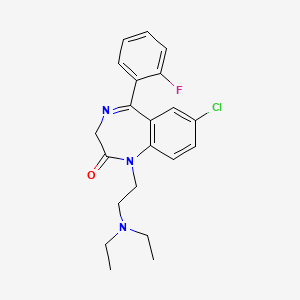

1. Apo Flurazepam
2. Apo-flurazepam
3. Dalmadorm
4. Dalmane
5. Dihydrochloride, Flurazepam
6. Dormodor
7. Flurazepam Dihydrochloride
8. Flurazepam Hydrochloride
9. Flurazepam Mono Perchlorate
10. Flurazepam Mono-perchlorate
11. Flurazepam Monohydrochloride
12. Hydrochloride, Flurazepam
13. Mono-perchlorate, Flurazepam
14. Monohydrochloride, Flurazepam
15. Staurodorm
1. 17617-23-1
2. Insumin
3. Dalmane
4. Flurazepamum
5. Flurazepam Hcl
6. 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-3h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
7. 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
8. 7-chloro-1-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2(3h)-one
9. Stauroderm
10. Noctosom
11. Ihp475989u
12. Dalmane-r
13. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 7-chloro-1-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-
14. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-
15. 7-chloro-1-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
16. Dea No. 2767
17. Ncgc00164573-01
18. Felmane
19. Dsstox_cid_3071
20. Dsstox_rid_76863
21. Dsstox_gsid_23071
22. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-7-chloro-1-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-5-(o-fluorophenyl)-
23. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(o-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-
24. Flurazepamum [inn-latin]
25. Flurazepam [inn:ban:jan]
26. 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
27. Insumin (tn)
28. Cas-17617-23-1
29. Ro-5-6901/3
30. Hsdb 3085
31. Einecs 241-591-7
32. Brn 0767925
33. Unii-ihp475989u
34. 7-chloro-1-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-5-(o-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
35. 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(o-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
36. Flurazepam [mi]
37. Flurazepam (jan/inn)
38. Flurazepam [inn]
39. Flurazepam [jan]
40. Flurazepam [hsdb]
41. Flurazepam [vandf]
42. Chembl968
43. Flurazepam [mart.]
44. Flurazepam [who-dd]
45. Schembl29793
46. 5-24-04-00322 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
47. Chebi:5128
48. Gtpl7188
49. Dtxsid1023071
50. 17617-23-1(free Base)
51. Zinc537752
52. Flurazepam 0.1 Mg/ml In Methanol
53. Flurazepam 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
54. Tox21_112201
55. Ro-56901
56. Akos015889971
57. Tox21_112201_1
58. Db00690
59. Ncgc00164573-02
60. Ro 56901/3
61. Db-044253
62. D00329
63. 617f231
64. A812156
65. Q418998
66. 7-chloranyl-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-3h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
67. Flurazepam Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
68. Flurazepam-d4 Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Methanol, Certified Reference Material
69. (e)-7-chloro-1-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1h-benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-2(3h)-one
70. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 7-chloro-1-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro
71. 7-chloro-1-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1h-benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-2(3h)-one
72. 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one #
73. Fl7
| Molecular Weight | 387.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H23ClFN3O |
| XLogP3 | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 387.1513682 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 387.1513682 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 35.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 540 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Flurazepam hydrochloride |
| Drug Label | Flurazepam hydrochloride is chemically 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(o-fluoro-phenyl)-1,3dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one dihydrochloride. It is a pale yellow, crystalline compound, freely soluble in alcohol and very soluble in water. It ha... |
| Active Ingredient | Flurazepam hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Flurazepam hydrochloride |
| Drug Label | Flurazepam hydrochloride is chemically 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(o-fluoro-phenyl)-1,3dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one dihydrochloride. It is a pale yellow, crystalline compound, freely soluble in alcohol and very soluble in water. It ha... |
