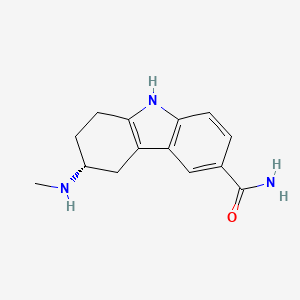

1. (+)-(r)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-(methylamino)carbazole-3-carboxamide Succinate (1:1), Monohydrate
2. 3-methylamino-6-carboxamido-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocarbazole
3. Allegro
4. Frova
5. Frovatriptan Succinate
6. Frovelan
7. Sb 209509
8. Vml-251
9. Vml251
1. Frova
2. 158747-02-5
3. Allergo Filmtabletten
4. Frovatriptan (inn)
5. (6r)-6-(methylamino)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5h-carbazole-3-carboxamide
6. Chembl1279
7. H82q2d5wa7
8. (r)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-(methylamino)carbazole-3-carboxamide
9. (3r)-3-(methylamino)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1h-carbazole-6-carboxamide
10. Allegro
11. Frovatriptan [inn]
12. 1h-carbazole-6-carboxamide, 2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-3-(methylamino)-, (3r)-
13. R-frovatriptan
14. Sb 209509
15. Auradol
16. Rilamig
17. Hsdb 7363
18. Frovatriptan [inn:ban]
19. Unii-h82q2d5wa7
20. Sb-209509
21. Frovatriptan [mi]
22. Frovatriptan [hsdb]
23. Allergo Filmtabletten (tn)
24. Frovatriptan [vandf]
25. Bidd:pxr0142
26. Schembl34410
27. Frovatriptan [mart.]
28. Frovatriptan [who-dd]
29. Gtpl7191
30. Dtxsid0023080
31. Zinc18635
32. Chebi:134991
33. Hy-b1658
34. Bdbm50073689
35. 1h-carbazole-6-carboxamide, 2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-3-(methylamino)-, (r)-
36. Db00998
37. Ncgc00408835-01
38. Cs-0013614
39. D07997
40. Q410195
41. (3r)-3-(methylamino)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1h-carbazole-6-carboximidic Acid
42. (r)-6-methylamino-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5h-carbazole-3-carboxylic Acid Amide
| Molecular Weight | 243.30 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H17N3O |
| XLogP3 | 1.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 243.137162174 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 243.137162174 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 70.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 333 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Tryptamines; Carbazoles
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Record for Frovatriptan(158747-02-5). Available from, as of March 15, 2006: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
Frovatriptan is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without aura in adults. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1555
As with other 5-HT1 agonists, sensations of pain, tightness, pressure and heaviness have been reported in the chest, throat, neck and jaw after treatment with frova. These events have not been associated with arrhythmias or ischemic ECG changes in clinical trials with FROVA. Because 5-HT1 agonists may cause coronary vasospasm, patients who experience signs or symptoms suggestive of angina following dosing should be evaluated for the presence of CAD. Patients shown to have CAD and those with Prinzmetal's variant angina should not receive 5-HT1 agonists. Patients who experience other symptoms or signs suggestive of decreased arterial flow, such as ischemic bowel syndrome or Raynaud's syndrome following the use of any 5-HT1 agonist are candidates for further evaluation. If a patient has no response for the first migraine attack treated with frova, the diagnosis of migraine should be reconsidered before frovatriptan is administered to treat any subsequent attacks.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1102
Cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, stroke and other cerebrovascular events have been reported in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists; and some have resulted in fatalities. In a number of cases, it appears possible that the cerebrovascular events were primary, the agonist having been administered in the incorrect belief that the symptoms experienced were a consequence of migraine, when they were not. It should be noted that patients with migraine may be at increased risk of certain cerebrovascular events (e.g. stroke, hemorrhage, transient ischemic attack).
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1102
Frovatriptan is not indicated in the management of hemiplegic or basilar migraine. Frovatriptan is not indicated for use in cluster headache, which is present in an older, predominately male population. Safety and efficacy of frovatriptan in this condition have not been established. Frovatriptan is not intended for the prophylactic therapy of migraine.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1555
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1556
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FROVATRIPTAN (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without aura in adults.
FDA Label
Frovatriptan is a second generation triptan 5-HT receptor agonist that binds with high affinity for 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors. It is structurally distinct from, but pharmacologically related to other selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists. Frovatriptan has no significant effects on GABAA mediated channel activity and has no significant affinity for benzodiazepine binding sites. Frovatriptan is believed to act on extracerebral, intracranial arteries and to inhibit excessive dilation of these vessels in migraine. Research has shown that migraine can be caused by the swelling of blood vessels around the brain. Frovatriptan eases the pain associated with migraine by narrowing these blood vessels. Frovatriptan has one of the highest affinities for the 5-HT1B of the second-generation triptan agonists.
