
1. Cordran
2. Flurandrenolone
3. Haelan
1. Fludroxycortide
2. Flurandrenolone
3. 1524-88-5
4. Cordran
5. Fluorandrenolone
6. Haelan
7. Fludroxicortidum
8. Flurandrenolone Acetonide
9. Fluorandrenolone Acetonide
10. Fludrossicortide [dcit]
11. Fludroxycortidum [inn-latin]
12. Fludroxicortida [inn-spanish]
13. Drenison
14. Drocort
15. Sermaka
16. Haldrone-f
17. Alondra-f
18. Fludroxicortide
19. Fludroxycortide [inn]
20. 8eul29xuqt
21. Mls000069556
22. Mls001148136
23. Nsc-757869
24. Fludroxicortida
25. Smr000058825
26. Floudroxycortide
27. Fludrossicortide
28. Fludroxycortidum
29. Cordran Sp
30. Flurandrenolide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
31. Flurandrenolide [usan]
32. L 33379
33. Dsstox_cid_27434
34. Dsstox_rid_82344
35. Dsstox_gsid_47434
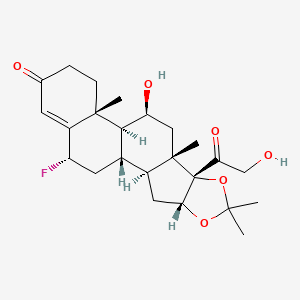
36. (2s,6ar,6bs,7s,8as,8bs,11ar,12as,12bs)-2-fluoro-7-hydroxy-8b-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-6a,8a,10,10-tetramethyl-5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,8b,11a,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-1h-naphtho[2',1':4,5]indeno[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-4(2h)-one
37. Hsdb 3084
38. Flurandrenolide (usp)
39. Cordran (tn)
40. Einecs 216-196-8
41. Unii-8eul29xuqt
42. Fludroxycortide (jan/inn)
43. Fludroxycortid
44. Flurandrenolide [usan:usp]
45. Acetonide Of 6alpha-fluoro-16alpha-hydroxyhydrocortisone
46. 6alpha-fluoro-16alpha-hydroxyhydrocortisone 16,17-acetonide
47. Ncgc00016586-01
48. (6?,11?,16?)-6-fluoro-11,21-dihydroxy-16,17-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(oxy)]-pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione
49. Cas-1524-88-5
50. Prestwick_1065
51. 6alpha-fluoro-11beta,16alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxyprogesterone Cyclic 16,17-acetal With Acetone
52. 6alpha-fluoro-11beta,16alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, Cyclic 16,17-acetal With Acetone
53. Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 6-fluoro-11,21-dihydroxy-16,17-((1-methylethylidene)bis(oxy))-, (6alpha,11beta,16alpha)-
54. Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 6alpha-fluoro-11beta,16alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, Cyclic 16,17-acetal With Acetone
55. Opera_id_1618
56. Prestwick0_000645
57. Prestwick1_000645
58. Prestwick2_000645
59. Prestwick3_000645
60. Schembl4694
61. Flurandrenolide [mi]
62. Bspbio_000649
63. Fludroxycortide [jan]
64. Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 6-alpha-fluoro-11-beta,16-alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, Cyclic 16,17-acetal With Acetone
