
1. Android F
2. Android-f
3. Fluoximesteron
4. Halotestin
5. Stenox
1. 76-43-7
2. Fluoxymestrone
3. Halotestin
4. Fluoximesterone
5. Androfluorene
6. Androfluorone
7. Fluotestin
8. Android-f
9. Ora-testryl
10. Androsterolo
11. Fluosterone
12. Flusteron
13. Flutestos
14. Oralsterone
15. Oratestin
16. Testoral
17. Ultandren
18. Ultandrene
19. Fluoximesteronum
20. Neo-ormonal
21. Ora Testryl
22. Fluoximesterona
23. Fluossimesterone [dcit]
24. Fluoxymesteronum
25. Fluoxymesteronum [inn-latin]
26. Fluoximesterona [inn-spanish]
27. Nsc-12165
28. Fluoxymesteron
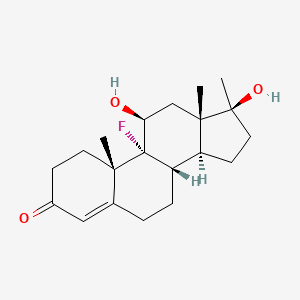
29. (8s,9r,10s,11s,13s,14s,17s)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-10,13,17-trimethyl-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
30. 9alpha-fluoro-11beta-hydroxy-17-methyltestosterone
31. Fluoxymesterone Ciii
32. U 6040
33. 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
34. Nsc 10704
35. Nsc-10704
36. Testosterone, 9-fluoro-11beta-hydroxy-17-methyl-
37. 9ju12s4yfy
38. Chebi:5120
39. Fxm
40. Anadroid-f
41. (11beta,17beta)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
42. 17alpha-methyl-9alpha-fluoro-11beta-hydroxytesterone
43. Component Of Halodrin
44. Fluossimesterone
45. 11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-9alpha-fluoro-17alpha-methyl-4-androster-3-one
46. Dsstox_cid_13512
47. Dsstox_rid_79080
48. Dsstox_gsid_33512
49. 9.alpha.-fluoro-11.beta.-hydroxy-17-methyltestosterone
50. Androxy
51. 9alpha-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
52. 9.alpha.-fluoro-11.beta.,17.beta.-dihydroxy-17.alpha.-methyl-4-androstene-3-one
53. Cas-76-43-7
54. Halotestin (tn)
55. (8s,9r,10s,11s,13s,14s,17s)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-10,13,17-trimethyl-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3(2h)-one
56. Ccris 9036
57. Hsdb 3333
58. Einecs 200-961-8
59. Testosterone, 9-fluoro-11.beta.-hydroxy-17-methyl-
60. Unii-9ju12s4yfy
61. Brn 2008796
62. 9-alpha-fluoro-11-beta-hydroxy-17-methyltestosterone
63. 17-alpha-methyl-9-alpha-fluoro-11-beta-hydroxytesterone
64. Ai3-52940
65. 9-fluoro-11-beta,17-beta-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
66. Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-methyl-, (11.beta.,17.beta.)-
67. 9alpha-fluoro-17alpha-methyl-11beta,17-dihydroxy-4-androsten-3-one
68. Ncgc00182970-01
69. 11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-9alpha-fluoro-17alpha-methyl-4-androsten-3-one
70. 9-alpha-fluoro-17-alpha-methyl-11-beta,17-dihydroxy-4-androsten-3-one
71. 9alpha-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17alpha-methyl-4-androstene-3-one
72. Androxy (tn)
73. 11-beta,17-beta-dihydroxy-9-alpha-fluoro-17-alpha-methyl-4-androster-3-one
74. 9-alpha-fluoro-11-beta,17-beta-dihydroxy-17-alpha-methyl-4-androstene-3-one
75. Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-methyl-, (11beta,17beta)-
