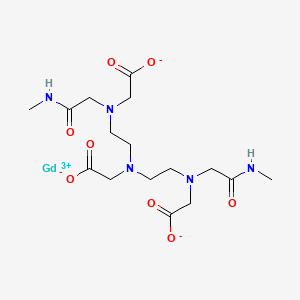

1. Gadodiamide
2. Gd-dtpa Bis-(methylamide)
3. Gd-dtpa-bma
4. Omniscan
5. Omniscan Unique Softpack
1. Gadodiamide
2. 131410-48-5
3. Omniscan
4. 2-[bis[2-[carboxylatomethyl-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]amino]ethyl]amino]acetate;gadolinium(3+)
5. 122795-43-1
6. Omniscan (tn)
7. Gadodiamide Anhydrous
8. Gadodiamide, Gd-dtpa-bma
9. 84f6u3j2r6
10. Gddtpa-bma
11. Gadodiamide (usp/inn)
12. Gadodiamide [mi]
13. Gadodiamide [inn]
14. S-041
15. Gadodiamide [hsdb]
16. Gadodiamide [usan]
17. Gadodiamide [vandf]
18. Gadodiamide [mart.]
19. Schembl73031
20. Gadodiamide [usp-rs]
21. Gadodiamide [who-dd]
22. Gadodiamide [orange Book]
23. Dtxsid201019701
24. Moli001033
25. Gadodiamide [usp Monograph]
26. Ac-925
27. Mfcd00867269
28. Akos015900642
29. Db-042031
30. D04284
31. 4-(n-(1,8-naphthalimido))-n-butyricacid
32. A806259
33. F02-0056
34. J-004857
35. (5,8-bis(carboxymethyl)-11-(2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl)-3-oxo-2,5,8,11-tetraazatridecan-13-oato(3-))gadolinium
36. (n,n-bis(2-((carboxymethyl)((methylcarbamoyl)methyl)amino)ethyl)glycinato(3-))gadolinium
37. 2-[bis[2-[[2-(methylamino)-2-oxidanylidene-ethyl]-(2-oxidanidyl-2-oxidanylidene-ethyl)amino]ethyl]amino]ethanoate; Gadolinium(3+)
38. 2-[bis[2-[carboxylatomethyl-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]amino]ethyl]amino]acetate; Gadolinium(3+)
39. Gadolinium(iii) 5,8-bis(carboxylatomethyl)-2-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]-10-oxo-2,5,8,11-tetraazadodecane-1-carboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 573.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H26GdN5O8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 13 |
| Exact Mass | 574.10225 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 574.10225 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 188 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 527 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Contrast Media
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Gadodiamide. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of October 23, 2014: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Omniscan is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use in MRI to visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity (or those thought to cause abnormalities in the blood-brain barrier) in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine, and associated tissues. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Omniscan (Gadodiamide) Injection (Revised: September 2013). Available from, as of October 27, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=1e9a37e2-f28a-4373-bf0f-3e9b60f42d8a
Omniscan is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use in MRI to facilitate the visualization of lesions with abnormal vascularity within the thoracic (noncardiac), abdominal, pelvic cavities, and the retroperitoneal space. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Omniscan (Gadodiamide) Injection (Revised: September 2013). Available from, as of October 27, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=1e9a37e2-f28a-4373-bf0f-3e9b60f42d8a
... To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of gadodiamide-enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) angiography with single and triple doses in the assessment of abdominal arterial stenoses ... One hundred five patients were included in the randomized, double-blind, phase III multicenter trial. Results of MR angiography with 0.1 mmol/kg and 0.3 mmol/kg doses of gadodiamide were compared with those of digital subtraction angiography (DSA) and according to dose ... No serious adverse events were observed. The mean contrast index at the region proximal to the primary stenosis was significantly higher in the triple-dose group (P = 0.03). Mean 95% CI values for the difference in depicted degree of stenosis between DSA and postcontrast MR angiography improved from -3.4% +/- 4.7 (SD) in the single-dose group to -1.2% +/- 4.7 in the triple-dose group. Mean values for overall image quality on the visual analogue scale improved with the triple dose (P = 0.02). Confidence in diagnosis was high at postcontrast MR angiography in 88% and 96% of cases in the single- and triple-dose groups, respectively ... Gadodiamide-enhanced MR angiography performed with single and triple doses is safe and effective for assessing major abdominal arterial stenoses. Although high agreement between MR angiography and DSA was achieved with both doses, triple-dose MR angiography was superior in the evaluations of image quality, degree of arterial stenoses, and confidence in diagnosis.