65. Flurandrenolide [hsdb]
66. Spbio_002570
67. Flurandrenolide [vandf]
68. Bpbio1_000715
69. Chebi:5127
70. Gtpl7606
71. Fludroxycortide [mart.]
72. Chembl1201012
73. Dtxsid2047434
74. Fludroxycortide [who-dd]
75. Flurandrenolide [usp-rs]
76. Hms1570a11
77. Hms2097a11
78. Hms2233c04
79. Hms3714a11
80. 6.alpha.-fluoro-11.beta.,16.alpha.,17,21-tetrahydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, Cyclic 16,17-acetal With Acetone
81. Hy-b1013
82. Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 6-fluoro-11,21-dihydroxy-16,17-((1-methylethylidene)bis(oxy))-, (6.alpha.,11.beta.,16.alpha.)-
83. Zinc4097308
84. Tox21_110509
85. Tox21_302611
86. Flurandrenolide [orange Book]
87. Tox21_110509_1
88. Ccg-220645
89. Cs-4526
90. Db00846
91. Flurandrenolide [usp Monograph]
92. Nsc 757869
93. Ncgc00023234-03
94. Ncgc00023234-05
95. Ncgc00256709-01
96. Cordran-n Component Flurandrenolide
97. Flurandrenolide Component Of Cordran-n
98. D00328
99. 524f885
100. Sr-01000003119
101. Q5462632
102. Sr-01000003119-3
103. W-108052
104. Brd-k00824317-001-03-0
105. (1s,2s,4r,8s,9s,11s,12s,13r,19s)-19-fluoro-11-hydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-6,6,9,13-tetramethyl-5,7-dioxapentacyclo[10.8.0.0^{2,9}.0^{4,8}.0^{13,18}]icos-17-en-16-one
106. (1s,2s,4r,8s,9s,11s,12s,13r,19s)-19-fluoro-11-hydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-6,6,9,13-tetramethyl-5,7-dioxapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.04,8.013,18]icos-17-en-16-one
107. (4r,8s,9s,11s,13r,19s)-19-fluoro-11-hydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-6,6,9,13-tetramethyl-5,7-dioxapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.04,8.013,18]icos-17-en-16-one
| Molecular Weight | 436.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H33FO6 |
| XLogP3 | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 436.22611693 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 436.22611693 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 93.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 868 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 9 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cordran |
| PubMed Health | Flurandrenolide (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Corticosteroid, Strong |
| Drug Label | Cordran Tape (Flurandrenolide Tape, USP) is a transparent, inconspicuous, plastic surgical tape, impervious to moisture. It contains Cordran (Flurandrenolide, USP), a potent corticosteroid for topical use. Flurandrenolide occurs as white to off-white... |
| Active Ingredient | Flurandrenolide |
| Dosage Form | Lotion; Tape |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.004mg/sq cm |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Pharms; Aqua Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cordran sp |
| PubMed Health | Flurandrenolide (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Corticosteroid, Strong |
| Active Ingredient | Flurandrenolide |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.025% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aqua Pharms |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cordran |
| PubMed Health | Flurandrenolide (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Corticosteroid, Strong |
| Drug Label | Cordran Tape (Flurandrenolide Tape, USP) is a transparent, inconspicuous, plastic surgical tape, impervious to moisture. It contains Cordran (Flurandrenolide, USP), a potent corticosteroid for topical use. Flurandrenolide occurs as white to off-white... |
| Active Ingredient | Flurandrenolide |
| Dosage Form | Lotion; Tape |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.004mg/sq cm |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Pharms; Aqua Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cordran sp |
| PubMed Health | Flurandrenolide (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Corticosteroid, Strong |
| Active Ingredient | Flurandrenolide |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.05%; 0.025% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aqua Pharms |
Glucocorticoids, Synthetic; Glucocorticoids, Topical
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Topical corticosteroids of low to medium potency are indicated in the treatment of corticosteroid-responsive dermatologic disorders /mild to moderate atopic dermatitis; contact dermatitis; mild nummular dermatitis; seborrheic dermatitis (facial and intertriginous areas); other mild to moderate forms of dermatitis; other mild to moderate inflammatory dermatoses; intertrigo; lichen planus (facial and intertriginous areas); discoid lupus erythematosus (facial and intertriginous areas); polymorphous light eruption; anogenital pruritus; pruritus senilis; psoriasis (facial and intertriginous areas); xerosis (inflammatory phase/. Occlusive dressings also may be required for chronic or severe cases of lichen simplex chronicus, psoriasis, eczema, atopic dermatitis, or chronic hand eczema. The more potent topical corticosteroids and/or occlusive dressings may be required for conditions such as discoid lupus erythematosus, lichen planus, granuloma annulare, psoriatic plaques, and psoriasis affecting the palms, soles, elbows, or knees. /Corticosteroids (topical); Included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 918