76. Fluoxymesterone [usp:inn:ban:jan]
77. Fluoro-9-alpha Dihydroxy-11-beta,17-beta Methyl-17-alpha Androstene-4 One-3 [french]
78. Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methyl-
79. Fluoro-9-alpha Dihydroxy-11-beta,17-beta Methyl-17-alpha Androstene-4 One-3
80. Schembl5096
81. Chembl1445
82. Fluoxymesterone [mi]
83. Fluoxymesterone [inn]
84. Fluoxymesterone [jan]
85. 4-08-00-02057 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
86. Mls001055414
87. Fluoxymesterone [hsdb]
88. Fluoxymesterone [vandf]
89. Gtpl2861
90. Fluoxymesterone [mart.]
91. Dtxsid8033512
92. Fluoxymesterone [who-dd]
93. Bdbm18189
94. Fluoxymesterone (jan/usp/inn)
95. Hms2272b06
96. Bcp10776
97. Nsc10704
98. Nsc12165
99. Zinc3875484
100. Tox21_113158
101. Tox21_200854
102. 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17alpha-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
103. Fluoxymesterone [orange Book]
104. Lmst02020025
105. Fluoxymesterone Ciii [usp-rs]
106. Akos015895109
107. Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methyl- (van)
108. Db01185
109. Fluoxymesterone [usp Monograph]
110. Fluoxymesterone, Solid (photosensitive)
111. Ncgc00091037-01
112. Ncgc00091037-02
113. Ncgc00258408-01
114. Ac-29744
115. Smr000686158
116. Fluoxymesterone 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
117. D00327
118. 010f480
119. A838701
120. Q410663
121. W-104363
122. 9-fluoro-11.beta.,17.beta.-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
123. (1r,2s,10s,11s,14s,15s,17s)-1-fluoro-14,17-dihydroxy-2,14,15-trimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0;{2,7}.0;{11,15}]heptadec-6-en-5-one
124. (8s,9r,10s,11s,13s,14s,17s)-9-fluoranyl-10,13,17-trimethyl-11,17-bis(oxidanyl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
| Molecular Weight | 336.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H29FO3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 336.21007294 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 336.21007294 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 57.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 630 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 7 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fluoxymesterone |
| PubMed Health | Fluoxymesterone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Hematopoietic |
| Drug Label | HALOTESTIN Tablets contain fluoxymesterone, an androgenic hormone.Fluoxymesterone is a white or nearly white, odorless, crystalline powder, melting at or about 240 C, with some decomposition. It is practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble... |
| Active Ingredient | Fluoxymesterone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Usl Pharma |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fluoxymesterone |
| PubMed Health | Fluoxymesterone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Hematopoietic |
| Drug Label | HALOTESTIN Tablets contain fluoxymesterone, an androgenic hormone.Fluoxymesterone is a white or nearly white, odorless, crystalline powder, melting at or about 240 C, with some decomposition. It is practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble... |
| Active Ingredient | Fluoxymesterone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Usl Pharma |
Anabolic Steroids; Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Androgens are primarily indicated in males as replacement therapy when congenital or acquired endogenous androgen absence or deficiency is associated with primary hypogonadal or secondary hypogonadism. Primary hypogonadism includes conditions such as testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, or vanishing testis syndrome; inborn errors in testosterone biosynthesis; or bilateral orchidectomy. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (secondary hypogonadism) conditions include gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) deficiency; or pituitary hypothalamic injury as a result of surgery, tumors, trauma, or radiation and are the most common forms of hypogonadism seen in older adults. Dosage adjustment is needed to accommodate individual clinical requirements for such life changes as induction of puberty, development of secondary sexual characteristics, impotence due to testicular failure, or infertility due to oligospermia.. /Androgens; Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 150
A 6 month or shorter course of an androgen is indicated for induction of puberty in patients with familial delayed puberty, a condition characterized by spontaneous, nonpathologic, late-onset puberty, if the patient does not respond to psychological treatment. /Androgens; Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 151
Androgens are used in the treatment of constitutional delay in growth. However, they are not longer considered the treatment of choice for most patients. /Androgens; NOT included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 151
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for FLUOXYMESTERONE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: X /CONTRAINDICATED IN PREGNANCY. Studies in animals or humans, or investigational or post-marketing reports, have demonstrated positive evidence of fetal abnormalities or risk which clearly outweights any possible benefit to the patient./
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 153
