


1. Alpha-flupenthixol
2. Cis-flupenthixol
3. Emergil
4. Fluanxol
5. Flupenthixol
6. Flupentixol
1. 51529-01-2
2. Flupenthixol Dihydrochloride
3. Emergil
4. Cis-(z)-flupenthixol Dihydrochloride
5. 2413-38-9
6. Flupentixol Hcl
7. Cis-(z)-flupentixol Dihydrochloride
8. Fupentixol Dihydrochloride
9. (z)-flupenthixol Dihydrochloride
10. Flupenthixol 2hcl
11. (e/z)-flupentixol Dihydrochloride
12. Flupenthixol, Dihydrochloride
13. Fx 703
14. Flupentixol Dihydrochloride Cis-(z)
15. 96l0z069n1
16. Cis-(z)-flupentixol (dihydrochloride)
17. Flupentixol Hydrochloride
18. (z)-4-[3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene]propyl]-1-piperazineethanol Dihydrochloride
19. 2-[4-[(3z)-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)thioxanthen-9-ylidene]propyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethanol;dihydrochloride
20. N 7009
21. 1-piperazineethanol, 4-(3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)-, Dihydrochloride, (z)-
22. (z)-4-(3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)-1-piperazineethanol Dihydrochloride
23. Einecs 219-321-4
24. Nsc 170952
25. Unii-96l0z069n1
26. Prestwick_902
27. Cis-flupenthixol 2hcl
28. Unii-hat84mlq6z
29. Hat84mlq6z
30. 1-piperazineethanol, 4-(3-(2-trifluoromethylthioxanth-9-ylidene)propyl)-, Dihydrochloride
31. 4-(3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)-1-piperazineethanol Dihydrochloride
32. Cis-flupenthixol Hydrochloride
33. 1-piperazineethanol, 4-(3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)-, Dihydrochloride
34. Cis-flupenthixol Dihydrochloride
35. (z)-flupentixol Dihydrochloride
36. Schembl1153162
37. Chembl1496351
38. Ex-a352
39. Chebi:180489
40. Flupentixol Dihydrochloride (jan)
41. Cis-(z)-flupentixoldihydrochloride
42. Dtxsid501017247
43. Hms1569c21
44. Cis(z)-flupentixol Dihydrochloride
45. 4-[3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene]propyl]-1-piperazineethanol Dihydrochloride
46. Cis-flupentixol Hydrochloride
47. Tox21_500528
48. Mfcd00069278
49. S3664
50. Akos025401529
51. Ac-2136
52. Ccg-221832
53. Lp00528
54. 1-piperazineethanol, 4-(3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)-, Dihydrochloride
55. Ncgc00093921-01
56. Ncgc00261213-01
57. .alpha.-flupenthixol Hydrochloride
58. 4-(3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)piperazine-1-ethanol Dihydrochloride
59. Bs-16961
60. Flupentixol Dihydrochloride, (z)-
61. Hy-15856
62. Thioxanthene, 9-(3-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazinyl)propylidene)-2-trifluoromethyl-, Dihydrochloride
63. B7578
64. Cs-0009393
65. Eu-0100528
66. F-114
67. D02236
68. 529f012
69. Sr-01000076232
70. J-015359
71. Sr-01000076232-1
72. Q27271910
73. Cis-(z)-flupenthixol Dihydrochloride, >=98% (hplc), Solid
74. (z)-2-(4-(3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethanol Dihydrochloride
75. (z)-4-[3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene]propyl]-1-piperazine-ethanol Dihydrochloride
76. 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-{(3z)-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene]propyl}piperazinediium Dichloride
77. 1-piperazineethanol, 4-((3z)-3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)-, Dihydrochloride
78. 1-piperazineethanol, 4-(3-((3z)-2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene)propyl)-, Hydrochloride (1:2)
79. 2-(4-{(3z)-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene]propyl}piperazin-1-yl)ethan-1-ol--hydrogen Chloride (1/2)
80. 2-(4-{(3z)-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene]propyl}piperazin-1-yl)ethanol Dihydrochloride
81. 4-[3-[(3z)-2-(trifluoromethyl)-9h-thioxanthen-9-ylidene]propyl]-1-piperazineethanol Hydrochloride
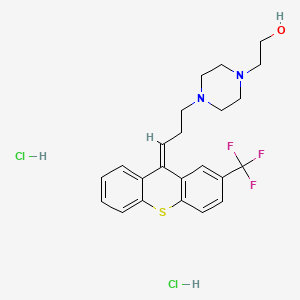
| Molecular Weight | 507.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H27Cl2F3N2OS |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 506.1173245 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 506.1173245 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 52 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 592 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)