


1. Am 833
2. Am-833
3. Am833
4. Quinodis
5. Ro 23 6240
6. Ro 23-6240
7. Ro 236240
1. 79660-72-3
2. Megalone
3. Megalocin
4. Fleroxicin
5. Quinodis
6. Fleroxacino
7. Fleroxacinum
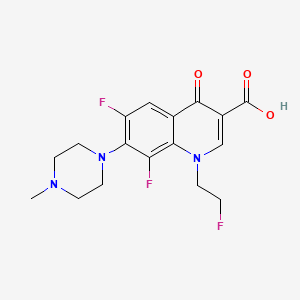
8. 6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-1,4-dihydro-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
9. Fleroxacine
10. Am-833
11. Ro 23-6240
12. Ro 23-6240/000
13. Flrx
14. Fleroxacin (quinodis)
15. Ro-236240
16. 6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
17. Chebi:31810
18. 6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
19. Ro-236240000
20. N804ldh51k
21. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-1,4-dihydro-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-
22. Ro-23-6240/000
23. Ncgc00167558-01
24. Fleroxacine [french]
25. Fleroxacinum [latin]
26. Fleroxacino [spanish]
27. Ro 23-6240;am-833
28. Am 833
29. 6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
30. Dsstox_cid_26714
31. Dsstox_rid_81846
32. Dsstox_gsid_46714
33. Megalosin
34. Megalocin (tn)
35. Megalone (tn)
36. Smr000466302
37. Cas-79660-72-3
38. Ccris 3972
39. Sr-01000759379
40. Brn 4300996
41. Unii-n804ldh51k
42. Fleroxacin (jan/usan/inn)
43. Fleroxacin,(s)
44. Fleroxacin [usan:inn:ban:jan]
45. Mfcd00864880
46. Fleroxacin [mi]
47. Fleroxacin [inn]
48. Fleroxacin [jan]
49. Fleroxacin [usan]
50. F0646
51. Fleroxacin [mart.]
52. Chembl6273
53. Fleroxacin [who-dd]
54. Schembl48145
55. Mls000759401
56. Mls006010715
57. Dtxsid1046714
58. Hms2090i08
59. Hms3715b11
60. Bcp28939
61. Hy-b0414
62. Rkl10075
63. Zinc3786299
64. Tox21_112553
65. Bdbm50247892
66. S2469
67. Zinc03786299
68. Akos015907011
69. Fleroxacin 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
70. Tox21_112553_1
71. Ccg-221125
72. Db04576
73. Ks-5124
74. Ncgc00167558-02
75. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-
76. Am-833;am833;am 833
77. Fleroxacin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
78. Ft-0630874
79. D01716
80. Fleroxacin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
81. Ab00640001-02
82. Ab00640001-03
83. Ab00640001_04
84. 660f723
85. A839732
86. Q3746573
87. Sr-01000759379-2
88. Sr-01000759379-3
89. 6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-1,4-dihydro-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid-
90. 6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylicacid
91. 6,8-difluoro-1-(2-fluoroethyl)-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid;fleroxacin
92. 79660-53-0
| Molecular Weight | 369.34 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H18F3N3O3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 369.13002593 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 369.13002593 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 64.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 595 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Fleroxacin is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial fluoroquinolone.
Fleroxacin is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial fluoroquinolone. It strongly inhibits the DNA-supercoiling activity of DNA gyrase.
Anti-Infective Agents
Substances that prevent infectious agents or organisms from spreading or kill infectious agents in order to prevent the spread of infection. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA08 - Fleroxacin
Absorption
Rapidly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration.
The inhibition of DNA gyrase and DNA topoisomerase 2 leads ultimately to cell death as these enzymes are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, strand supercoiling repair, and recombination.