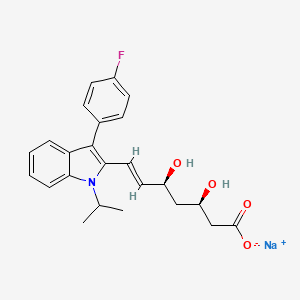

1. 7-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1h-indol-2-yl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoate
2. Fluindostatin
3. Fluvastatin
4. Fluvastatin Sodium Salt
5. Lescol
6. Xu 62 320
7. Xu 62-320
8. Xu 62320
9. Xu-62320
10. Xu62320
1. Fluvastatin Sodium Salt
2. 93957-55-2
3. Lescol
4. 94061-80-0
5. Vastin
6. (3r,5s)-fluvastatin Sodium Salt
7. Fluvastatin (sodium)
8. Fluvastatin
9. Canef
10. Sri 62320
11. Sri-62320
12. Fluvastatin Sodium (lescol)
13. (3r,5s)-fluvastatin Sodium
14. Fractal
15. Locol
16. Lescol Xl
17. Sodium (3r,5s,e)-7-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate
18. Sodium;(e,3r,5s)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-propan-2-ylindol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate
19. Dsstox_cid_24758
20. Dsstox_rid_80451
21. Dsstox_gsid_44758
22. Lochol
23. Fluvastatin Sodium Hydrate
24. Cranoc
25. Smr000550480
26. Xu-62-320
27. Ab01274723-01
28. Xilep Xl
29. Fluindostatin Sodium
30. Cas-93957-55-2
31. Prestwick_1032
32. Fluyastatin Sodium Salt
33. (+)-fluvastatin Sodium
34. Fluvastatin Sodium,(s)
35. Xu 62320 Sodium
36. Ncgc00164604-01
37. (relative Stereochemistry)
38. Fluvastatin Sodium- Bio-x
39. Schembl41502
40. Mls001165673
41. Mls001304715
42. Mls006010060
43. Chebi:77602
44. Fluvastatin For System Suitability
45. Dtxsid501009854
46. Hms1570l19
47. Hms2233n10
48. (+)-(3r,5s)-fluvastatin Sodium
49. (3r,5s)-(+)-fluvastatin Sodium
50. (3s,5r)-7-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic Acid Sodium Salt
51. Tox21_112226
52. Hy-14664a
53. Mfcd00929076
54. S1909
55. Xu-620
56. Akos016340657
57. Tox21_112226_1
58. Ac-6856
59. Ccg-264930
60. Cs-1969
61. Ks-1062
62. Ncgc00263525-01
63. (3r,5s)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic Acid Sodium Salt
64. Bf164477
65. Sw197104-2
66. H11964
67. A844750
68. Q27147203
69. (3r,5s,6e)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic Acid
70. (3r,5s,6e)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy Hept-6-enoic Acid Sodium Salt
71. (3r,5s,6e)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic Acid Sodium Salt
72. (3s,5r)-rel-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic Acid Sodium Salt
73. (e)-(3r,5s)-(+)-7-[3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-hept-6-enoic Acid Sodium Salt
74. (e)-(3r,5s)-7-[3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-hept-6-enoic Acid Sodium Salt
75. (e)-(3r,5s)-7-[3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-hept-6enoic Acid Sodium Salt
76. 6-heptenoic Acid, 7-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1h-indol-2-yl)-3,5-dihydroxy-, Monosodium Salt, (s-(r*,s*-(e)))-
77. Sodium (3r,5s,6e)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate
78. Sodium (e)-(3r,5s)-7-[3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-hept-6-enoate
79. Sodium 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-hept-6-enoate;fluvastatin Sodium
80. Sodium(3r,5s,e)-7-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1h-indol-2-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate
| Molecular Weight | 433.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H25FNNaO4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 433.16653072 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 433.16653072 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 85.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 596 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fluvastatin sodium |
| PubMed Health | Fluvastatin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | Lescol (fluvastatin sodium), is a water-soluble cholesterol lowering agent which acts through the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Fluvastatin sodium is [R*,S*-(E)]-()-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-m... |
| Active Ingredient | Fluvastatin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Capsule |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | eq 20mg base; eq 40mg base; 80mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Par Pharm; Teva Pharms |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lescol |
| PubMed Health | Fluvastatin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | Lescol (fluvastatin sodium), is a water-soluble cholesterol lowering agent which acts through the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Fluvastatin sodium is [R*,S*-(E)]-()-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-m... |
| Active Ingredient | Fluvastatin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 20mg base; eq 40mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lescol xl |
| Drug Label | Lescol (fluvastatin sodium), is a water-soluble cholesterol lowering agent which acts through the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Fluvastatin sodium is [R*,S*-(E)]-()-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-m... |
| Active Ingredient | Fluvastatin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 80mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fluvastatin sodium |
| PubMed Health | Fluvastatin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | Lescol (fluvastatin sodium), is a water-soluble cholesterol lowering agent which acts through the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Fluvastatin sodium is [R*,S*-(E)]-()-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-m... |