Cholestatic hepatitis and jaundice and abnormal liver function test results may occur in patients receiving 17-alpha-alkylandrogens such as fluoxymesterone. These adverse hepatic effects may occur at relatively low doses of the drug. Drug-induced jaundice usually is reversible following discontinuance of the drug. Fluoxymesterone should be discontinued if cholestatic jaundice or hepatitis occurs, or if liver function test results become abnormal during therapy with the drug; the etiology of these disorders should be determined. Peliosis of the liver and hepatocellular neoplasms, including hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma, have been reported rarely in patients receiving long-term administration of androgenic anabolic steroids. Peliosis of the liver can be a life-threatening or fatal complication of androgen therapy.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2946
Fluoxymesterone is contraindicated in males with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate. The manufacturers state that the drug also is contraindicated in patients with serious cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease and in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug. Because of the potential risk of serious adverse health effects, fluoxymesterone should not be used for enhancement of athletic performance or physique.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2946
Use of androgens to enhance athletic performance is illegal. Increases in muscle mass and muscle strength can be sufficient to enhance athletic performance. However, the risk of unwanted effects, such as suppression of spermatogenesis, testicular atrophy, menstrual disturbances, virilization in females, peliosis hepatis (hepatic parenchymal injury), hepatotoxicity, potential adverse effects on cardiovascular health, and development of hepatic cancer, counter athletic benefits received from androgens and make their use in athletes inappropriate. Furthermore, behavioral disturbances, including aggressive or violent behavior, have been reported with supraphysiological self-administered doses in athletics. /Androgens/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 151
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FLUOXYMESTERONE (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In males, used as replacement therapy in conditions associated with symptoms of deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone. In females, for palliation of androgenresponsive recurrent mammary cancer in women who are more than one year but less than five years postmenopausal.
Fluoxymesterone is a synthetic androgen, or male hormone, similar to testosterone. Fluoxymesterone works by attaching itself to androgen receptors; this causes it to interact with the parts of the cell involved in the making of proteins. It may cause an increase in the synthesis of some proteins or a decrease in the synthesis of others. These proteins have a variety of effects, including blocking the growth of some types of breast cancer cells, stimulating cells that cause male sexual characteristics, and stimulating the production of red blood cells.
Anabolic Agents
These compounds stimulate anabolism and inhibit catabolism. They stimulate the development of muscle mass, strength, and power. (See all compounds classified as Anabolic Agents.)
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G03 - Sex hormones and modulators of the genital system
G03B - Androgens
G03BA - 3-oxoandrosten (4) derivatives
G03BA01 - Fluoxymesterone
Absorption
Oral absorption is less than 44%.
It is not known whether fluoxymesterone is distributed into milk.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2946
Less than 5% is excreted in urine as free steroid and glucuronide conjugate over a 24 hour period after doses of 20 to 200 mg.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 153
Presence of 17-alpha alkyl group reduces susceptibility to hepatic enzyme degradation, which slows metabolism and allows oral administration. Inactivation of testosterone occurs primarily in the liver
Presence of 17-alpha alkyl group reduces susceptibility to hepatic enzyme degradation, which slows metabolism and allows oral administration.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 152
9.2 hours
Approximately 9.2 hours
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 152
Fluoxymesterone is a synthetic androgenic anabolic steroid and is approximately 5 times as potent as natural methyltestosterone. Like testosterone and other androgenic hormones, fluoxymesterone binds to the androgen receptor. It produces retention of nitrogen, sodium, potassium, and phosphorus; increases protein anabolism; decreases amino acid catabolism and decreased urinary excretion of calcium. The antitumour activity of fluoxymesterone appears related to reduction or competitive inhibition of prolactin receptors or estrogen receptors or production.
Androgens are highly lipid-soluble and enter cells of target tissues by passive diffusion. Testosterone or 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a metabolite produced from testosterone by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, binds to an intracellular androgen receptor. The hormone receptor complex translocates into the nucleus and attaches to specific hormone receptor elements on the chromosome to initiate or suppress transcription and protein synthesis. Testosterone can produce estrogenic effects as a result of its conversion to estrogen. /Androgens/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 151
Exogenous administration of androgens inhibits the release of endogenous testosterone via feedback inhibition of pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH). Following administration of large doses of exogenous androgens, spermatogenesis also may be suppressed as a result of feedback inhibition of pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Androgens reportedly stimulate the production of erythrocytes, apparently by enhancing the production of erythropoietic stimulating factor. /Androgens/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2946