


1. 1206101-20-3
2. Glpg0634
3. 1206161-97-8
4. Glpg-0634
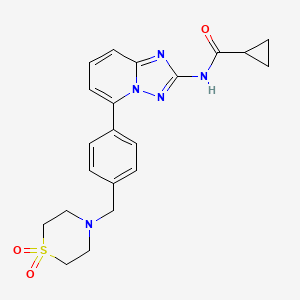
5. N-(5-(4-((1,1-dioxidothiomorpholino)methyl)phenyl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide
6. Filgotinib (glpg0634)
7. Filgotinib(glpg0634)
8. Gs-6034 Free Base
9. 3xvl385q0m
10. Gplg0634
11. N-[5-[4-[(1,1-dioxo-1,4-thiazinan-4-yl)methyl]phenyl]-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl]cyclopropanecarboxamide
12. G146034
13. G-146034
14. N-[5-[4-[(1,1-dioxido-4-thiomorpholinyl)methyl]phenyl][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl]cyclopropanecarboxamide
15. Jyseleca
16. Filgotinib [inn]
17. N-(5-(4-((1,1-dioxidothiomorpholino)methyl)phenyl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide.
18. Filgotinib [usan:inn]
19. Unii-3xvl385q0m
20. Glpg 0634
21. N-(5-{4-[(1,1-dioxidothiomorpholin-4-yl)methyl]phenyl}[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide
22. Glpg0634-analogue
23. Filgotinib (usan/inn)
24. Filgotinib [usan]
25. Filgotinib; Gplg0634
26. Filgotinib [who-dd]
27. Schembl253559
28. Filgotinib Pound Glpg0643)
29. Gtpl7913
30. Chembl3301607
31. Amy3802
32. Dtxsid80152935
33. Ex-a741
34. Bdbm103727
35. Hms3653p15
36. Hms3673e07
37. Bcp08496
38. Mfcd20527867
39. Nsc800100
40. S7605
41. Zinc96174616
42. Akos025291103
43. Ccg-268951
44. Db14845
45. Nsc-800100
46. Sb16799
47. Ncgc00345855-01
48. Ncgc00345855-07
49. As-16295
50. Bf159062
51. Da-33603
52. Da-33604
53. Hy-18300
54. Ft-0700114
55. Ft-0761510
56. Sw220020-1
57. A14232
58. D10871
59. P12798
60. Us8563545, 1
61. A892158
62. J-690063
63. Syn1158;glpg 0634; Glpg-0634; Filgotinib
64. Q19904163
65. Cyclopropanecarboxamide, N-(5-(4-((1,1-dioxido-4-thiomorpholinyl)methyl)phenyl)(1,2,4)triazolo(1,5-a)pyridin-2-yl)-
66. Glpg0634;n-[5-[4-[(1,1-dioxido-4-thiomorpholinyl)methyl]phenyl][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl]cyclopropanecarboxamide
67. N-(5-(4-((1,1-oxo-.lambda.6-thiomorpholin-4-yl)methyl)phenyl((1,2,4)triazolo(1,5-a)pyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 425.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H23N5O3S |
| XLogP3 | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 425.15216079 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 425.15216079 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 105 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 715 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Filgotinib is indicated for the treatment of active moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis alone or in combination with methotrexate. Filgotinib is currently reserved for patients who are unable to tolerate or who have not responded adequately to one or more disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDS). Filgotinib is also indicated for treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adult patients who had an inadequate response with, lost response to, or were intolerant to either conventional therapy or a biologic agent.
Treatment of chronic idiopathic arthritis (including rheumatoid arthritis , ankylosing spondylarthritis , psoriatic arthritis , and juvenile idiopathic arthritis )
Rheumatoid arthritis
Jyseleca is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis in adult patients who have responded inadequately to, or who are intolerant to one or more disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Jyseleca may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate (MTX).
Ulcerative colitis
Jyseleca is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who have had an inadequate response with, lost response to, or were intolerant to either conventional therapy or a biologic agent.
Treatment of Crohn's disease, Treatment of ulcerative colitis
In addition to targeted Janus kinase (JAK) 1 inhibition, filgotinib targets pro-inflammatory cytokine signalling by inhibiting IL-6 induced STAT1 phosphorylation. Serum C-reactive protein levels are also reduced in response to filgotinib administration.
L04AA
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L04 - Immunosuppressants
L04A - Immunosuppressants
L04AA - Selective immunosuppressants
L04AA45 - Filgotinib
Absorption
Filgotinib is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Median peak plasma concentrations occurred 2-3 hours post-dose for filgotinib and 5 hours post-dose for GS-829845. Steady-state concentrations can be observed in 2-3 days for filgotinib and in 4 days for GS-829845. Food does not appear to have a significant effect on the absorption of filgotinib; therefore, the medication can be administered without regard to food. After repeated oral dosing of filgotinib 200 mg, the reported Cmax and AUC values of filgotinib were 2.15 ug/mL and 6.77 ugxh/mL, respectively. For GS-829845 (the major metabolite) the reported Cmax was 4.43 ug/mL and the reported AUC was 83.2 ugxh/mL.
Route of Elimination
Of the total administered dose of filgotinib, approximately 87% undergoes renal elimination while 15% undergoes faecal elimination.
Carboxylesterase enzymes are involved in the metabolism of filgotinib. The carboxylesterase 2 (CES2) isoform is chiefly responsible for metabolizing filgotinib to its major metabolite, GS-829845. Although carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) plays a less prominent role in the biotransformation of filgotinib, in vitro studies have demonstrated that CES1 will partially compensate in the event of CES2 saturation. GS-829845 is thus far the only major circulating metabolite to have been identified.
The half-life of filgotinib is estimated to be 7 hours, while the half-life of its active metabolite GS-829845 is estimated to be 19 hours.
There are four Janus kinase (JAK) enzymes including JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2. JAK1 mediates inflammatory cytokine signaling, while JAK2 and JAK3 are important components of hematologic and immune functions. Filgotinib selectively inhibits JAK1 and is for example nearly 30-fold more selective for JAK1 compared to JAK2. The Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway is implicated in several inflammatory pathologies and has been found to be continuously active in patients who have RA. Sustained activation of this pathway contributes to aberrant processes which lead to disease progression including elevated levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and reduced cell apoptosis in RA affected synovial tissues. Filgotinib acts on the JAK-STAT pathway by selectively inhibiting JAK1 phosphorylation and preventing STAT activation, which ultimately results in reduced proinflammatory cytokine signaling.