| Active Ingredient | Fluvastatin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Capsule |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | eq 20mg base; eq 40mg base; 80mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Par Pharm; Teva Pharms |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lescol |
| PubMed Health | Fluvastatin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | Lescol (fluvastatin sodium), is a water-soluble cholesterol lowering agent which acts through the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Fluvastatin sodium is [R*,S*-(E)]-()-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-m... |
| Active Ingredient | Fluvastatin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 20mg base; eq 40mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lescol xl |
| Drug Label | Lescol (fluvastatin sodium), is a water-soluble cholesterol lowering agent which acts through the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Fluvastatin sodium is [R*,S*-(E)]-()-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-m... |
| Active Ingredient | Fluvastatin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 80mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
Anticholesteremic Agents; Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Fluvastatin. Online file (MeSH, 2016). Available from, as of November 1, 2016: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2016/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Fluvastatin capsules are indicated: as an adjunct to diet to reduce elevated total cholesterol (Total-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride (TG) and apolipoprotein B (Apo B) levels, and to increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Type IIa and IIb); As an adjunct to diet to reduce Total-C, LDL-C, and Apo B levels in adolescent boys and adolescent girls who are at least one year post-menarche, 10 to 16 years of age, with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and the following findings are present: 1. LDL-C remains >/= 190 mg/dL or 2. LDL-C remains >/= 160 mg/dL and: there is a positive family history of premature cardiovascular disease or two or more other cardiovascular disease risk factors are present. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
In patients with clinically evident coronary heart disease (CHD), fluvastatin capsules are indicated to: reduce the risk of undergoing coronary revascularization procedures and slow the progression of coronary atherosclerosis. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Fluvastatin has reduced total and LDL-cholesterol concentrations in a few patients with hypercholesterolemia associated with or exacerbated by diabetes mellitus (diabetic dyslipidemia), renal insufficiency,cardiac or renal transplantation, or nephrotic syndrome (nephrotic hyperlipidemia). Fluvastatin also has been shown to decrease proteinuria in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Additional studies are necessary to determine the role, if any, of fluvastatin therapy in patients with these disorders. /NOT included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 1849
Rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria have been reported with fluvastatin capsules and other drugs in this class.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
There have been rare postmarketing reports of fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure in patients taking statins, including fluvastatin. If serious liver injury with clinical symptoms and/or hyperbilirubinemia or jaundice occurs during treatment with fluvastatin sodium, promptly interrupt therapy. If an alternate etiology is not found do not restart fluvastatin sodium.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Fluvastatin is secreted into the breast milk of animals and because HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have the potential to cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who require treatment with fluvastatin capsules should be advised not to breastfeed their infants.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Fluvastatin capsules are contraindicated in women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives are essential for fetal development. Fluvastatin capsules may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process and the discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on the outcome of long-term therapy of primary hypercholesterolemia. Fluvastatin capsules should be administered to women of childbearing age only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive and have been informed of the potential hazards. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, fluvastatin capsules should be discontinued and the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Fluvastatin (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
C - Cardiovascular system
C10 - Lipid modifying agents
C10A - Lipid modifying agents, plain
C10AA - Hmg coa reductase inhibitors
C10AA04 - Fluvastatin
/MILK/ Based on animal data, fluvastatin is present in breast milk in a 2:1 ratio (milk:plasma).