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
Endogenous compounds and drugs that bind to and activate SEROTONIN RECEPTORS. Many serotonin receptor agonists are used as ANTIDEPRESSANTS; ANXIOLYTICS; and in the treatment of MIGRAINE DISORDERS. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin Receptor Agonists.)
N02CC07
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N02 - Analgesics
N02C - Antimigraine preparations
N02CC - Selective serotonin (5ht1) agonists
N02CC07 - Frovatriptan
Absorption
Frovatriptan is rapidly absorbed from the duodenum, but has low oral bioavailability.
Route of Elimination
Radiolabeled compounds excreted in urine were unchanged frovatriptan, hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan and desmethyl frovatriptan, together with several other minor metabolites. Less than 10% of frovatriptan was excreted in urine after an oral dose.
Volume of Distribution
4.2 L/kg [males]
3 L/kg [females]
Clearance
220 mL/min [male receiving IV dose of 0.8 mg]
130 mL/min [Female receiving IV dose of 0.8 mg]
Protein binding: Low (approximately 15%) to serum proteins.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1556
Volume of distribution (VolD): Steady state : 4.2 L/kg in males and 3.0 L/kg in females.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1556
The absolute bioavailability of an oral dose of frovatriptan is about 20% in males and 30% in females. The rate and extent of absorption are not affected by administration with food.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1556
Elimination: Renal: Following a single oral 2.5 mg dose of radiolabeled frovatriptan, 32% of the dose was recovered in urine. Radiolabeled compounds excreted in the urine were unchanged frovatriptan, hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, desmethyl frovatriptan and several other minor metabolites. Fecal: Following a single oral 2.5 mg dose of radiolabeled frovatriptan, 62% of the dose was recovered in feces.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1556
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for FROVATRIPTAN (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In vitro, cytochrome P450 1A2 appears to be the principal enzyme involved in the metabolism of frovatriptan to several metabolites including hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan and desmethyl frovatriptan, and several other minor metabolites. Desmethyl frovatriptan has lower affinity for 5-HT1B/1D receptors compared to the parent compound. The N-acetyl desmethyl metabolite has no significant affinity for 5-HT receptors. The activity of the other metabolites is unknown.
In vitro, cytochrome P450 1A2 appears to be the principal enzyme involved in the metabolism of frovatriptan. Following administration of a single oral dose of radiolabeled frovatriptan 2.5 mg to healthy male and female subjects, 32% of the dose was recovered in urine and 62% in feces. Radiolabeled compounds excreted in urine were unchanged frovatriptan, hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan and desmethyl frovatriptan, together with several other minor metabolites. Desmethyl frovatriptan has lower affinity for 5-HT1B/1D receptors compared to the parent compound. The N-acetyl desmethyl metabolite has no significant affinity for 5-HT receptors. The activity of the other metabolites is unknown.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1101
26 hours
Elimination: Intravenous administration: Approximately 26 hours.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1556
Three distinct pharmacological actions have been implicated in the antimigraine effect of the triptans: (1) stimulation of presynaptic 5-HT1D receptors, which serves to inhibit both dural vasodilation and inflammation; (2) direct inhibition of trigeminal nuclei cell excitability via 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonism in the brainstem and (3) vasoconstriction of meningeal, dural, cerebral or pial vessels as a result of vascular 5-HT1B receptor agonism.
Frovatriptan is believed to act on extracerebral, intracranial arteries and to inhibit excessive dilation of these vessels in migraine. In anesthetized dogs and cats, intravenous administration of frovatriptan produced selective constriction of the carotid vascular bed and had no effect on blood pressure (both species) or coronary resistance (in dogs).
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1101
Frovatriptan succinate is a selective agonist of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) type 1B and 1D receptors. Frovatriptan is structurally distinct from, but pharmacologically related to, other selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists (e.g., almotriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan). Because the mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of migraine are not clearly understood, the precise mechanism of action of 5-HT1 receptor agonists in the management of migraine has yet to be established. However, current data suggest that 5-HT1 receptor agonists, including frovatriptan, may ameliorate migraine through selective constriction of certain intracranial blood vessels, inhibition of neuropeptide release, and/or reduced transmission in the trigeminal pain pathway.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2461
Frovatriptan has no significant effects on GABAA mediated channel activity and has not significant affinity for benzodiazepine binding sites. Frovatriptan is believed to act on extracerebral, intracranial arteries and to inhibit excessive dilation of these vessels in migraine.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1555