
1. Dificid
2. Lipiarmycin
3. Lipiarmycin A3
4. Lipiarmycin A4
5. Lipiarmycin B
6. Lipiarmycin B3
7. Lipiarmycin B4
8. Par 101
9. Par-101
10. Par101
11. Tiacumicin B
12. Tiacumicin C
1. Tiacumicin B
2. Dificid
3. Dificlir
4. Lipiarmycin
5. Opt-80
6. 873857-62-6
7. Par-101
8. Clostomicin B1
9. Lipiarmicin
10. Difimicin
11. Z5n076g8yq
12. Lipiarmycin A3
13. R-tiacumicin B
14. Lipiarmycin A 3
15. Fidaxomicin [usan]
16. Fidaxomicin [usan:inn]
17. Unii-z5n076g8yq
18. Lipiarrmycin
19. Par 01
20. Clostomycin B1
21. Fidaxomicin (dificid)
22. Brn 5228707
23. Fidaxomicin [mi]
24. Fidaxomicin [inn]
25. Fidaxomicin [jan]
26. Fidaxomicin [vandf]
27. Fidaxomicin [who-dd]
28. Chembl1255800
29. Schembl10000818
30. Fidaxomicin, >=98% (hplc)
31. Gtpl10909
32. Fidaxomicin [orange Book]
33. Dtxsid901016415
34. Fi8
35. Mfcd27976367
36. Db08874
37. F1216
38. Opt-80;par-101;clostomicin B1;tiacumicin B
39. Q5446672
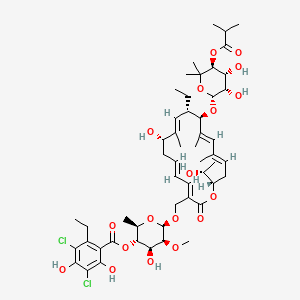
40. (2r,3s,4s,5s,6r)-6-{[(3e,5e,8s,9e,11s,12r,13e,15e,18s)-12-{[(2r,3s,4r,5s)-3,4-dihydroxy-6,6-dimethyl-5-[(2-methylpropanoyl)oxy]oxan-2-yl]oxy}-11-ethyl-8-hydroxy-18-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-9,13,15-trimethyl-2-oxo-1-oxacyclooctadeca-3,5,9,13,15-pentaen-3-yl]methoxy}-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2-methyloxan-3-yl 3,5-dichloro-2-ethyl-4,6-dihydroxybenzoate
41. [(2r,3s,4s,5s,6r)-6-[[(3e,5e,8s,9e,11s,12r,13e,15e,18s)-12-[(2r,3s,4r,5s)-3,4-dihydroxy-6,6-dimethyl-5-(2-methylpropanoyloxy)oxan-2-yl]oxy-11-ethyl-8-hydroxy-18-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-9,13,15-trimethyl-2-oxo-1-oxacyclooctadeca-3,5,9,13,15-pentaen-3-yl]methoxy]-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2-methyloxan-3-yl] 3,5-dichloro-2-ethyl-4,6-dihydroxybenzoate
| Molecular Weight | 1058.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C52H74Cl2O18 |
| XLogP3 | 6.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 18 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 15 |
| Exact Mass | 1056.4252209 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1056.4252209 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 267 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 72 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1970 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 14 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dificid |
| PubMed Health | Fidaxomicin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | DIFICID (fidaxomicin) is a macrolide antibacterial drug for oral administration. Its CAS chemical name is Oxacyclooctadeca-3,5,9,13,15-pentaen-2-one, 3-[[[6-deoxy-4-O-(3,5-dichloro-2-ethyl-4,6-dihydroxybenzoyl)-2-O-methyl--D-mannopyranosyl]oxy]meth... |
| Active Ingredient | Fidaxomicin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Cubist Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dificid |
| PubMed Health | Fidaxomicin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | DIFICID (fidaxomicin) is a macrolide antibacterial drug for oral administration. Its CAS chemical name is Oxacyclooctadeca-3,5,9,13,15-pentaen-2-one, 3-[[[6-deoxy-4-O-(3,5-dichloro-2-ethyl-4,6-dihydroxybenzoyl)-2-O-methyl--D-mannopyranosyl]oxy]meth... |
| Active Ingredient | Fidaxomicin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Cubist Pharms |
Fidaxomicin is indicated for the treatment of _Clostridioides_ (formerly _Clostridium_) _difficile_-associated diarrhea in adult and pediatric patients 6 months of age and older. Fidaxomicin should only be used in patients with proven or strongly suspected _C. difficile_ infection to reduce the risk of development of drug-resistant bacteria and maximize the therapeutic effectiveness of fidaxomicin and other antimicrobial agents.