| Active Ingredient | Flurazepam hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
Anti-Anxiety Agents, Benzodiazepine; GABA Modulators; Sedatives, Nonbarbiturate
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
A BENZODIAZEPINE WIDELY USED IN ALL TYPES OF INSOMNIA SUCH AS DIFFICULTY IN FALLING ASLEEP, FREQUENT NOCTURNAL AWAKENINGS, &/OR EARLY MORNING AWAKENING. IT IS ALSO USEFUL IN ACUTE & CHRONIC MEDICAL SITUATIONS IN WHICH RESTFUL SLEEP IS DESIRABLE. /FLURAZEPAM DIHYDROCHLORIDE/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1007
FOR PATIENTS RECEIVING ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS, FLURAZEPAM IS SUITABLE & SAFE HYPNOTIC AGENT
Evaluations of Drug Interactions. 2nd ed. and supplements. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Assn., 1976, 1978., p. 277
HYPNOTIC EFFECTS BEGIN IN AN AVERAGE OF 17 MINUTES AFTER ORAL ADMIN & LAST 7 TO 8 HR. IN A SMALL CONTROLLED SLEEP STUDY, FLURAZEPAM WAS REPORTED TO MAINTAIN ITS EFFECTIVENESS FOR UP TO 4 WK. /FLURAZEPAM DIHYDROCHLORIDE/
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 218
Sedative /Flurazepam dihydrochloride/
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 657
THE EFFICACY OF DRUG BEYOND 22 CONSECUTIVE NIGHTS OF USE IS NOT KNOWN. IN ONE STUDY, PATIENTS RATED FLURAZEPAM MORE HIGHLY THAN SECOBARBITAL ... . FLURAZEPAM SHOULD BE USED CAUTIOUSLY WHEN HEPATIC OR RENAL FUNCTION IS IMPAIRED. /FLURAZEPAM DIHYDROCHLORIDE/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 125
CAUTION: ABUSE MAY LEAD TO HABITUATION OR ADDICTION. /FLURAZEPAM DIHYDROCHLORIDE/
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 601
PATIENT STATUS EPILEPTICUS IN PATIENTS WITH LENNOX-GASTAUT SYNDROME (PETIT MAL VARIANT). /BENZODIAZEPINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 217
PATIENTS ON THESE DRUGS SHOULD BE WARNED ... NOT TO OPERATE A MOTOR VEHICLE OR HAZARDOUS MACHINERY ... /BENZODIAZEPINES/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1005
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FLURAZEPAM (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For short-term and intermittent use in patients with recurring insomnia and poor sleeping habits
Flurazepam, a benzodiazepine derivative, is a hypnotic agent which does not appear to decrease dream time as measured by rapid eye movements (REM). Furthermore, it decreases sleep latency and number of awakenings for a consequent increase in total sleep time.
Hypnotics and Sedatives
Drugs used to induce drowsiness or sleep or to reduce psychological excitement or anxiety. (See all compounds classified as Hypnotics and Sedatives.)
Anti-Anxiety Agents
Agents that alleviate ANXIETY, tension, and ANXIETY DISORDERS, promote sedation, and have a calming effect without affecting clarity of consciousness or neurologic conditions. ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS are commonly used in the symptomatic treatment of anxiety but are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Anxiety Agents.)
GABA Modulators
Substances that do not act as agonists or antagonists but do affect the GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID receptor-ionophore complex. GABA-A receptors (RECEPTORS, GABA-A) appear to have at least three allosteric sites at which modulators act: a site at which BENZODIAZEPINES act by increasing the opening frequency of GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID-activated chloride channels; a site at which BARBITURATES act to prolong the duration of channel opening; and a site at which some steroids may act. GENERAL ANESTHETICS probably act at least partly by potentiating GABAergic responses, but they are not included here. (See all compounds classified as GABA Modulators.)
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05C - Hypnotics and sedatives
N05CD - Benzodiazepine derivatives
N05CD01 - Flurazepam
Absorption
Flurazepam hydrochloride is rapidly (30 minutes) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
Route of Elimination
Flurazepam is rapidly metabolized and is excreted primarily in the urine. Less than 1% of the dose is excreted in the urine as N1-desalkyl-flurazepam.
