


1. Arbutamine Hydrochloride
2. Arbutamine Hydrochloride, (r)-isomer
3. Genesa
1. 128470-16-6
2. Arbutaminum
3. Arbutamina
4. B07l15yaev
5. Chebi:50580
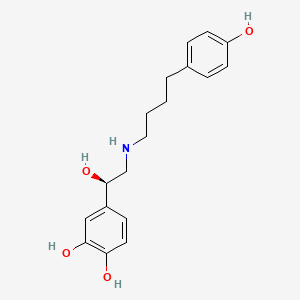
6. 4-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butylamino]ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol
7. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-[[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl]amino]ethyl]-
8. 4-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-{[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl]amino}ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol
9. Arbutamine [inn:ban]
10. Arbutaminum [inn-latin]
11. Arbutamina [inn-spanish]
12. Unii-b07l15yaev
13. Arbutamine [mi]
14. Arbutamine [inn]
15. Arbutamine [vandf]
16. Arbutamine [who-dd]
17. Schembl521645
18. Chembl1201251
19. Dtxsid00155908
20. Db01102
21. Hy-16056
22. Cs-0006131
23. Q4784959
24. (r)-3,4-dihydroxy-.alpha.-(((4-(p-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)methyl)benzyl Alcohol
25. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-(1-hydroxy-2-((4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)ethyl)-, (1r)
| Molecular Weight | 317.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H23NO4 |
| XLogP3 | 0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 317.16270821 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 317.16270821 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 93 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 320 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used to elicit acute cardiovascular responses (cardiac stumulant), similar to those produced by exercise, in order to aid in diagnosing the presence or absence of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients who cannot exercise adequately.
Adrenergic beta-Agonists
Drugs that selectively bind to and activate beta-adrenergic receptors. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Agonists.)
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C01 - Cardiac therapy
C01C - Cardiac stimulants excl. cardiac glycosides
C01CA - Adrenergic and dopaminergic agents
C01CA22 - Arbutamine
Primarily metabolized to methoxyarbutamine. Another possible metabolite is ketoarbutamine. The metabolites of arbutamine appear to have less pharmacological activity and a longer half-life and than the parental drug.
Elimination half-life is approximately 8 minutes.
Arbutamine is a synthetic catecholamine with positive chronotropic and inotropic properties. The chronotropic (increase in heart rate) and inotropic (increase in force of contraction) effects of arbutamine serve to mimic exercise by increasing cardiac work (producing stress) and provoke myocardial ischemia in patients with compromised coronary arteries. The increase in heart rate caused by arbutamine is thought to limit regional subendocardial perfusion, thereby limiting tissue oxygenation. In functional assays, arbutamine is more selective for beta-adrenergic receptors than for alpha-adrenergic receptors. The beta-agonist activity of arbutamine provides cardiac stress by increasing heart rate, cardiac contractility, and systolic blood pressure. The degree of hypotension that occurs for a given chronotropic activity is less with arbutamine than, for example, with isoproterenol because alpha receptor activity is retained.