FDA Label
Dificlir film-coated tablets is indicated for the treatment of Clostridioides difficile infections (CDI) also known as C. difficile-associated diarrhoea (CDAD) in adult and paediatric patients with a body weight of at least 12. 5 kg.
Consideration should be given to official guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
Dificlir granules for oral suspension is indicated for the treatment of Clostridioides difficile infections (CDI) also known as C. difficile-associated diarrhoea (CDAD) in adults and paediatric patients from birth to < 18 years of age.
Consideration should be given to official guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
Fidaxomicin has a narrow-spectrum antibacterial profile, with potent bactericidal activity specifically against C. difficile. The minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of organisms for fidaxomicin against _C. difficile_ ranged from 0.0078 to 2 g/mL _in vitro_. The bactericidal activity of fidaxomicin is time-dependent. Other than _C. difficile_, fidaxomicin has moderate inhibitory activity against Gram-positive bacteria (_S. aureus_ and _Enterococcus spp._) and poor activity against normal colonic flora, including anaerobes and enteric Gram-negative bacilli. Isolates of _C. difficile_ that are resistant to rifamycins or other antimicrobial classes (such as cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, clindamycin) were not shown to be cross-resistant to fidaxomicin.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
A07AA12
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A07 - Antidiarrheals, intestinal antiinflammatory/antiinfective agents
A07A - Intestinal antiinfectives
A07AA - Antibiotics
A07AA12 - Fidaxomicin
Absorption
Following oral administration of a single dose of 200 mg fidaxomicin in healthy adults, the Cmax of fidaxomicin and its main metabolite OP-1118 were 5.20 2.81 ng/mL and 12.0 6.06, respectively. The median Tmax of fidaxomicin was 2 hours. The systemic absorption of fidaxomicin following oral administration is minimal. In a food-effect study involving healthy adults in either with a high-fat meal versus under fasting conditions, the Cmax of fidaxomicin and OP-1118 were decreased by 21.5% and 33.4%, respectively; however, this effect is deemed to be clinically insignificant as the therapeutic action of fidaxomicin does not depend on drug concentrations in the systemic circulation.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration, fidaxomicin is mainly excreted in feces. More than 92% of the dose was recovered in the faces as either the unchanged parent drug or metabolites in one study consisting of healthy adults receiving single doses of 200 mg and 300 mg of fidaxomicin. In another study of healthy adults, approximately 0.59% fo the oral dose (200 mg) administered was recovered in the urine as the main metabolite, OP-1118.
Volume of Distribution
Fidaxomicin is mainly confined to the gastrointestinal tract when orally administered. There is limited information on the volume of distribution of fidaxomicin.
Clearance
There is limited information on the clearance of fidaxomicin.
Following oral administration, fidaxomicin is transformed to its main and pharmacologically active metabolite, OP-1118, via hydrolysis at the isobutyryl ester. As cytochrome enzymes are not involved in the metabolism of fidaxomicin, it is speculated that this biotransformation is mediated by gastric acid or enzymatic activity of intestinal microsomes.
Following oral administration of a single dose of 200 mg fidaxomicin in healthy adults, the elimination half-life of fidaxomicin was approximately 11.7 4.80 hours.
_Clostridium difficile_ is a Gram-positive bacterium that causes various gastrointestinal complications, such as antibiotic-associated diarrhea. _C. difficile_ infection can be caused by antibiotic therapy, resulting in the disruption of the human gut flora leads to an overgrowth of _C. difficile_. The consequences of _C. difficile_ infection can be mild to severe and sometimes fatal. Fidaxomicin gets hydrolyzed to its active metabolite, OP-1118, upon oral administration. Both compounds mediate a bactericidal activity against _C. difficile_ by inhibiting bacterial RNA polymerase at the initiation phase of the transcription cycle. The RNA polymerase is an essential bacterial enzyme that regulates gene expression, catalyzes nucleic acid interactions, and promotes several bacterial enzymatic reactions critical for bacterial survival. The core RNA polymerase is composed of a complex of different subunits and contains the active site. To initiate bacterial transcription, the active site of the core RNA polymerase binds to a promoter-specificity initiation factor, which locates and binds to a promoter region of the DNA. The DNA-RNA polymerase interaction promotes subsequent steps of transcription, which involves the separation of DNA strands. Fidaxomicin binds to the DNA template-RNA polymerase complex, thereby preventing the initial separation of DNA strands during transcription and inhibiting messenger RNA synthesis. The narrow spectrum of antimicrobial activity of fidaxomicin may be explained by the unique target site of fidaxomicin and differing subunits of the core structure of RNA polymerase among bacterial species.