Flurandrenolide shares the actions of the other topical corticosteroids and is used for the relief of the inflammatory manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 3531
MEDICATION (VET): Glucocorticoids have profound effects on nearly all cell types and organ systems, particularly immunologic and inflammatory activity. They may be used in either an anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive capacity, depending on the dosage selected. Glucocorticoids are used for hypersensitivity dermatoses, contact dermatitis, immune-mediated diseases (eg, pemphigus, pemphigoid, lupus erythematosus), and neoplasia (eg, mast cell tumor, lymphoma). ... They may be administered PO, IV, IM, or SC. /Glucocorticoids/
Kahn, C.M. (Ed.); The Merck Veterinary Manual 9th ed. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station, NJ. 2005, p. 2008
VET: AVOID COVERING OVER 5-10% OF BODY SURFACE, ESP IN PREGNANT ANIMALS.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 225
The following may occur more frequently with occlusive dressings: Maceration of the skin, Secondary infection, Skin atrophy, Striae Miliaria. /Topical corticosteroids/
Prescribing Information for Cordran (Flurandrenolide); Aqua Pharmaceuticals; 2006. Available from, as of November 18, 2007: https://www.aquapharm.com/prod_cordran.html
The following local adverse reactions are reported infrequently with topical corticosteroids but may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: Burning, Itching, Irritation, Dryness, Folliculitis, Hypertrichosis, Acneform eruptions, Hypopigmentation, Perioral dermatitis, Allergic contact dermatitis. /Topical corticosteroids/
Prescribing Information for Cordran (Flurandrenolide); Aqua Pharmaceuticals; 2006. Available from, as of November 18, 2007: https://www.aquapharm.com/prod_cordran.html
Pediatric patients may demonstrate greater susceptibility to topical corticosteroid-induced HPA axis suppression and Cushing's syndrome than do mature patients because of a larger skin surface area to body weight ratio. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, Cushing's syndrome, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in pediatric patients receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in pediatric patients include linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, low plasma cortisol levels, and absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema. Administration of topical corticosteroids to pediatric patients should be limited to the least amount compatible with an effective therapeutic regimen. Chronic corticosteroid therapy may interfere with the growth and development of pediatric patients. /Topical corticosteroids/
Prescribing Information for Cordran (Flurandrenolide); Aqua Pharmaceuticals; 2006. Available from, as of November 18, 2007: https://www.aquapharm.com/prod_cordran.html
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FLURANDRENOLIDE (36 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses, particularly dry, scaling localized lesions
Flurandrenolide is primarily effective because of its anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive actions.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Substances that reduce or suppress INFLAMMATION. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents.)
Glucocorticoids
A group of CORTICOSTEROIDS that affect carbohydrate metabolism (GLUCONEOGENESIS, liver glycogen deposition, elevation of BLOOD SUGAR), inhibit ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE secretion, and possess pronounced anti-inflammatory activity. They also play a role in fat and protein metabolism, maintenance of arterial blood pressure, alteration of the connective tissue response to injury, reduction in the number of circulating lymphocytes, and functioning of the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Glucocorticoids.)
D - Dermatologicals
D07 - Corticosteroids, dermatological preparations
D07A - Corticosteroids, plain
D07AC - Corticosteroids, potent (group iii)
D07AC07 - Fludroxycortide
Absorption
Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to those of systemically administered corticosteroids
Route of Elimination
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. They are metabolized primarily in the liver and then excreted in the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile.