PMID:11274548 Thurnher SA et al; Radiology 219 (1): 137-46 (2001)
... The safety and diagnostic efficacy of MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine) in the central nervous system (CNS) were evaluated in a double-blind, multicenter, phase III clinical trial ... Two hundred five patients highly suspected of having a CNS lesion (by previous imaging exam) were enrolled at 16 sites in the United States. Patients were randomized to one of three incremental dosing regimens. Magnetic resonance imaging with Omniscan (gadodiamide) at doses of 0.1 and 0.3 mmol/kg was compared with MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine) at doses of 0.05 and 0.15 mmol/kg and at 0.1 and 0.2 mmol/kg ... Compared with predose images alone, efficacy was demonstrated in each of the gadobenate dimeglumine and gadodiamide groups (single and cumulative doses) as indicated by the level of diagnostic information, number of lesions detected, and contrast-to-noise ratio measurements. The level of diagnostic information from gadobenate dimeglumine at 0.1 mmol/kg was equivalent to that with gadodiamide at the same dose. One of the two blinded reviewers found equivalence between the gadobenate dimeglumine 0.05 mmol/kg dose and gadodiamide at 0.1 mmol/kg. Both reviewers found the level of diagnostic information to be equivalent after the second dose of contrast for all three dosing regimens. The cumulative doses of gadobenate dimeglumine were well tolerated and as safe as gadodiamide ... Gadobenate dimeglumine is comparable to gadodiamide in terms of safety and efficacy for imaging of CNS lesions, with a possible advantage in imaging applications owing to enhanced T1 relaxivity.
PMID:11224753 Runge VM et al; Invest Radiol 36(2):65-71 (2001)
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE AND NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF). NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE: Inadvertent intrathecal use of OMNISCAN has caused convulsions, coma, sensory and motor neurologic deficits. NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF): Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. Do not administer Omniscan to patients with: chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 sq m), or acute kidney injury. Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. Do not exceed the recommended Omniscan dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any readministration
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Omniscan (Gadodiamide) Injection (Revised: September 2013). Available from, as of October 27, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=1e9a37e2-f28a-4373-bf0f-3e9b60f42d8a
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced MRI or other modalities. The GBCA-associated NSF risk appears highest for patients with chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 sq m) as well as patients with acute kidney injury. Do not administer Omniscan to these patients. The risk appears lower for patients with chronic, moderate kidney disease (GFR 30-59 mL/min/1.73 sq m) and little, if any, for patients with chronic, mild kidney disease (GFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73 sq m). NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. ... Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. Features of acute kidney injury consist of rapid (over hours to days) and usually reversible decrease in kidney function, commonly in the setting of surgery, severe infection, injury or drug-induced kidney toxicity. Serum creatinine levels and estimated GFR may not reliably assess renal function in the setting of acute kidney injury. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, diabetes mellitus or chronic hypertension), estimate the GFR through laboratory testing. Among the factors that may increase the risk for NSF are repeated or higher than recommended doses of a GBCA and the degree of renal impairment at the time of exposure. Record the specific GBCA and the dose administered to a patient. When administering Omniscan, do not exceed the recommended dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug prior to any readministration
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Omniscan (Gadodiamide) Injection (Revised: September 2013). Available from, as of October 27, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=1e9a37e2-f28a-4373-bf0f-3e9b60f42d8a
Anaphylactoid and anaphylactic reactions, with cardiovascular, respiratory and/or cutaneous manifestations, resulting in death have occurred. Personnel trained in resuscitation techniques and resuscitation equipment should be present prior to Omniscan administration. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, stop Omniscan Injection and immediately begin appropriate therapy. Observe patients closely, particularly those with a history of drug reactions, asthma, allergy or other hypersensitivity disorders, during and up to several hours after Omniscan Injection.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Omniscan (Gadodiamide) Injection (Revised: September 2013). Available from, as of October 27, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=1e9a37e2-f28a-4373-bf0f-3e9b60f42d8a
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Omniscan (Gadodiamide) Injection (Revised: September 2013). Available from, as of October 27, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=1e9a37e2-f28a-4373-bf0f-3e9b60f42d8a
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for GADODIAMIDE (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Contrast Media
Substances used to allow enhanced visualization of tissues. (See all compounds classified as Contrast Media.)
V - Various
V08 - Contrast media
V08C - Magnetic resonance imaging contrast media
V08CA - Paramagnetic contrast media
V08CA03 - Gadodiamide
The objective of this study was to determine the gadolinium (Gd) concentration remaining in human bone tissue after administration of standard clinical doses of 2 Gd-based contrast agents: ProHance and Omniscan. After administration of 0.1 mmol/kg of Gd chelate to patients undergoing hip replacement surgery, bone specimens were collected and analyzed, and compared with an age-matched control population without a history of Gd chelate administration. Bone specimens were collected fresh, refrigerated, and subsequently frozen. After grinding and freeze-drying, tissue digestion was performed using Teflon bombs and concentrated nitric acid. A method for analysis of Gd in bone specimens was developed and validated using inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS). Results were compared with a previous study using a different technique for analysis of the same tissue specimens. Tissue retention was 1.77+/-0.704 microg Gd/g bone (n=9) for Omniscan and 0.477+/-0.271 microg Gd/g bone (n=10) for ProHance measured by ICP-MS. These findings confirmed results from the previous ICP-AES study. Omniscan (Gd[DTPA-BMA]) left approximately 4 times (previous study 2.5 times) more Gd behind in bone than did ProHance (Gd[HP-DO3A]).
