
1. Aluminum Formate
2. Ammonium Formate
3. Ammonium Tetraformate
4. Calcium Formate
5. Chromic Formate
6. Cobalt(ii) Formate Dihydrate
7. Cobaltous Formate
8. Cupric Formate
9. Formate
10. Formic Acid, 14c-labeled
11. Formic Acid, Aluminum Salt
12. Formic Acid, Ammonium (2:1) Salt
13. Formic Acid, Ammonium (4:1) Salt
14. Formic Acid, Ammonium Salt
15. Formic Acid, Cadmium Salt
16. Formic Acid, Calcium Salt
17. Formic Acid, Cesium Salt
18. Formic Acid, Cobalt (+2) Salt
19. Formic Acid, Copper (+2) Salt
20. Formic Acid, Copper Salt
21. Formic Acid, Copper, Ammonium Salt
22. Formic Acid, Copper, Nickel Salt
23. Formic Acid, Cromium (+3) Salt
24. Formic Acid, Cromium (+3), Sodium (4:1:1) Salt
25. Formic Acid, Lead (+2) Salt
26. Formic Acid, Lead Salt
27. Formic Acid, Lithium Salt
28. Formic Acid, Magnesium Salt
29. Formic Acid, Nickel (+2) Salt
30. Formic Acid, Nickel Salt
31. Formic Acid, Potassium Salt
32. Formic Acid, Rubidium Salt
33. Formic Acid, Sodium Salt
34. Formic Acid, Sodium Salt, 13c-labeled
35. Formic Acid, Sodium Salt, 14c-labeled
36. Formic Acid, Strontium Salt
37. Formic Acid, Thallium (+1) Salt
38. Formic Acid, Zinc Salt
39. Lead Formate
40. Lithium Formate
41. Magnesium Formate
42. Methanoic Acid
43. Nickel Formate
44. Nickel Formate Dihydrate
45. Potassium Formate
46. Sodium Formate
47. Strontium Formate
48. Zinc Formate
1. Methanoic Acid
2. 64-18-6
3. Formylic Acid
4. Aminic Acid
5. Bilorin
6. Hydrogen Carboxylic Acid
7. Formisoton
8. Myrmicyl
9. Formira
10. Collo-bueglatt
11. Collo-didax
12. Acide Formique
13. Add-f
14. Ameisensaeure
15. C1 Acid
16. Rcra Waste Number U123
17. Spirit Of Formic Acid
18. Formic Acid (natural)
19. Mierenzuur [dutch]
20. Mierenzuur
21. Formicum Acidum
22. Kwas Metaniowy
23. Acido Formico
24. Ameisensaeure [german]
25. Kyselina Mravenci
26. Acide Formique [french]
27. Acido Formico [italian]
28. Fema No. 2487
29. Kwas Metaniowy [polish]
30. Kyselina Mravenci [czech]
31. Hcooh
32. Ameisensaure
33. Ccris 6039
34. Sybest
35. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 214900
36. Ai3-24237
37. Rcra Waste No. U123
38. Un1779
39. Formic Acid, Dimer
40. Methanoic Acid Monomer
41. Hco2h
42. Mfcd00003297
43. Wonderbond Hardener M 600l
44. 0yiw783rg1
45. Chebi:30751
46. Aminate
47. Formylate
48. Methanoate
49. Formic Acid [un1779] [corrosive]
50. Formic Acid, 88%
51. 0.1% Fa In Water
52. Hydrogen Carboxylate
53. 0.1% Fa In Water,
54. 0.1% Fa In Acn
55. 0.1% Fa In Acn,
56. 0.1% Formic Acid In Water (v/v)
57. Cal-ex™ Ii Fixative/decalcifier
58. 14523-98-9
59. 0.1% Formic Acid In Acetonitrile (v/v)
