

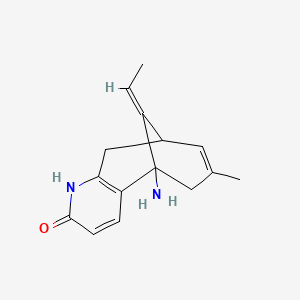

1. Huperzine A
2. Huperzine A, (5alpha,9beta,11z)-(-)-isomer
3. Fordine
1. Huperzine A
2. 120786-18-7
3. ( Inverted Exclamation Marka)-huperzine A
4. Fordine
5. Huperizine A
6. (-)-huperzine A
7. (+)-huperzine A
8. (-)-huperzine A (hupa)
9. Huperzinea
10. Ncgc00159362-02
11. 102518-79-6
12. (?)-huperazine A
13. Schembl679315
14. Chembl394259
15. Schembl1047469
16. Chebi:91724
17. Huperzine A [(-)-huperzine A]
18. Dtxsid801115670
19. Hms1362i05
20. Hms1792i05
21. Hms3403i05
22. 103735-86-0
23. Akos022661860
24. Akos026750633
25. Cs-1089
26. Ncgc00163246-02
27. Ncgc00163246-03
28. 5,9-methanocycloocta(b)pyridin-2(1h)-one, 5-amino-11-ethylidene-5,6,9,10-tetrahydro-7-methyl-
29. As-75811
30. Hy-17388
31. (+/-)-huperzine A, Synthetic, >=98% (tlc)
32. Brd-a47065382-001-02-9
33. (11e)-5-amino-11-ethylidene-5,6,9,10-tetrahydro-7-methyl-5,9-methanocycloocta[b]pyridin-2(1h)-one
34. (13e)-1-amino-13-ethylidene-11-methyl-6-azatricyclo[7.3.1.0^{2,7}]trideca-2(7),3,5,10-tetraen-5-ol
35. (afae'a Centa' Nota Inverted Exclamation Markafasa'a Inverted Exclamation Markafae'adaggeratrade Markafa Centa Centa' Nota Inverted Exclamation Marka'a Not)-huperzine A
| Molecular Weight | 242.32 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H18N2O |
| XLogP3 | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 242.141913202 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 242.141913202 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 55.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 551 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
Neuroprotective Agents
Drugs intended to prevent damage to the brain or spinal cord from ischemia, stroke, convulsions, or trauma. Some must be administered before the event, but others may be effective for some time after. They act by a variety of mechanisms, but often directly or indirectly minimize the damage produced by endogenous excitatory amino acids. (See all compounds classified as Neuroprotective Agents.)