


1. Sch 14714
1. 38677-85-9
2. Flunixine
3. Sch 14714
4. Flunixino
5. Flunixinum
6. Sch-14714
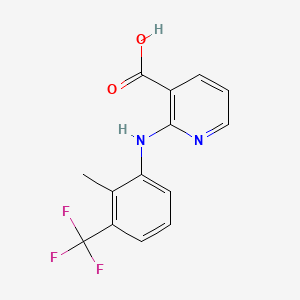
7. 2-((2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)nicotinic Acid
8. Chebi:76138
9. 2-{[2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}nicotinic Acid
10. 2-[2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
11. 356ib1o400
12. 2-[[2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
13. 3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid, 2-((2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)-
14. Flunixin [usan]
15. Flunixine [inn-french]
16. Flunixinum [inn-latin]
17. Flunixino [inn-spanish]
18. 2-((2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)-3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid
19. 2-[[2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]-3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid
20. 3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid, 2-[[2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]-
21. Flunixin [usan:inn:ban]
22. Flunixin-meglumin
23. Unii-356ib1o400
24. 2(2'-methyl-3'-trifluoromethylanilino)nicotinic Acid
25. Flunixin (usan/inn)
26. Flunixin [inn]
27. Flunixin [mi]
28. 2-(alpha(sup 3),alpha(sup 3),alpha(sup 3)-trifluoro-2,3-xylidino)nicotinic Acid
29. Schembl42911
30. Mls004712071
31. Flunixin [green Book]
32. Sch14714
33. Zinc1467
34. Chembl1617398
35. Dtxsid4048565
36. 2-[2-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenylamino]nicotinic Acid
37. Bcp12991
38. Bdbm50201618
39. Mfcd00072033
40. Akos015963218
41. Ac-1265
42. Db11518
43. Flunixin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
44. Smr000857255
45. Ft-0626444
46. Flunixin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
47. Vu0244596-2
48. D04215
49. 677f859
50. Q906934
51. Sr-01000883753
52. Sr-01000883753-1
53. 2-(2-methyl-3-trifluoromethylanilino) Nicotinic Acid
54. Brd-k99984802-098-03-2
55. Brd-k99984802-100-01-0
56. Brd-k99984802-100-06-9
57. 2-(alpha(3),alpha(3),alpha(3)-trifluoro-2,3-xylidino)nicotinic Acid
58. 2-(.alpha.(sup 3),.alpha.(sup 3),.alpha.(sup 3)-trifluoro-2,3-xylidino)nicotinic Acid.
59. Jbo
| Molecular Weight | 296.24 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H11F3N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 296.07726208 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 296.07726208 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 62.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 376 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Antipyretics
Drugs that are used to reduce body temperature in fever. (See all compounds classified as Antipyretics.)