60. Hsdb 1646
61. Einecs 200-579-1
62. Unii-0yiw783rg1
63. Amasil
64. Forrnic Acid
65. Methoic Acid
66. Icosatrienoic Acids
67. Eicosatrienoic Acids
68. Fatty Acid 20:3
69. Fatty Acid 26:0
70. Formic Acid, Natural
71. H-cooh
72. Formic Acid, Acs Grade
73. Formic Acid [mi]
74. Bmse000203
75. Formic Acid [fcc]
76. Ec 200-579-1
77. Formic Acid, 95-97%
78. Formic Acid [fhfi]
79. Formic Acid [hsdb]
80. Formic Acid [inci]
81. Formic Acid, Lc/ms Grade
82. Formic Acid [vandf]
83. Formic Acid [mart.]
84. Formic Acid, P.a., 85%
85. Formic Acid [usp-rs]
86. Formic Acid [who-dd]
87. Formic Acid (fragrance Grade)
88. Formic Acid, Ar, >=90%
89. Formic Acid, Ar, >=98%
90. Formic Acid, Lr, >=85%
91. Formic Acid, Lr, >=98%
92. Formicum Acidum [hpus]
93. Chembl116736
94. Formic Acid, Purum, >=85%
95. Formic Acid (industrial Grade)
96. Dtxsid2024115
97. Chebi:36036
98. Chebi:191874
99. Formic Acid [ep Monograph]
100. Amy11055
101. Bcp23013
102. Formic Acid Ampoules (lcms Grade)
103. Formic Acid, >=95%, Fcc, Fg
104. Formic Acid, Technical Grade, 85%
105. Formic Acid 88% Reagent Grade Acs
106. Formic Acid, Acs Reagent, >=96%
107. Stl264243
108. Formic Acid, Reagent Grade, >=95%
109. Varromed Component Formic Acid
110. Akos000269044
111. Formic Acid Solution, 1.0m In Water
112. Formic Acid, Acs Reagent, 88-91%
113. Water With 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
114. Ccg-266004
115. Db01942
116. Un 1779
117. Formic Acid, Acs Reagent, >=96.0%
118. Formic Acid Component Of Varromed
119. Ncgc00248718-01
120. Bp-21436
121. E236
122. Formic Acid [ema Epar Veterinary]
123. Db-029851
124. C20:3
125. F0513
126. F0654
127. Formic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
128. Formic Acid, Jis Special Grade, >=98.0%
129. Formic Acid, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 95%
130. Ft-0626533
131. Ft-0626535
132. Ft-0626537
133. Ft-0668804
134. C00058
135. Formic Acid, Saj First Grade, 88.0-89.5%
136. Formic Acid Solution, Bioultra, 1.0 M In H2o
137. A834666
138. Q161233
139. Formic Acid, P.a., Acs Reagent, 98.0-100.0%
140. J-521387
141. Q27110013
142. F1908-0082
143. Formate Standard For Ic, 1.000 G/l In H2o, Analytical Standard
144. Formic Acid, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Ph. Eur., >=98%
145. Formic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
146. Formic Acid, Puriss., Meets Analytical Specifications Of Dac, Fcc, 98.0-100%
147. 82069-14-5
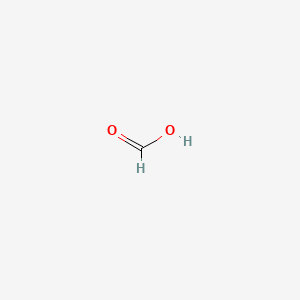
| Molecular Weight | 46.025 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CH2O2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 46.005479302 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 46.005479302 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 3 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 10.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Medication (vet): appears to prevent candida growth in partridges exposed to candida after receiving treated feed (20 mL of 6% solution/100 g feed for 1 week and then 2% soln). Similarly, a 15% solution can be used to control an outbreak of candida albicans.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 228
THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Caustic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 727
Absorption
Formic acid is readily metabolized and eliminated by the body.
Formic acid is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, via the lungs and the intact skin. The absorbed substance is degraded to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water and is partially excreted unchanged in the urine.
EPA/Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics; High Production Volume (HPV) Challenge Program's Robust Summaries and Test Plans. Formates (December 2001). Available from, as of July 12, 2005: https://www.epa.gov/hpv/pubs/hpvrstp.htm
The dose-dependent elimination of formate was investigated in the rat using both in vitro and in vivo systems. The in situ perfused liver was used to define the kinetics of hepatic metabolism and obtain initial in vitro estimates of the hepatic metabolism parameters. Formate was eliminated from the perfused rat liver following the Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Estimates of the Michaelis-Menten parameters obtained from the perfused liver studies were used in a two-compartment pharmacokinetic model of the dose-dependent elimination of formate in vivo. A good fit of the model to the observed in vivo data was obtained. Initial estimates of the Michaelis-Menten parameters, Vmax and Km, obtained from the perfused liver model, were within 40% of the final fitted values of these parameters in the in vivo model.
EPA/Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics; High Production Volume (HPV) Challenge Program's Robust Summaries and Test Plans. Formates (December 2001). Available from, as of July 12, 2005: https://www.epa.gov/hpv/pubs/hpvrstp.htm
Some formic acid may be excreted unchanged, the amt depending on the species, dose, and route of admin.