HYPNOTIC, FLURAZEPAM HYDROCHLORIDE, HAS BEEN SHOWN TO BE RAPIDLY & COMPLETELY ABSORBED IN DOG & MAN. ELIMINATION IS ALSO RAPID & DUE SOLELY TO BIOTRANSFORMATION. /FLURAZEPAM HYDROCHLORIDE/
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 444
ORAL ... ((14)CARBON) FLURAZEPAM ... IN DOG & MAN ... ELIMINATED MAINLY IN 3 DAYS. DOG EXCRETED 36 & 49% OF (14)CARBON IN URINE & FECES (PROBABLY VIA BILE) FOLLOWING ORAL DOSE & 27 & 54% FOLLOWING IV DOSE. AFTER ORAL DOSE, HUMANS EXCRETED ... IN FECES (9%) & ... IN URINE (81%). PLASMA (14)CARBON ... PEAKED IN 1 HR FOLLOWING ORAL DOSE IN BOTH SPECIES.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 87
ALL BENZODIAZEPINES BIND TO HUMAN PLASMA ALBUMIN. THE EXTENT OF BINDING VARIES FROM PROBABLY ONLY A FEW PERCENT WITH FLURAZEPAM TO NEARLY 99% WITH DIAZEPAM.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 347
THE BIOAVAILABILITY OF FLURAZEPAM VARIES BETWEEN 30 & 60%. AFTER A SINGLE ORAL DOSE OF 30 MG, THE PLASMA CONCN RISES TO A PEAK OF 1 TO 2 NG/ML AT 1 HR & FALLS RAPIDLY WITH HALF-LIFE OF ABOUT 3 HR... AFTER A 30 MG DOSE OF FLURAZEPAM, THE PEAK CONCN (AT 1 TO 3 HR) OF THE DESALKYL METABOLITE IS 0.5 TO 1.8 NG/ML & THAT OF THE DESAMINO COMPOUNDS IS 6 TO 8 NG/ML. THE ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE OF THE DESAMINO COMPOUND IS 10 TO 20 HR & THAT OF THE DESALKYL METABOLITE IS 1 DAY OR LONGER. THEREFORE, WITH DAILY ADMIN, THESE METABOLITES ACCUMULATE TO RATHER HIGH CONCN OVER A PERIOD OF SEVERAL DAYS TO A FEW WK. SINCE PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITY IS ATTRIBUTABLE TO THESE METABOLITES, A FEW DAYS OF DAILY ADMIN ARE REQUIRED FOR THE ONSET OF THE FULL EFFECT OF FLURAZEPAM, & RESIDUAL EFFECTS ("HANGOVER") ARE COMMON. LESS THAN 0.2% OF FLURAZEPAM IS EXCRETED UNCHANGED; 30 TO 55% OF THE DRUG IS CONVERTED TO THE DESAMINO METABOLITE.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 348
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for FLURAZEPAM (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Flurazepam is rapidly metabolized and is excreted primarily in the urine. Both hydroxyethyl flurazepam (the major metabolite) and N-desalkyl flurazepam are active. The N-desalkyl metabolite is slowly excreted in the urine as the conjugated form
IT IS METABOLIZED IN LIVER. THE DIETHYLAMINE GROUP IS DESETHYLATED, THEN DEAMINATED, EVENTUALLY TO YIELD ALCOHOL, THE MAJOR METABOLITE IN MAN. ALCOHOL IS CONJUGATED TO FORM THE GLUCURONIDE. THE PHENYL RING IS ALSO HYDROXYLATED AT THE ORTHO POSITION, THEN CONJUGATED. THE HETEROCYCLIC RING IS ALSO HYDROXYLATED. /FLURAZEPAM DIHYDROCHLORIDE/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 125
YIELDS 7-CHLORO-1-(2-ETHYLAMINOETHYL)-5-(2-FLUOROPHENYL)-1,3-DIHYDRO-2H- 1,4-BENZODIAZEPIN-2-ONE IN MAN & IN DOG & YIELDS 7-CHLORO-5-(2-FLUOROPHENYL)-1,3-DIHYDRO-2H-1,4-BENZODIAZEPIN-2-ONE IN MAN. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. C-23
YIELDS 7-CHLORO-1-(N-ETHYL-N-(2-HYDROXYETHYL)AMINOETHYL)-5-(2-FLUOROPHENYL)- 1,3-DIHYDRO-2H-1,4-BENZODIAZEPIN-2-ONE IN MAN & YIELDS 7-CHLORO-5-(2-FLUOROPHENYL)-1,3-DIHYDRO-3-HYDROXY-2H-1,4-BENZODIAZEPIN-2-ONE IN DOGS. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. C-23
AFTER CHRONIC ORAL DOSES OF FLURAZEPAM TO HUMAN SUBJECTS, UNCHANGED DRUG COULD NOT BE DETECTED IN BLOOD, & MAJOR CMPD PRESENT WAS N-DEALKYL-FLURAZEPAM. BIOLOGICAL HALF-LIFE OF THIS METABOLITE RANGED FROM 47-100 HR.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 120
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for FLURAZEPAM (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The mean apparent half-life of flurazepam is 2.3 hours. The half life of elimination of N1-des-alkyl- flurazepam ranged from 47 to 100 hours
Half-life of flurazepam in plasma is 2 to 3 hr, but that of a major active metabolite (N-desalkylflurazepam) is 50 hr or more.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 353
Elimination half-lives of metabolites: Desalkylflurazepam (47-100 hr) and N-1-Hydroxyethylflurazepam (2-4 hr) /From table/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 1331
MEAN HALF-LIFE (IN HOURS) ARE: 74 FOR YOUNG MALES & 160 FOR ELDERLY MALES; 90 FOR YOUNG FEMALES & 120 FOR ELDERLY FEMALES. /FLURAZEPAM HYDROCHLORIDE/
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 218
Flurazepam binds to an allosteric site on GABA-A receptors. Binding potentiates the action of GABA on GABA-A receptors by opening the chloride channel within the receptor, causing chloride influx and hyperpolarization.