PMID:16481910 White GW et al; Invest Radiol 41 (3): 272-8 (2006)
Twenty-seven patients--nine with severely reduced renal function (glomerular filtration rate, 2-10 mL/min), nine undergoing hemodialysis, and nine undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis--were followed up for 5, 8, and 22 days, respectively, after receiving gadodiamide injection (0.1 mmol per kilogram body weight). Gadodiamide injection caused no changes in renal function. In patients with severely reduced renal function, the elimination half-life of gadodiamide injection was prolonged (34.3 hours +/- 22.9) compared with data in healthy volunteers (1.3 hours +/- 0.25). An average of 65% of the gadodiamide injected was eliminated during a hemodialysis session. After 22 days of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, 69% of the total amount of gadodiamide was excreted; this reflects the low peritoneal clearance. In all patients, no metabolism or transmetallation of gadodiamide was found. ...
PMID:9653466 Joffe P et al; Acad Radiol 5 (7): 491-502 (1998)
The pharmacokinetic behavior of gadodiamide was consistent with its extracellular distribution. ... Gadodiamide was shown to be excreted rapidly, primarily through the kidneys. In rats, 94% of the administered dose was excreted in the urine within the first 24 hours after administration. Approximately 1% to 4% appeared in the feces during the same period.
PMID:8486501 Harpur ES et al; Invest Radiol 28 (Suppl 1): S28-43 (1993)
... /In rats/ following iv dosing of gadodiamide (NaCa DTPA-BMA) (0.015 mmol/kg) in a (14)C-labeled form, plasma concentrations of the drug declined rapidly with an elimination half-live of 0.31 hr, a distribution volume of 244 mL/kg and a plasma clearance of 9.2 mL/min/kg. These results demonstrate that NaCa DTPA-BMA distributes into the extracellular fluid compartment and is renally excreted via glomerular filtration. Of the dose of radioactivity given, 86.6% was excreted in urine by 4 hr after injection, and 95.3% in urine and 3.3% in feces by 120 hr. ...
PMID:8821523 Okazaki O et al; Arzneimittelforschung 46 (1): 79-83 (1996)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for GADODIAMIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In addition, experiments were done /in rats/ to clarify the in vivo metabolism of gadodiamide (NaCa DTPA-BMA). Results show small quantities of transchelated forms of NaCa DTPA-BMA in urine. HPLC analysis demonstrated these metabolites were the Zn and Cu forms of the drug, resulting from displacement of the Ca ion in the NaCa DTPA-BMA molecule by endogeneous Zn or Cu. Further analyses by HPLC and ICP-AES demonstrate that the unchanged parent drug, the Zn and the Cu forms occur in relative quantities of approximately 92%, 7%, and 1%, respectively. This demonstrates that the Ca ion in caldiamide sodium can be replaced by Zn or Cu ions in vivo, but only to a small extent.
PMID:8821523 Okazaki O et al; Arzneimittelforschung 46 (1): 79-83 (1996)
... /In rats/ following iv dosing of gadodiamide (NaCa DTPA-BMA) (0.015 mmol/kg) in a (14)C-labeled form, plasma concentrations of the drug declined rapidly with an elimination half-live of 0.31 hr ...
PMID:8821523 Okazaki O et al; Arzneimittelforschung 46 (1): 79-83 (1996)
The pharmacokinetic behavior of gadodiamide was consistent with its extracellular distribution. Its half-life in rats, rabbits, and monkeys was short, 18, 38, and 75 minutes, respectively.
PMID:8486501 Harpur ES et al; Invest Radiol 28 Suppl 1:S28-43 (1993)
The pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered gadodiamide in normal subjects conforms to an open, two-compartment model with mean distribution and elimination half-lives (reported as mean + or - SD) of 3.7 + or - 2.7 minutes and 77.8 + or - 16 minutes, respectively.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Omniscan (Gadodiamide) Injection (Revised: September 2013). Available from, as of October 27, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=1e9a37e2-f28a-4373-bf0f-3e9b60f42d8a
... The average half-time of gadodiamide was 1.93 hr (SD 0.55) /in thirteen hemodialysis patients with abdominal disease receiving iv gadodiamide (0.1 mmol/kg body weight)/.
PMID:16958426 Saitoh T et al; Radiat Med 24 (6): 445-51 (2006)
Twenty-seven patients--nine with severely reduced renal function (glomerular filtration rate, 2-10 mL/min), nine undergoing hemodialysis, and nine undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis--were followed up for 5, 8, and 22 days, respectively, after receiving gadodiamide injection (0.1 mmol per kilogram body weight). Gadodiamide injection caused no changes in renal function. In patients with severely reduced renal function, the elimination half-life of gadodiamide injection was prolonged (34.3 hours +/- 22.9) compared with data in healthy volunteers (1.3 hours +/- 0.25). ...
PMID:9653466 Joffe P et al; Acad Radiol 5 (7): 491-502 (1998)