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Following oral administration of the capsule, fluvastatin reaches peak concentrations in less than 1 hour. The absolute bioavailability is 24% (range 9% to 50%) after administration of a 10 mg dose.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Fluvastatin is 98% bound to plasma proteins. The mean volume of distribution (VDss) is estimated at 0.35 L/kg. At therapeutic concentrations, the protein binding of fluvastatin is not affected by warfarin, salicylic acid and glyburide.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Fluvastatin administered as fluvastatin sodium extended-release 80 mg tablets reaches peak concentration in approximately 3 hours under fasting conditions, after a low fat meal, or 2.5 hours after a low fat meal. The mean relative bioavailability of the extended-release tablet is approximately 29% (range: 9% to 66%) compared to that of the fluvastatin immediate-release capsule administered under fasting conditions. Administration of a high fat meal delayed the absorption (Tmax: 6 hr) and increased the bioavailability of the extended-release tablet by approximately 50%. However, the maximum concentration of fluvastatin sodium extended-release tablets seen after a high fat meal is less than the peak concentration following a single dose or twice daily dose of the 40 mg fluvastatin capsule.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Fluvastatin (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In vitro data indicate that fluvastatin metabolism involves multiple Cytochrome P450 (CYP) isozymes. CYP2C9 isoenzyme is primarily involved in the metabolism of fluvastatin (approximately 75%), while CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes are involved to a much less extent, i.e., approximately 5% and approximately 20%, respectively.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Fluvastatin is metabolized in the liver, primarily via hydroxylation of the indole ring at the 5 and 6 positions. N-dealkylation and beta-oxidation of the side-chain also occurs. The hydroxy metabolites have some pharmacologic activity, but do not circulate in the blood. Fluvastatin has two enantiomers. Both enantiomers of fluvastatin are metabolized in a similar manner.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
The elimination half-life of fluvastatin is approximately 3 hours.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Fluvastatin sodium is a competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) to mevalonate, a precursor of sterols, including cholesterol. The inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis reduces the cholesterol in hepatic cells, which stimulates the synthesis of LDL receptors and thereby increases the uptake of LDL particles. The end result of these biochemical processes is a reduction of the plasma cholesterol concentration.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Fluvastatin Tablet (Updated: March 2016). Available from, as of November 4, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=aad8b373-0aec-4efb-8e61-3d8114b31127#i4i_section_id_5f2eb94b-4cdf-4517-9ad8-298e02fe9677
Statins are largely used in clinics in the treatment of patients with cardiovascular diseases for their effect on lowering circulating cholesterol. Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LOX-1), the primary receptor for ox-LDL, plays a central role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disorders. We have recently shown that chronic exposure of cells to lovastatin disrupts LOX-1 receptor cluster distribution in plasma membranes, leading to a marked loss of LOX-1 function. Here we investigated the molecular mechanism of statin-mediated LOX-1 inhibition and we demonstrate that all tested statins /including fluvastatin/ are able to displace the binding of fluorescent ox-LDL to LOX-1 by a direct interaction with LOX-1 receptors in a cell-based binding assay. Molecular docking simulations confirm the interaction and indicate that statins completely fill the hydrophobic tunnel that crosses the C-type lectin-like (CTLD) recognition domain of LOX-1. Classical molecular dynamics simulation technique applied to the LOX-1 CTLD, considered in the entire receptor structure with or without a statin ligand inside the tunnel, indicates that the presence of a ligand largely increases the dimer stability. Electrophoretic separation and western blot confirm that different statins binding stabilize the dimer assembly of LOX-1 receptors in vivo. The simulative and experimental results allow us to propose a CTLD clamp motion, which enables the receptor-substrate coupling. These findings reveal a novel and significant functional effect of statins.
PMID:25950192 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4614984 Biocca S et al; Cell Cycle 14 (10): 1583-95 (2015)
Epidemiological studies suggest that statins (hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors) could reduce the risk of Alzheimer disease. Although one possible explanation is through an effect on beta-amyloid (Abeta) metabolism, its effect remains to be elucidated. Here, we explored the molecular mechanisms of how statins influence Abeta metabolism. Fluvastatin at clinical doses significantly reduced Abeta and amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragment (APP-CTF) levels among APP metabolites in the brain of C57BL/6 mice. Chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of lysosomal inhibitors blocked these effects, indicating that up-regulation of the lysosomal degradation of endogenous APP-CTFs is involved in reduced Abeta production. Biochemical analysis suggested that this was mediated by enhanced trafficking of APP-CTFs from endosomes to lysosomes, associated with marked changes of Rab proteins, which regulate endosomal function. In primary neurons, fluvastatin enhanced the degradation of APP-CTFs through an isoprenoid-dependent mechanism. Because our previous study suggests additive effects of fluvastatin on Abeta metabolism, we examined Abeta clearance rates by using the brain efflux index method and found its increased rates at high Abeta levels from brain. As LRP1 in brain microvessels was increased, up-regulation of LRP1-mediated Abeta clearance at the blood-brain barrier might be involved. In cultured brain microvessel endothelial cells, fluvastatin increased LRP1 and the uptake of Abeta, which was blocked by LRP1 antagonists, through an isoprenoid-dependent mechanism. Overall, the present study demonstrated that fluvastatin reduced Abeta level by an isoprenoid-dependent mechanism. ...
PMID:20472556 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2903370 Shinohara M et al; J Biol Chem 285 (29): 22091-102 (2010)