

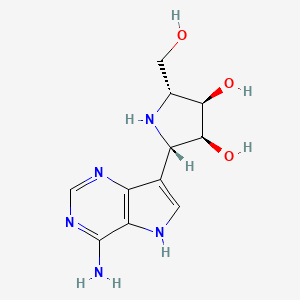

1. 2-(4-amino-5h-pyrrolo(3,2-d)pyrimidin-7-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidine-3,4-diol
2. Bcx-4430
3. Bcx4430
4. Imma Cpd
5. Immucillin A
6. Immucillin-a
1. 249503-25-1
2. Immucillin A
3. Immucillin-a
4. Bcx4430
5. Bcx-4430
6. Bcx 4430 Free Base
7. (2s,3s,4r,5r)-2-(4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidine-3,4-diol
8. Olf97f86a7
9. Bcx4430 Freebase
10. Imma Cpd
11. 3,4-pyrrolidinediol,2-(4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2s,3s,4r,5r
12. Bcx4430 (freebase)
13. Unii-olf97f86a7
14. (2s,3s,4r,5r)-2-{4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-7-yl}-5-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidine-3,4-diol
15. Ua2
16. Bcx4430freebase
17. Galidesivir [inn]
18. Galidesivir [who-dd]
19. Chembl1236524
20. Schembl12468816
21. Gtpl11920
22. Ex-a6295
23. Bdbm50513995
24. Hy-18649a
25. Zinc13492903
26. Cs-3779
27. Db11676
28. Ncgc00485882-01
29. Bcx-4430 Freebase;immucillin-a;galidesivir
30. P14655
31. A900809
32. (1s)-1-(9-carbaadenine-9-yl)-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-ribitol
33. 3,4-pyrrolidinediol, 2-(4-amino-5h-pyrrolo(3,2-d)pyrimidin-7-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-, (2s,3s,4r,5r)-
34. Galidesivir; Bcx4430; Bcx 4430; Bcx-4430;(2s,3s,4r,5r)-2-(4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidine-3,4-diol
| Molecular Weight | 265.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H15N5O3 |
| XLogP3 | -2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 265.11748936 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 265.11748936 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 140 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 334 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Galidesivir is an adenosine analogue with a broad-spectrum antiviral activity against RNA viruses, including flaviviruses, togaviruses, bunyaviruses, arenaviruses, paramyxoviruses, coronaviruses, filoviruses, orthomyxoviruses, and picornaviruses.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
Galidesivir works by binding to viral RNA polymerase where the natural nucleotide would bind, leading to the structural change in the viral enzyme due to altered electrostatic interactions. Disruption of viral RNA polymerase activity results in premature termination of the elongating RNA strand.