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin increase percutaneous absorption. ... Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are bound to plasma proteins in varying degrees. They are metabolized primarily in the liver and then excreted in the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile. /Topical corticosteroids/
Prescribing Information for Cordran (Flurandrenolide); Aqua Pharmaceuticals; 2006. Available from, as of November 18, 2007: https://www.aquapharm.com/prod_cordran.html
Primarily hepatic
/Topical corticosteroids/ are metabolized primarily in the liver and then excreted in the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile. /Topical corticosteroids/
Prescribing Information for Cordran (Flurandrenolide); Aqua Pharmaceuticals; 2006. Available from, as of November 18, 2007: https://www.aquapharm.com/prod_cordran.html
Flurandrenolide is a topical corticosteroid. It is normally applied to a plastic tape called Cordran. Cordran is primarily effective because of its anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive actions. Flurandrenolide, which is slowly released from the Cordran tape, binds to the cytosolic glucocorticoid receptor. After binding the receptor the newly formed receptor-ligand complex translocates itself into the cell nucleus, where it binds to many glucocorticoid response elements (GRE) in the promoter region of the target genes. The DNA bound receptor then interacts with basic transcription factors, causing the increase in expression of specific target genes. The anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids are thought to involve lipocortins, phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins which, through inhibition arachidonic acid, control the biosynthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Specifically glucocorticoids induce lipocortin-1 (annexin-1) synthesis, which then binds to cell membranes preventing the phospholipase A2 from coming into contact with its substrate arachidonic acid. This leads to diminished eicosanoid production. Cyclooxygenase (both COX-1 and COX-2) expression is also suppressed, potentiating the effect. In another words, the two main products in inflammation Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes are inhibited by the action of Glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids also stimulate the lipocortin-1 escaping to the extracellular space, where it binds to the leukocyte membrane receptors and inhibits various inflammatory events: epithelial adhesion, emigration, chemotaxis, phagocytosis, respiratory burst and the release of various inflammatory mediators (lysosomal enzymes, cytokines, tissue plasminogen activator, chemokines etc.) from neutrophils, macrophages and mastocytes. Additionally the immune system is suppressed by corticosteroids due to a decrease in the function of the lymphatic system, a reduction in immunoglobulin and complement concentrations, the precipitation of lymphocytopenia, and interference with antigen-antibody binding. Like other glucocorticoid agents Fluocinolone acetonide acts as a physiological antagonist to insulin by decreasing glycogenesis (formation of glycogen). It also promotes the breakdown of lipids (lipolysis), and proteins, leading to the mobilization of extrahepatic amino acids and ketone bodies. This leads to increased circulating glucose concentrations (in the blood). There is also decreased glycogen formation in the liver.
The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of topical corticosteroids is not completely understood. Various laboratory methods, including vasoconstrictor assays, are used to compare and predict potencies and/or clinical efficacies of the topical corticosteroids. There is some evidence to suggest that a recognizable correlation exists between vasoconstrictor potency and therapeutic efficacy in man. Corticosteroids with antiinflammatory activity may stabilize cellular and lysosomal membranes. There is also the suggestion that the effect on the membranes of lysosomes prevents the release of proteolytic enzymes and, thus, plays a part in reducing inflammation. /Topical corticosteroids/
Prescribing Information for Cordran (Flurandrenolide); Aqua Pharmaceuticals; 2006. Available from, as of November 18, 2007: https://www.aquapharm.com/prod_cordran.html
Glucocorticoids are capable of suppressing the inflammatory process through numerous pathways. They interact with specific intracellular receptor proteins in target tissues to alter the expression of corticosteroid-responsive genes. Glucocorticoid-specific receptors in the cell cytoplasm bind with steroid ligands to form hormone-receptor complexes that eventually translocate to the cell nucleus. There these complexes bind to specific DNA sequences and alter their expression. The complexes may induce the transcription of mRNA leading to synthesis of new proteins. Such proteins include lipocortin, a protein known to inhibit PLA2a and thereby block the synthesis of prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and PAF. Glucocorticoids also inhibit the production of other mediators including AA metabolites such as COX, cytokines, the interleukins, adhesion molecules, and enzymes such as collagenase. /Glucocorticoids/
Kahn, C.M. (Ed.); The Merck Veterinary Manual 9th ed. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station, NJ. 2005, p. 2128
Corticosteroids diffuse across cell membranes and complex with specific cytoplasmic receptors. These complexes then enter the cell nucleus, bind to DNA (chromatin), and stimulate transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and subsequent protein synthesis of various inhibitory enzymes responsible for the anti-inflammatory effects of topical corticosteroids. These anti-inflammatory effects include inhibition of early processes such as edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilatation, movement of phagocttes into the area, and phagocytic activities. Later processes, such as capillary production, collagen deposition, and keloid formation also are inhibited by corticosteroids. The overall actions of topical corticosteroids are catabolic. /Corticosteroids (topical)/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 919