Clayton, G. D. and F. E. Clayton (eds.). Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume 2A, 2B, 2C: Toxicology. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1981-1982., p. 4908
During hemodialysis in a methanol poisoned patient, formate elimination followed first order kinetics with a plasma half-life of 165 min. The mean dialyzer (1.6 at 59 mL) clearance of formate was 148 mL/min at a blood flow of 215 mL/min. Distribution volume was 0.5 L/kg. Formate is more effectively removed by hemodialysis than methanol. /Formate/
PMID:6660049 Jacobsen D et al; Acta Med Scand 214 (5): 409-12 (1983)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for FORMIC ACID (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Formate is a normal constituent of intermediary metabolism ... /of formic acid/. Formate is metabolized in the rat primarily via the one carbon pool, but in some circumstances the catalase-peroxidative pathway may serve as an alternative route of oxidation. Oxidation occurs in a variety of organs and tissues, including liver, lung, and erythrocytes, the end products being carbon dioxide and water.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V5 p.697
Enzyme pathways involved in detoxification of hydrogen peroxide, formaldehyde, and formic acid, which are produced as a consequence of oxidative demethylation by the cytochrome P-450 system, were examined in isolated hepatocytes from phenobarbital pretreated rats. The formaldehyde produced during oxidative demethylation in isolated hepatocytes is rapidly oxidized to formic acid. Depletion of cellular reduced glutathione by pretreatment of rats with diethylmaleate decreases the rate of formic acid production, and therefore, it appears that formaldehyde produced by oxidative demethylation is oxidized by formaldehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme which requires but does not consume reduced glutathione. Because of the rapid nonenzymatic reaction of formaldehyde with reduced glutathione, this enzyme system may be viewed as essential to prevent the loss of reduced glutathione due to S-hydroxymethylglutathione formation. Reduced glutathione concentration in isolated hepatocytes decreased rapidly following addition of substrates undergoing oxidative demethylation. Addition of other cytochrome P-450 substrates which do not undergo demethylation did not result in such a dramatic oxidation of reduced glutathione. Formic acid, produced during oxidative demethylation acts as a substrate for the peroxidatic mode of catalase, but also binds to catalase as an anionic ligand. This binding decreases the catalase concentration detectable by cyanide titration and therefore appears to inhibit the catalytic reaction mode.
PMID:567217 Jones DP et al; J Biol Chem 253 (17): 6031-7 (1978)
The major part of the absorbed formic acid is metabolized in the liver, but partially also in the intestinal mucosa, lungs, kidneys and spleen. Formic acid is oxidized in relation to folate and according to a catalase-peroxidative mechanism. Formic acid is metabolized into CO2 considerably more slowly in primates than in rats. The species sensitivity to methanol intoxication (metabolic acidosis caused by formic acid) is possibly dependent on the tetrahydrofolate concentration.
EPA/Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics; High Production Volume (HPV) Challenge Program's Robust Summaries and Test Plans. Formates (December 2001). Available from, as of July 12, 2005: https://www.epa.gov/hpv/pubs/hpvrstp.htm
Formic acid was excreted in the urine of rabbits during inhalation of methyl alcohol ... .
Clayton, G. D. and F. E. Clayton (eds.). Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume 2A, 2B, 2C: Toxicology. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1981-1982., p. 4535
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for FORMIC ACID (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
... Mean half-life of serum formate was 2.6 hr, when methanol metabolism was assumed blocked by fomepizole and no folinic acid was given. ... /formate/
PMID:16035197 Hovda KE et al; Clin Toxicol (Phila). 43 (4): 221-7 (2005)
The biologic half-life /of formic acid/ is between 15 minutes and 1 hour.
EPA/Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics; High Production Volume (HPV) Challenge Program's Robust Summaries and Test Plans. Formates (December 2001). Available from, as of July 12, 2005: https://www.epa.gov/hpv/pubs/hpvrstp.htm
Formic acid is an inhibitor of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase causing histotoxic hypoxia. The most significant acid load results from the hypoxic metabolism. Urinary acidification is affected by formic acid.
Sheftel, V.O.; Indirect Food Additives and Polymers. Migration and Toxicology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL. 2000., p. 914
Formic acid is a mitochondrial toxin, and exerts effects primarily in areas (such as the retina or basal ganglia) that poorly tolerate an interruption in the energy supplied by oxidative phosphorylation.
Goldfrank, L.R. (ed). Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies. 7th Edition McGraw-Hill New York, New York 2002., p. 200