (compound B and compound AR), not previously reported in other species, were characterized in cynomolgus monkeys. More importantly, previously unknown metabolites, fenofibric acid taurine conjugate and reduced fenofibric acid taurine conjugate were identified, revealing a previously unrecognized conjugation pathway for fenofibrate.
PMID:19251819 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2683687 Liu A et al; Drug Metab Dispos 37 (6): 1157-63 (2009).
Fenofibrate has been widely used for the treatment of dyslipidemia with a long history. Species differences of its metabolism were reported, but its metabolites in rodent have not been fully investigated. Urine and plasma samples were collected before and after oral dosages of fenofibrate in Sprague-Dawley rats. Urine samples were subjected to ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS) analysis, and projection to latent structures discriminant analysis was used for the identification of metabolites. New metabolites in urine and plasma were also studied by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The metabolism pathway was studied in rat hepatocytes. Synthesized and purchased authentic compounds were used for metabolite identification by LC-MS/MS. Five ever-reported metabolites were identified and another four new ones were found. Among these new metabolites, fenofibric acid taurine and reduced fenofibric acid taurine indicate new phase II conjugation pathway of fenofibrate.
PMID:19350456 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2794380 Liu A et al; Xenobiotica 39 (4): 345-54 (2009).
Following oral administration, fenofibrate is rapidly hydrolyzed by esterases to the active metabolite, fenofibric acid; no unchanged fenofibrate is detected in plasma. Fenofibric acid is primarily conjugated with glucuronic acid and then excreted in urine. A small amount of fenofibric acid is reduced at the carbonyl moiety to a benzhydrol metabolite which is, in turn, conjugated with glucuronic acid and excreted in urine. In vivo metabolism data indicate that neither fenofibrate nor fenofibric acid undergo oxidative metabolism (e.g., cytochrome P450) to a significant extent.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 521
The metabolism and disposition of orally administered single doses of (14)C fenofibrate (isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2- methylpropionate) have been studied in rat, guinea pig, and dog. In rats, the urinary excretion of (14)C in 5 days varied from 11 to 51% of the dose and was markedly dependent upon the dose form given. The interpretation of these data in terms of factors affecting the absorption of fenofibrate from the gut is complicated by the enterohepatic recirculation of metabolites. The tissue distribution of (14)C after oral administration of an ethanolic solution of fenofibrate has been studied in the rat. The only tissues in which the concentration of (14)C exceeded that in the blood were the organs of absorption and elimination, the gut, liver, and kidneys. Guinea pigs excreted 53% of the dose in the urine in 5 days, with a further 34% in the feces, while in dogs the corresponding figures were 9% and 81%, respectively. In all three species, all the urinary metabolites were products of ester hydrolysis, and the principal excretion product was "reduced fenofibric acid" which arose by subsequent carbonyl reduction. Glucuronidation of fenofibric acid and "reduced fenofibric acid" was a very minor reaction in the rat and guinea pig and was not detected in the dog. In addition, polar unknown metabolite(s) were detected in all three species, but were not investigated further. The results are discussed in terms of the comparative disposition of fenofibrate and other hypolipidemic agents and the contribution of these findings to the safety assessment of such drugs.
PMID:2898351 Weil A et al; Drug Metab Dispos 16 (2): 302-9 (1988).
Fenofibric acid, the active metabolite of fenofibrate, has a half life of 23 hours. Fenofibrate has a half life of 19-27 hours in healthy subjects and up to 143 hours in patients with renal failure.
Fenofibric acid is eliminated with a half-life of 20 hours, allowing once daily administration in a clinical setting. /Fenofibric acid/
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 521
Fenofibrate activates peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPAR), increasing lipolysis, activating lipoprotein lipase, and reducing apoprotein C-III. PPAR is a nuclear receptor and its activation alters lipid, glucose, and amino acid homeostasis. Activation of PPAR activates transcription of gene transcription and translation that generates peroxisomes filled with hydrogen peroxide, reactive oxygen species, and hydroxyl radicals that also participate in lipolysis. This mechanism of increased lipid metabolism is also associated with increased oxidative stress on the liver. In rare cases this stress can lead to cirrhosis and chronic active hepatitis.
Fenofibrate is a synthetic ligand for the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and has been widely used in the treatment of metabolic disorders, especially hyperlipemia, due to its lipid-lowering effect. The molecular mechanism of lipid-lowering is relatively well defined: an activated PPARalpha forms a PPAR-RXR heterodimer and this regulates the transcription of genes involved in energy metabolism by binding to PPAR response elements in their promoter regions, so-called "trans-activation". In addition, fenofibrate also has anti-inflammatory and anti-athrogenic effects in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. /There is/ limited information about the anti-inflammatory mechanism of fenofibrate; however, "trans-repression" which suppresses production of inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules probably contributes to this mechanism. Furthermore, there are reports that fenofibrate affects endothelial cells in a PPARalpha-independent manner. In order to identify PPARalpha-dependently and PPARalpha-independently regulated transcripts, ... microarray data from human endothelial cells treated with fenofibrate, and with and without siRNA-mediated knock-down of PPARalpha /were obtained/. ... Dynamic Bayesian transcriptome networks /were used/ to reveal PPARalpha-dependent and -independent pathways. Transcriptome network analysis identified growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) as a hub gene having PPARalpha-independently regulated transcripts as its direct downstream children. This result suggests that GDF15 may be PPARalpha-independent master-regulator of fenofibrate action in human endothelial cells.
PMID:19357976 Araki H et al; Angiogenesis 12 (3): 221-9 ( 2009).
The effects of fenofibric acid seen in clinical practice have been explained in vivo in transgenic mice and in vitro in human hepatocyte cultures by the activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor a (PPARa). Through this mechanism, fenofibrate increases lipolysis and elimination of triglyceride-rich particles from plasma by activating lipoprotein lipase and reducing production of apoprotein C-III (an inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase activity). The resulting fall in triglycerides produces an alteration in the size and composition of LDL from small, dense particles (which are thought to be atherogenic due to their susceptibility to oxidation), to large buoyant particles. These larger particles have a greater affinity for cholesterol receptors and are catabolized rapidly. Activation of PPARa also induces an increase in the synthesis of apoproteins A-I, A-II and HDL-cholesterol.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 520
... /This study/ investigated whether fenofibrate affects serum levels of retinol-binding protein-4 (RBP4), an adipocytokine that has recently been shown to link obesity and insulin resistance. Fenofibrate treatment significantly decreased serum RBP4 levels of dyslipidemic patients, which correlated with reduced body weight and increased insulin sensitivity. ... the effect of fenofibrate on RBP4 expression in obese rats /were also examined/. Fenofibrate greatly decreased RBP4 mRNA levels in adipose tissue but not in the liver, which correlated with decreased serum RBP4 levels and increased insulin sensitivity in obese rats. Consistent with a direct effect on RBP4 expression, fenofibrate treatment significantly reduced the mRNA expression levels of RPB4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. ...
PMID:19088257 Wu H et al; Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296 (4): E628-34 (2009).