EFFECTS OF FLURAZEPAM ON EEG DIFFER FROM THOSE OF BARBITURATES IN THAT FAST ACTIVITY SEEMS TO BE INCREASED ONLY IN FRONTAL LOBE & DOES NOT SPREAD TO OCCIPITAL LOBE. IN DOSES UP TO 30 MG IT NEITHER AFFECTS REM SLEEP NOR CAUSES A REBOUND AFTER WITHDRAWAL, BUT DOSES OF 60 MG SUPPRESS REM SLEEP WITHOUT REBOUND. FLURAZEPAM DECREASES SLEEP LATENCY, TIME IN STAGE 4, & WAKE TIME, & INCREASES TOTAL SLEEP TIME FOR AS LONG AS 22 NIGHTS OF USE. /FLURAZEPAM DIHYDROCHLORIDE/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 125
MOST BENZODIAZEPINES DECREASE SLEEP LATENCY, ESPECIALLY WHEN FIRST USED, & DIMINISH THE NUMBER OF AWAKENINGS & TIME SPENT IN STAGE 0 (A STAGE OF WAKEFULNESS). THEY HAVE BEEN SHOWN TO INCREASE THE AWAKENING THRESHOLD. TIME IN STAGE 1 (DESCENDING DROWSINESS) IS USUALLY DECREASED BY FLURAZEPAM ... . TIME SPENT IN STAGE 2 (WHICH IS THE MAJOR FRACTION OF NON-RAPID EYE MOVEMENT (REM) SLEEP) IS INCREASED BY ALL BENZODIAZEPINES. BENZODIAZEPINES PROMINENTLY DECREASE THE TIME SPENT IN SLOW-WAVE SLEEP (SWS; STAGES 3 & 4); USUALLY BOTH STAGES 3 & 4 ARE SHORTENED ... . ALL BENZODIAZEPINES INCREASE REM LATENCY (TIME FROM ONSET OF SPINDLE SLEEP TO THE FIRST REM BURST), EXCEPT THAT FLURAZEPAM HAS BEEN REPORTED TO SHORTEN LATENCY IN SOME INSOMNIAC NEUROTIC OR PSYCHOTIC INDIVIDUALS. ... REM SLEEP MAY NOT BE SHORTENED WHEN LOWER DOSES OF FLURAZEPAM ... /WAS/ USED, EVEN THOUGH SUBSTANTIAL SHORTENING OF SLOW-WAVE SLEEP & PROLONGATION OF STAGE 2 SLEEP MAY OCCUR. ... DESPITE THE SHORTENING OF STAGE-4 & REM SLEEP, THE NET EFFECT OF ADMIN OF BENZODIAZEPINES IS AN INCREASE IN TOTAL SLEEP TIME.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 342
WITH FLURAZEPAM ... THE REBOUND IN REM SLEEP APPEARS TO BE SLIGHT OR NEGLIGIBLE. DURING THE PERIOD OF SUCH REBOUND THE NUMBER OF DREAMS PER NIGHT IS ABOUT THE SAME AS BEFORE THE DRUG WAS TAKEN, BUT THEIR BIZARRE CHARACTER MAY INCREASE. THERE IS ALSO USUALLY A REBOUND IN SLOW-WAVE SLEEP WHICH MAY EXCEED THE REBOUND IN REM SLEEP. WITHDRAWAL OF FLURAZEPAM CAUSES ONLY A SLIGHT REBOUND. ... TOTAL WAKE TIME IS NOT CHANGED AFTER WITHDRAWAL OF FLURAZEPAM.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 344
THE BENZODIAZEPINES SELECTIVELY ACT ON POLYSYNAPTIC & NOT MONOSYNAPTIC NEURONAL PATHWAYS THROUGHOUT THE CNS. THE ACTION IS MAINLY THAT OF PRESYNAPTIC INHIBITION, ALTHOUGH AT SOME SITES, SUCH AS IN CUNEATE NUCLEUS, THERE MAY BE POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION; WHETHER INHIBITION IS PRESYNAPTIC OR POSTSYNAPTIC, IT SIMULATES THAT OF GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID. POLYSYNAPTIC RESPONSES MAY BE DIMINISHED OR AUGMENTED, ACCORDING TO WHETHER SYNAPTIC INHIBITION SUBSERVES AN INHIBITORY OR FACILITATORY FUNCTION IN THE INTEGRATED RESPONSE. /BENZODIAZEPINES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 344
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for FLURAZEPAM (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.